Amatuximab: Exploring Mesothelin-Targeted Therapy for Cancer Research
What You Need to Know About Amatuximab
Is Amatuximab safe?
Amatuximab has shown a manageable safety profile in clinical trials, with most side effects being mild to moderate. Severe adverse reactions have been rare but should be closely monitored in clinical settings.
What is Amatuximab used for?
What role does Amatuximab play in mesothelioma treatment?
Amatuximab has been evaluated in mesothelioma due to its ability to bind to mesothelin, potentially disrupting tumor growth and progression. It is a focus of ongoing research for improving treatment outcomes.
1.) Understanding Amatuximab
Amatuximab is a monoclonal antibody developed to target mesothelin, a protein frequently overexpressed in cancers such as mesothelioma and ovarian cancer. Its specificity for mesothelin makes it a promising candidate for cancer research, especially in developing targeted therapies. Originally developed by Morphotek under the name MORAb-009, Amatuximab has received orphan drug designation from the FDA for treating mesothelioma.
Amatuximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody specifically developed to target mesothelin, a glycoprotein overexpressed in several cancers, including mesothelioma, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, and certain types of lung cancer. Mesothelin is minimally expressed on normal mesothelial cells but is highly upregulated in malignant tumors, making it an ideal target for cancer-specific therapies. Amatuximab binds with high specificity to mesothelin, blocking its interaction with CA-125 (also known as MUC16), a process believed to facilitate tumor adhesion and metastasis. This inhibition disrupts tumor progression and potentially enhances the immune system's ability to attack cancer cells.
Developed by Morphotek, Inc. under the initial name MORAb-009, Amatuximab has been explored for its potential to serve as a cornerstone in targeted cancer immunotherapy. Its mechanism of action includes direct inhibition of tumor growth through mesothelin blockade, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), and enhancing tumor susceptibility to immune cell-mediated destruction. These combined effects make it a versatile tool in oncology.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted orphan drug designation to Amatuximab for the treatment of mesothelioma, recognizing the unmet clinical need for therapies in this rare but aggressive cancer. Clinical trials have shown promising results, including tumor growth stabilization and extended survival in combination with standard chemotherapies such as cisplatin and pemetrexed.
Amatuximab's specificity for mesothelin, combined with its ability to integrate with existing cancer treatment regimens, underscores its potential to improve outcomes in patients with mesothelioma and other mesothelin-expressing malignancies.
Prefer to Listen? Check out the Amatuximab Podcast Episode
2.) Mechanism of Action of Amatuximab
Amatuximab’s mechanism of action revolves around its ability to bind with high specificity to mesothelin, a cell-surface glycoprotein that is overexpressed in a range of malignancies, including mesothelioma, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, and certain subtypes of lung cancer. Mesothelin plays a crucial role in tumor biology by mediating cell adhesion, particularly through its interaction with CA-125 (also known as MUC16), a mucin-like glycoprotein commonly overexpressed in ovarian and other cancers. This interaction facilitates tumor cell attachment, enhances metastasis, and creates an environment conducive to tumor growth.
Amatuximab binds to mesothelin, Amatuximab disrupts its interaction with CA-125, effectively preventing the adhesion of tumor cells to surrounding tissues and the metastatic spread of cancer. This mechanism not only hinders tumor progression but also renders cancer cells more susceptible to therapeutic interventions. The inhibition of the mesothelin-CA-125 axis may also reduce immune evasion mechanisms often exploited by tumors, making Amatuximab an attractive candidate for use in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors, which enhance T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity.
Additionally, Amatuximab engages the immune system directly through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). By recruiting natural killer (NK) cells and other immune effector cells to the site of the tumor, it enhances the immune-mediated destruction of cancer cells. Preclinical studies and early clinical trials have demonstrated that combining Amatuximab with standard chemotherapies, such as cisplatin and pemetrexed, or with emerging immunotherapies, can improve overall treatment efficacy by attacking cancer through complementary mechanisms.
This targeted and multifaceted approach highlights Amatuximab’s potential as a cornerstone in the treatment of mesothelin-expressing malignancies.

3.) Clinical Applications of Amatuximab
Amatuximab has shown significant potential in the treatment of mesothelin-expressing cancers, particularly mesothelioma and ovarian cancer, where mesothelin overexpression is a hallmark of disease progression. Early-phase clinical trials have focused on evaluating its safety, tolerability, and therapeutic efficacy, both as a monotherapy and in combination with standard treatments such as chemotherapy. These studies have demonstrated that Amatuximab is generally well-tolerated, with manageable side effects, and has shown encouraging signals of efficacy, including stabilization of tumor growth and prolonged survival in some patient populations.
In mesothelioma, a rare but aggressive cancer with limited treatment options, Amatuximab has been tested in combination with chemotherapy regimens such as cisplatin and pemetrexed. Results from these trials indicate that the addition of Amatuximab may improve outcomes by enhancing chemotherapy's cytotoxic effects while also leveraging immune-mediated mechanisms to attack cancer cells. Its orphan drug designation by the FDA for mesothelioma underscores its potential to fill a critical gap in treatment.
For ovarian cancer, which often exhibits high mesothelin levels, clinical investigations suggest that Amatuximab could play a role in reducing tumor burden and preventing metastasis. Furthermore, ongoing trials are exploring its synergy with emerging immunotherapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, to potentiate T-cell responses against tumors.
Recent research has expanded Amatuximab’s potential applications to other cancers, including pancreatic and lung cancers, where mesothelin is similarly overexpressed. These studies aim to better define patient populations that could benefit most from Amatuximab and optimize its use in combination regimens. The growing interest in mesothelin-targeting therapies highlights the importance of Amatuximab in advancing cancer treatment and addressing unmet needs in oncology.
4.) Advancing Research on Amatuximab with Biosimilars
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to an already-approved reference product, with no clinically meaningful differences in safety, purity, or potency. Biosimilars play a crucial role in expanding research opportunities and improving access to cutting-edge biologic therapies.
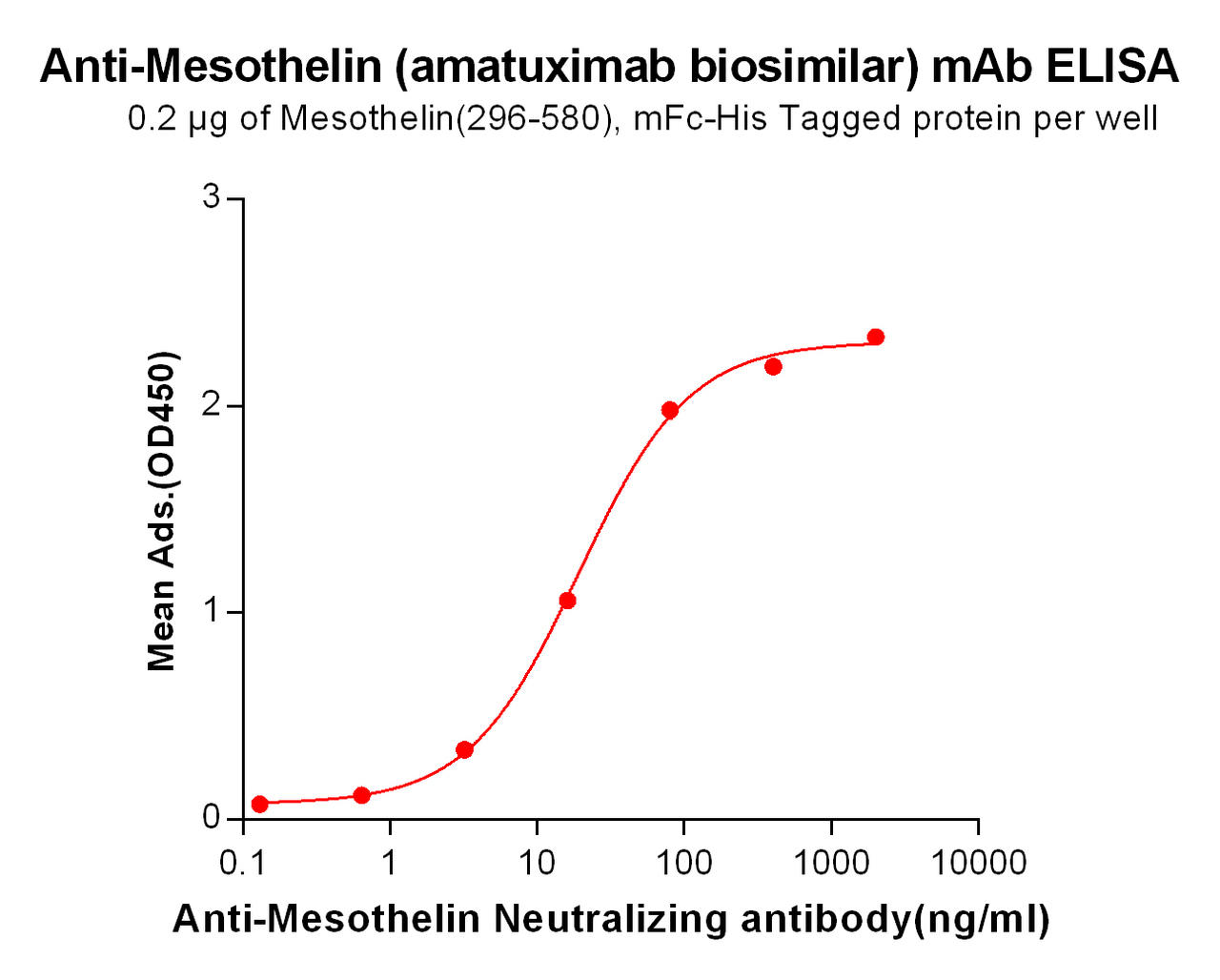
| Amatuximab (Anti-Mesothelin) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | MSLN |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does Amatuximab Biosimilar Support Research?
Our biosimilar product, Amatuximab Biosimilar, mirrors the properties of the original antibody, making it an invaluable tool for preclinical studies and drug development. Researchers can use this biosimilar to explore novel combinations, optimize therapeutic approaches, and study the effects of mesothelin inhibition in various cancers.
Benefits of Using Amatuximab Biosimilar
- Consistency: Provides a reliable model for studying mesothelin-targeted therapies.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Offers a more accessible alternative for research purposes.
- Flexibility: Supports various applications, including drug screening and mechanism-of-action studies.
Note: This product is for research use only and not for clinical or diagnostic purposes.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025




