Adalimumab: Mechanism, Clinical Applications, and the Role of Biosimilars
Quick Facts About Adalimumab
What is Adalimumab?
Adalimumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody designed to neutralize tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), a key cytokine involved in inflammation.
How does Adalimumab work?
Adalimumab binds to TNF-α, preventing its interaction with receptors, thereby reducing inflammation and improving autoimmune disease management.
What conditions does Adalimumab treat?
Adalimumab is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
Is Adalimumab safe?
Adalimumab has a well-documented safety profile but may cause side effects such as infections, injection site reactions, and increased risk of malignancies.
1.) Understanding Adalimumab
Adalimumab has revolutionized the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases by providing a highly targeted therapy that inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), a key cytokine responsible for driving inflammation in a variety of chronic conditions. Approved under the brand name Humira, it has become one of the most widely used biologic therapies in immunology, offering significant relief for patients suffering from disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis. By neutralizing TNF-α, adalimumab effectively reduces inflammation, prevents tissue damage, and improves overall disease management, leading to better long-term outcomes for patients.
One of the key advantages of adalimumab over earlier biologics is its fully human monoclonal antibody structure. Unlike chimeric or murine-derived biologics, which can provoke immune reactions, adalimumab's humanized design reduces immunogenicity, minimizing the risk of anti-drug antibodies that could affect the drug’s efficacy. This makes adalimumab a more sustainable long-term treatment option for patients, with fewer concerns about treatment resistance or reduced effectiveness over time.
Adalimumab is administered subcutaneously, typically every two weeks, offering a convenient dosing regimen that improves patient adherence and convenience. Beyond its established role in autoimmune disorders, adalimumab has also demonstrated efficacy in treating dermatological conditions such as psoriasis and ophthalmic conditions like uveitis, showcasing its versatility as a therapeutic option across multiple specialties.
With the expiration of Humira's patent exclusivity, several biosimilar versions have emerged, improving global access to the medication while maintaining equivalent efficacy and safety profiles. Ongoing research continues to optimize adalimumab’s use through combination therapies and personalized dosing strategies, further solidifying its position as a cornerstone of modern immunotherapy.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Adalimumab
Adalimumab exerts its therapeutic effects by specifically targeting and neutralizing TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory cytokine that plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases. TNF-α is involved in the inflammatory cascade, activating immune cells, stimulating the release of additional pro-inflammatory cytokines, and contributing to tissue damage in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, psoriasis, and ankylosing spondylitis. By binding to both soluble and membrane-bound TNF-α, adalimumab prevents its interaction with TNF receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) on immune and endothelial cells, thereby disrupting the inflammatory response at its source.
This inhibition of TNF-α leads to a downstream suppression of other inflammatory mediators, including interleukin-1 (IL-1) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which are critical in perpetuating immune system overactivation. As a result, adalimumab not only alleviates symptoms like pain, swelling, and skin lesions but also reduces long-term tissue damage and slows disease progression, providing significant benefits for patients with chronic autoimmune conditions. This targeted approach is particularly advantageous when compared to conventional immunosuppressants, which often have broader systemic effects that increase the risk of infections and other side effects.
Clinical studies have consistently demonstrated that TNF-α inhibitors like adalimumab offer substantial improvements in disease management, reducing flare-ups, minimizing the need for corticosteroids, and improving overall quality of life. Furthermore, by modulating immune function without causing widespread immune suppression, adalimumab maintains a more favorable safety profile than traditional therapies.
Given its specificity and proven effectiveness, adalimumab continues to be a leading choice for autoimmune disease treatment, with ongoing research exploring its potential in treating additional inflammatory conditions and investigating novel combination therapies to enhance its therapeutic outcomes.
3.) Clinical Applications of Adalimumab
Adalimumab has transformed the standard of care for multiple autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, providing effective disease control across a wide range of conditions. Its FDA-approved indications include:
1. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Adalimumab has significantly improved the management of RA by reducing joint inflammation, preventing structural damage, and preserving joint function. When used in combination with methotrexate, it provides superior outcomes compared to conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) alone.
2. Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
For patients with PsA, adalimumab alleviates both joint and skin symptoms, reducing disease severity and improving quality of life. It has been shown to decrease pain, swelling, and stiffness while also addressing the underlying skin manifestations of psoriasis.
3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Adalimumab is widely used in the treatment of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, where it helps control intestinal inflammation, reduce symptom severity, and induce remission. It is particularly beneficial for patients who have not responded adequately to conventional therapies.
4. Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
In patients with AS, adalimumab reduces spinal inflammation and improves mobility, providing long-term symptom relief and preventing disease progression.
Is Adalimumab safe?
Adalimumab effectively treats moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis by reducing inflammation and skin lesions, making it a key option for patients unresponsive to topical therapies.
Beyond these established uses, ongoing research is exploring adalimumab’s efficacy in rare autoimmune diseases and other inflammatory conditions. Its broad therapeutic potential underscores its importance in immunotherapy, with continued advancements aimed at optimizing treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Adalimumab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to an already approved reference biologic, with no clinically meaningful differences in efficacy, safety, or immunogenicity. Biosimilars help expand access to biologic therapies while reducing treatment costs.
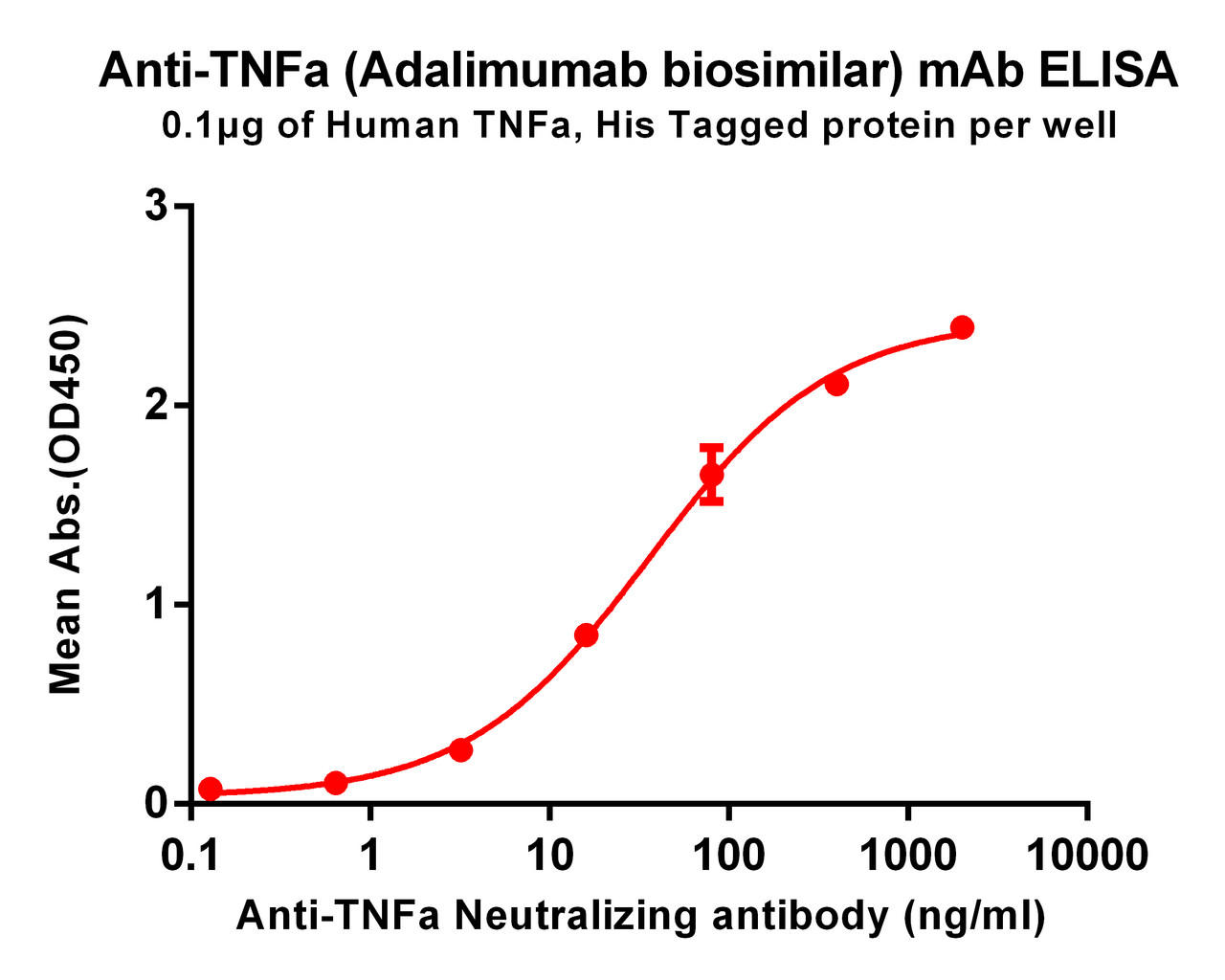
| Adalimumab (Anti-TNFa) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | TNFa |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does an Adalimumab Biosimilar Compare to the Original?
Biosimilars of Adalimumab undergo rigorous testing to ensure they match the reference product in structure, function, and therapeutic performance. They offer a more affordable alternative without compromising quality or effectiveness.
Advantages of Adalimumab Biosimilars in Research
Note: Biosimilars are intended for research purposes and not for direct patient use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Marina Alberto, PhD
Marina Alberto, PhD, holds a robust academic background in Biotechnology, earning her Bachelor’s Degree and PhD in Science and Technology from Quilmes National University. Her research spans cancer immunotherapy, glycan profiling, and vaccine development, including innovative projects on pediatric leukemia diagnosis and cancer-associated carbohydrate-mimetic vaccines. She currently serves as a Technical Support and Sales Specialist at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



