Relatlimab: Unlocking the Potential of LAG-3 Inhibition in Cancer Research
Quick Facts About Relatlimab
What is Relatlimab?
Relatlimab is a monoclonal antibody that targets LAG-3 (Lymphocyte Activation Gene-3), a key immune checkpoint involved in T-cell regulation.
How Does Relatlimab Work?
Relatlimab blocks LAG-3, enhancing T-cell activity and improving immune responses against cancer, particularly when combined with PD-1 inhibitors.
What Are the Clinical Applications of Relatlimab?
It is primarily used in treating melanoma, especially in combination with nivolumab, for patients with advanced or unresectable tumors.
1.) Understanding Relatlimab
Relatlimab is a next-generation immune checkpoint inhibitor that targets Lymphocyte-Activation Gene 3 (LAG-3), a protein that plays a crucial role in regulating T-cell activity. LAG-3 is frequently upregulated in exhausted T cells within the tumor microenvironment, contributing to immune evasion by cancer cells. By blocking LAG-3, Relatlimab restores T-cell activation and proliferation, enabling a more robust and sustained immune response against tumors. This innovative mechanism of action represents a significant advancement in cancer immunotherapy, particularly for tumors that have developed resistance to other immune checkpoint inhibitors such as PD-1 (e.g., nivolumab) and PD-L1 inhibitors (e.g., pembrolizumab).
Clinical studies have demonstrated that Relatlimab is especially effective when combined with PD-1 inhibitors, showing enhanced anti-tumor efficacy. The dual inhibition of LAG-3 and PD-1 results in a stronger immune response, which has proven beneficial in several malignancies, including melanoma. Moreover, ongoing trials are expanding the evaluation of Relatlimab in various other cancers, such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other solid tumors, where it may offer new hope for patients whose cancers are resistant to conventional treatments.
In combination therapies, Relatlimab has the potential to overcome immune resistance mechanisms, providing promising synergistic effects that could redefine current treatment strategies. As immunotherapy evolves, Relatlimab stands at the forefront of novel checkpoint inhibitors, significantly expanding the scope of cancer treatment. With continued research, it holds the promise of improving outcomes for patients with advanced, refractory, or otherwise difficult-to-treat malignancies, offering new hope where existing therapies may fall short.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Relatlimab
Relatlimab is a cutting-edge immune checkpoint inhibitor that targets LAG-3, a receptor expressed on T cells that become dysfunctional following chronic antigen exposure. LAG-3 normally downregulates T-cell activity to prevent overactive immune responses that could lead to autoimmunity. However, cancer cells exploit this immune regulatory mechanism to evade destruction by the immune system. By specifically blocking LAG-3, Relatlimab reactivates exhausted T cells, allowing them to regain their ability to proliferate and effectively attack tumor cells. This represents a significant advancement in immunotherapy, particularly for cancers resistant to other immune checkpoint inhibitors.
A key application of Relatlimab is its combination with nivolumab, a PD-1 inhibitor. Both PD-1 and LAG-3 are immune checkpoint receptors that suppress T-cell function, but they operate through distinct mechanisms. By targeting both pathways simultaneously, the combination of Relatlimab and nivolumab creates a synergistic effect that enhances T-cell activation, reduces immune exhaustion, and prolongs anti-tumor responses. Clinical trials have demonstrated that dual inhibition of PD-1 and LAG-3 leads to superior outcomes compared to PD-1 inhibition alone, offering new hope for patients with cancers that have become resistant to monotherapy.
Preclinical data indicate that dual checkpoint inhibition can provide deeper and more durable responses, especially in malignancies that have previously shown resistance to other immunotherapies. Relatlimab's specificity for LAG-3 may also contribute to a more favorable safety profile, with reduced off-target effects. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing dosing strategies, identifying biomarkers for patient selection, and assessing the drug's potential in treating a range of cancers, positioning Relatlimab as a powerful agent in the next generation of cancer immunotherapies.
3.) Clinical Applications of Relatlimab
Relatlimab has demonstrated substantial clinical promise, particularly in advanced melanoma, where its combination with nivolumab has shown compelling results. In the Phase 3 RELATIVITY-047 trial, the combination therapy significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared to nivolumab alone in patients with previously untreated metastatic or unresectable melanoma. This trial marks a key milestone in solidifying Relatlimab's place in the immunotherapy landscape, offering a potent alternative to monotherapy and paving the way for new treatment options for melanoma patients.
Beyond melanoma, the therapeutic potential of Relatlimab is being actively explored in various other malignancies, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and other solid tumors. Early clinical findings suggest that blocking LAG-3 can enhance the effectiveness of existing immunotherapies, particularly in tumors exhibiting high levels of immune exhaustion. This has prompted further investigation into Relatlimab's synergy with other treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy, radiation, and other immune-modulating agents. These studies aim to expand its utility and provide novel therapeutic options for a broader patient population.
Relatlimab’s ability to boost immune responses, improve the durability of treatment, and overcome resistance mechanisms positions it as a valuable tool in modern oncology. If ongoing trials confirm its success across multiple tumor types, Relatlimab has the potential to become a cornerstone in combination immunotherapy. It offers new hope for patients with cancers that have been challenging to treat with existing therapies, reinforcing the evolving landscape of immune checkpoint blockade and cancer immunotherapy.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Relatlimab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a highly similar alternative to an approved biologic drug, offering comparable efficacy and safety. In research, biosimilars serve as crucial tools for studying drug mechanisms, optimizing treatments, and expanding access to investigational therapies.
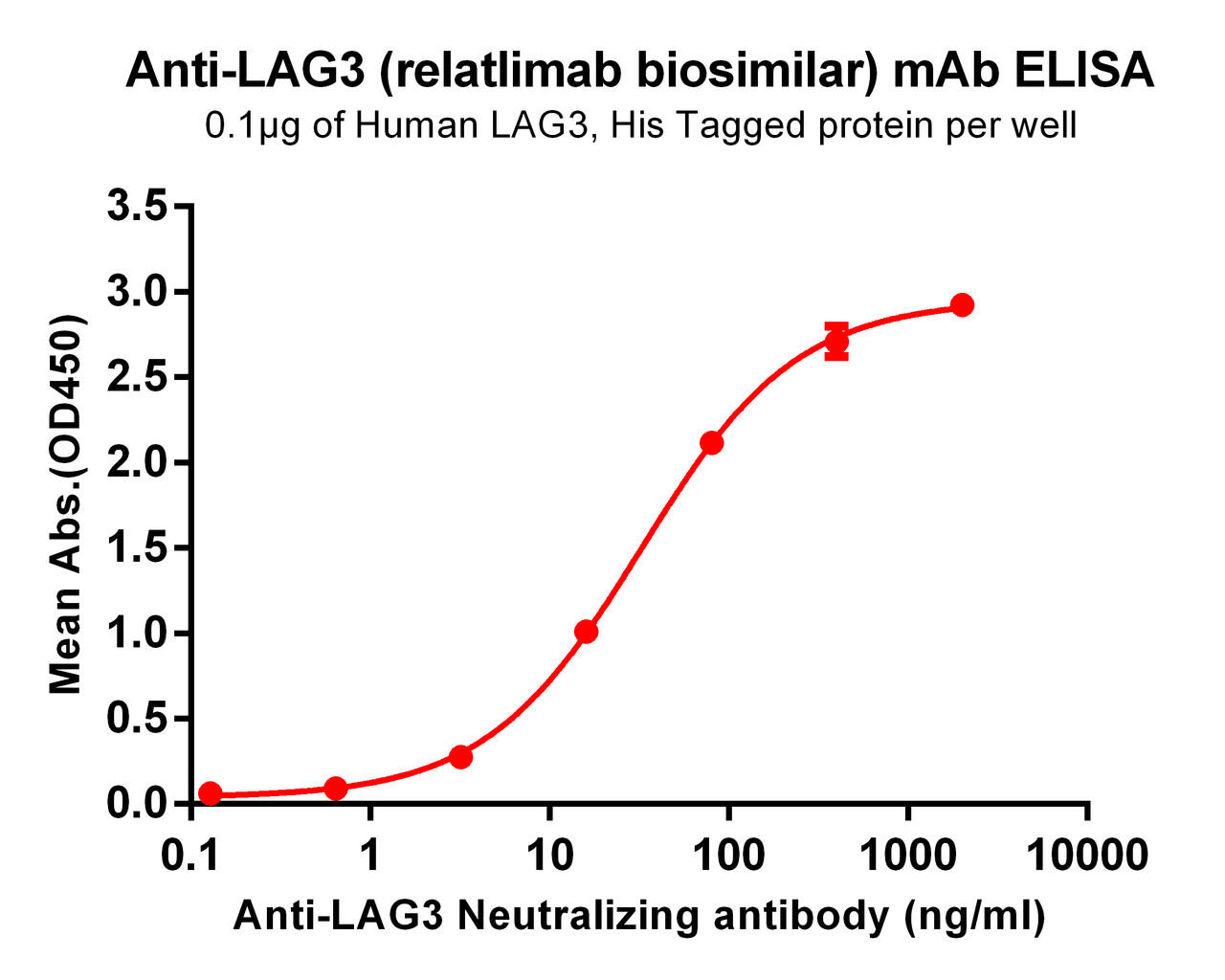
| Relatlimab (Anti-LAG3) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | LAG3 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does a Relatlimab Biosimilar Compare?
A biosimilar of Relatlimab retains the same LAG-3 targeting mechanism, making it valuable for preclinical studies, mechanistic research, and combination therapy exploration. While not interchangeable for clinical use, research-grade biosimilars provide cost-effective solutions for advancing scientific discovery.
Advantages of Research Biosimilars
- Cost-effective: Enables broader preclinical evaluations without the high cost of proprietary drugs.
- Accessible: Facilitates research into LAG-3 inhibition across different cancer models.
- Scalable: Supports high-throughput screening and combination therapy studies.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
The Relatlimab biosimilar is intended for research applications and is not approved for clinical use.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



