Bevacizumab: Mechanism, Clinical Applications, and Biosimilar Insights
Quick Facts About Bevacizumab
What is Bevacizumab?
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), inhibiting angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels) to restrict tumor growth.
How does Bevacizumab work?
It binds to VEGF, preventing it from interacting with its receptors on endothelial cells, thereby reducing blood supply to tumors and slowing their progression.
What are the clinical applications of Bevacizumab?
Bevacizumab is used in the treatment of multiple cancers, including colorectal, lung, and ovarian cancers, as well as certain eye conditions such as age-related macular degeneration.
What are the common side effects of Bevacizumab?
Side effects include hypertension, bleeding, gastrointestinal perforation, and proteinuria. Regular monitoring is required for patients undergoing treatment.
1.) Understanding Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab is a groundbreaking monoclonal antibody that has significantly impacted the treatment of multiple solid tumors through its targeted anti-angiogenic mechanism. Developed as the first FDA-approved inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), Bevacizumab has become a cornerstone in cancer therapy by effectively disrupting tumor vascularization. Angiogenesis, the process of new blood vessel formation, is critical for tumor growth and metastasis. By inhibiting VEGF, Bevacizumab blocks this essential process, depriving tumors of the nutrients and oxygen needed to sustain rapid growth, ultimately slowing disease progression and improving patient outcomes.
Primarily, Bevacizumab is used in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), renal cell carcinoma, and glioblastoma. Its ability to inhibit angiogenesis has revolutionized the way certain cancers are managed, offering patients prolonged progression-free survival and enhanced quality of life. Beyond oncology, Bevacizumab is also widely used off-label in ophthalmology, where it has proven to be an effective and cost-efficient treatment for retinal diseases such as wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic macular edema, offering a viable alternative to other anti-VEGF therapies like ranibizumab and aflibercept.
Recent research is investigating Bevacizumab’s potential in combination with other immunotherapies, particularly immune checkpoint inhibitors like PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. By improving immune cell infiltration into tumors and modulating the tumor microenvironment, Bevacizumab may enhance the efficacy of these therapies, offering new hope for patients with treatment-resistant cancers. As ongoing trials continue to explore Bevacizumab's synergistic effects, it is poised to remain a critical component of precision oncology and personalized medicine.
2.) Mechanism of Action of Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab exerts its anti-cancer effects by inhibiting VEGF-A, a signaling protein that plays a critical role in angiogenesis. Under normal physiological conditions, VEGF-A is essential for wound healing, tissue regeneration, and vascular homeostasis. However, in malignancies, tumors hijack the VEGF pathway to stimulate the formation of an abnormal blood vessel network, providing the necessary oxygen and nutrients for unchecked proliferation. The overexpression of VEGF-A in various cancers correlates with increased tumor aggressiveness, resistance to therapy, and poor prognosis.
Bevacizumab works by binding to VEGF-A, preventing it from interacting with VEGF receptors (VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2) on endothelial cells. This blockade halts the pro-angiogenic signaling cascade, leading to several beneficial effects:
- Inhibition of Tumor Angiogenesis: By cutting off the tumor’s blood supply, Bevacizumab limits growth and metastasis.
- Normalization of Tumor Vasculature: It reduces abnormal vessel permeability, leading to improved oxygenation and drug delivery when combined with chemotherapy.
- Reduction of Intratumoral Pressure: This improves perfusion and enhances the penetration of other therapeutic agents, maximizing their efficacy.
Additionally, Bevacizumab’s vascular normalization effect helps improve the tumor microenvironment, making tumors more susceptible to immunotherapy. Preclinical and clinical studies indicate that VEGF inhibition can enhance immune response by reducing immune suppression and increasing the infiltration of cytotoxic T cells into the tumor. This has led to the exploration of Bevacizumab in combination with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and other immunotherapies. The ongoing search for predictive biomarkers, such as circulating VEGF levels and tumor hypoxia signatures, aims to optimize patient selection and personalize treatment strategies for better clinical outcomes.
3.) Clinical Applications of Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab has demonstrated clinical benefits across multiple cancer types and continues to be a subject of ongoing research for expanded applications. Its primary FDA-approved indications include:
1. Colorectal Cancer: Bevacizumab is a standard component of treatment regimens for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), often combined with chemotherapy protocols such as FOLFOX (5-FU, leucovorin, oxaliplatin) and FOLFIRI (5-FU, leucovorin, irinotecan). Clinical trials have shown that adding Bevacizumab significantly improves progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in mCRC patients, making it a key part of first- and second-line therapy.
2. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Used in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy, Bevacizumab enhances disease control in advanced or metastatic NSCLC. Its anti-angiogenic mechanism reduces tumor vascularity, leading to prolonged survival. Ongoing trials are evaluating its role in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors to enhance response rates in NSCLC patients.
3. Glioblastoma: Approved for recurrent glioblastoma, Bevacizumab helps manage tumor-associated edema and improves PFS. While it does not significantly extend OS, it offers symptomatic relief and enhances quality of life by reducing intracranial pressure.
4. Ovarian Cancer: Bevacizumab is used in combination with chemotherapy for both platinum-sensitive and platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. It has shown efficacy in delaying disease progression and is a key agent in maintenance therapy.
5. Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): When combined with interferon-alpha, Bevacizumab enhances immune response and delays tumor progression in metastatic RCC. It is also being studied in combination with newer tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors.
6. Ophthalmic Applications: Bevacizumab is widely used off-label for wet AMD, diabetic retinopathy, and retinal vein occlusion. Despite being originally developed for oncology, its affordability and efficacy have made it a preferred choice in ophthalmology.
Future directions for Bevacizumab include evaluating its role in neoadjuvant settings, refining biomarkers for patient selection, and expanding its use in combination therapies. As research advances, Bevacizumab remains a vital drug in both oncology and ophthalmology.
4.) Exploring Biosimilars for Bevacizumab
What is a Biosimilar?
A biosimilar is a highly similar version of an approved biologic drug, developed to offer comparable efficacy, safety, and quality. Unlike generic drugs, biosimilars undergo rigorous testing to ensure they match the original biologic’s characteristics.
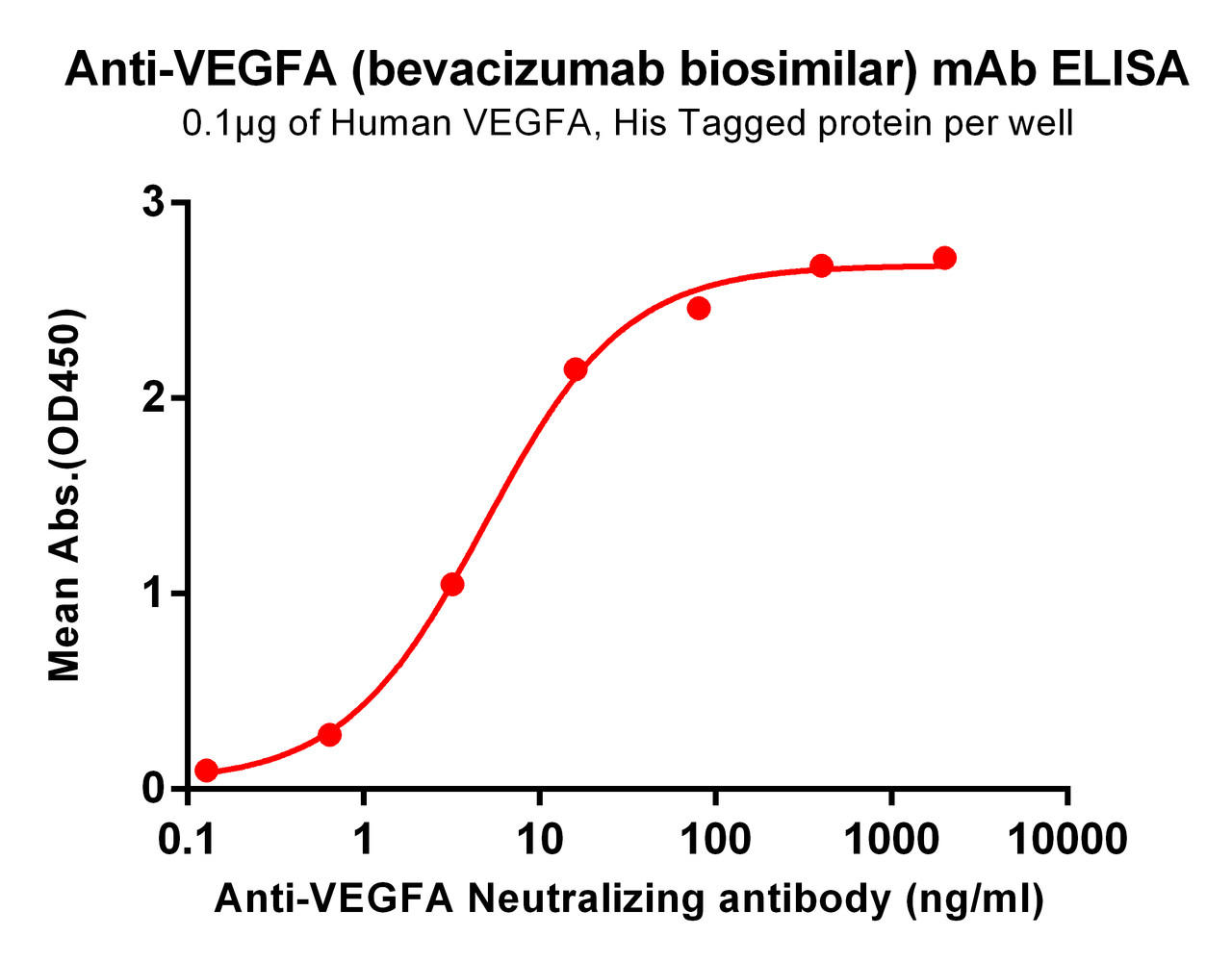
| Bevacizumab (Anti-VEGFA) Biosimilar Antibody | |
|---|---|
| Antibody Type: | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Protein: | VEGFA |
| Reactivity: | Human |
How Does a Bevacizumab Biosimilar Compare?
Biosimilars of Bevacizumab provide a cost-effective alternative for research and clinical use. These products maintain the same mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and therapeutic effects, making them valuable tools in oncology research.
Benefits for Research Applications
Bevacizumab biosimilars are widely used in preclinical and translational research. Their availability allows scientists to:
- Study VEGF inhibition mechanisms in various cancers.
- Develop combination therapies with immunotherapeutic agents.
- Evaluate resistance mechanisms and predictive biomarkers for anti-angiogenic therapy.
Research Use Only Disclaimer:
Bevacizumab biosimilars discussed here are for research use only and not intended for clinical application.
Discover Our Biosimilar Range
At Assay Genie, we specialize in providing high-quality biosimilars for research use! Check out our full biosimilar range to learn more.

By Chris McNally, PhD
Chris McNally, PhD, has a strong foundation in Biomedical Science, completing a PhD scholarship in collaboration with Randox Laboratories and Ulster University. Chris has published extensively in prostate cancer research, focusing on biomarker discovery, cancer risk stratification, and molecular mechanisms such as hypoxia-induced regulation. He currently serves as a Business Development Manager at Assay Genie.
Recent Posts
-
Enavatuzumab: Revolutionizing Cancer Research Through Novel Therapeutics
Quick Facts About EnavatuzumabWhat is Enavatuzumab?Enavatuzumab is a monoclonal antibo …17th Dec 2025 -
Alemtuzumab: Mechanism, Applications, and Biosimilar Advancements
Quick Facts About AlemtuzumabWhat is Alemtuzumab?Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody …17th Dec 2025 -
Validation of MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit - A highly sensitive visual determination method for Mycoplasma detection.
The MycoGenie Rapid Mycoplasma Detection Kit enables the detection of 28 Mycoplasma sp …3rd Mar 2025



