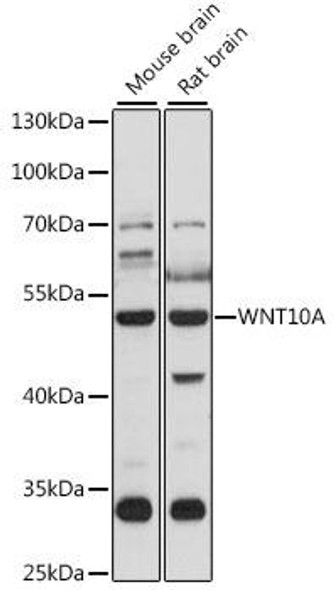
WNT10A Antibody (PACO20922)
- SKU:
- PACO20922
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Applications:
- ELISA
- IHC
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Conjugation:
- Unconjugated
Description
WNT10A Antibody (PACO20922)
The Wnt10A Polyclonal Antibody (PAC020922) is a vital tool for researchers studying Wnt10A, a signaling protein involved in various cellular processes, including embryogenesis, tissue regeneration, and cancer development. This antibody, produced in rabbits, exhibits high specificity for human samples and has been validated for use in Western blotting applications. By binding to the Wnt10A protein, researchers can accurately detect and analyze its expression in different cell types, making it an excellent choice for investigations in developmental biology and oncology.Wnt10A is a key player in the Wnt signaling pathway, which regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue homeostasis.
Dysregulation of Wnt signaling, including aberrant Wnt10A expression, is associated with numerous diseases, such as cancer and developmental disorders. Understanding the role of Wnt10A in these pathological conditions is essential for developing targeted therapies and diagnostic tools. By utilizing the Wnt10A Polyclonal Antibody, researchers can gain valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying these diseases and potentially identify novel therapeutic targets.
| Antibody Name: | WNT10A Antibody (PACO20922) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO20922 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:1000-1:2000, IHC:1:10-1:50 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide of human WNT10A |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
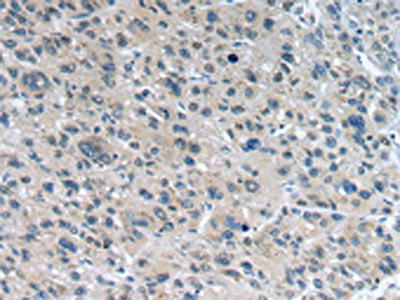 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using PACO20922(WNT10A Antibody) at dilution 1/25, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
| Background: | The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. It is strongly expressed in the cell lines of promyelocytic leukemia and Burkitt's lymphoma. In addition, it and another family member, the WNT6 gene, are strongly coexpressed in colorectal cancer cell lines. The gene overexpression may play key roles in carcinogenesis through activation of the WNT-beta-catenin-TCF signaling pathway. This gene and the WNT6 gene are clustered in the chromosome 2q35 region. |
| Synonyms: | wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10A |
| UniProt Protein Function: | WNT10A: Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors. Probable developmental protein. May be a signaling molecule important in CNS development. Is likely to signal over only few cell diameters. Defects in WNT10A are a cause of ectodermal dysplasia anhidrotic (EDA); also known ectodermal dysplasia hypohidrotic autosomal recessive (HED). Ectodermal dysplasia defines a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. EDA is characterized by sparse hair (atrichosis or hypotrichosis), abnormal or missing teeth and the inability to sweat due to the absence of sweat glands. Most patients carrying WNT10A mutations present with sweating anomalies. However, comparison with EDA cases harboring mutations in the ectodysplasin pathway identifies some phenotypic differences. Dermatological features (anomalies of hair and sweat glands) are less severe in patients carrying WNT10A mutations and facial dysmorphism can be absent. The dental phenotype consists in microdontia, whereas teeth agenesis is more frequent in patients carrying mutations in the ectodysplasin pathway. Defects in WNT10A are a cause of odonto-onycho-dermal dysplasia (OODD). OODD is a rare autosomal recessive ectodermal dysplasia in which the presenting phenotype is dry hair, severe hypodontia, smooth tongue with marked reduction of fungiform and filiform papillae, onychodysplasia, keratoderma and hyperhidrosis of palms and soles, and hyperkeratosis of the skin. Defects in WNT10A are a cause of Schopf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome (SSPS). SSPS is rare ectodermal dysplasia, characterized chiefly by cysts of the eyelid margins, palmoplantar keratoderma, hypodontia, hypotrichosis and nail dystrophy. Multiple eyelid apocrine hidrocystomas are the hallmark of this condition, although they usually appear in adulthood. The concomitant presence of eccrine syringofibroadenoma in most patients and of other adnexal skin tumors in some affected subjects indicates that Schopf-Schulz-Passarge syndrome is a genodermatosis with skin appendage neoplasms. Belongs to the Wnt family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted, signal peptide; Secreted Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2q35 Cellular Component: extracellular space; proteinaceous extracellular matrix; extracellular region Molecular Function:frizzled binding Biological Process: skin development; neuron differentiation; odontogenesis; tongue development; hair follicle morphogenesis; Wnt receptor signaling pathway; cell fate commitment; hair follicle development; epidermis morphogenesis; sebaceous gland development; neural crest cell differentiation; regulation of odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth Disease: Schopf-schulz-passarge Syndrome; Tooth Agenesis, Selective, 4; Odontoonychodermal Dysplasia |
| NCBI Summary: | The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. It is strongly expressed in the cell lines of promyelocytic leukemia and Burkitt's lymphoma. In addition, it and another family member, the WNT6 gene, are strongly coexpressed in colorectal cancer cell lines. The gene overexpression may play key roles in carcinogenesis through activation of the WNT-beta-catenin-TCF signaling pathway. This gene and the WNT6 gene are clustered in the chromosome 2q35 region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9GZT5 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 14424011 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 80326 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9GZT5.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9GZT5,Q53S44, Q96TA7, Q9H7S8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9GZT5 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46,444 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Protein Wnt-10a |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | WNT10A |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | OODD; SSPS; STHAG4 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | protein Wnt-10a |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Protein Wnt-10a |
| UniProt Gene Name: | WNT10A |
| UniProt Entry Name: | WN10A_HUMAN |
| Antibodies | ELISA Kits |
| Anti-WNT10A Antibody (CAB14668) | Human WNT10A ELISA Kit |
| Anti-WNT10A Antibody (CAB15602) | Human Protein Wnt-10a (WNT10A) ELISA Kit |
| Secondary Antibody |
| Anti-HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Antibody (CABS014) |
| Recommended Products |
| Anti-FITC Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Antibody (CABS011) |
| Anti-HRP-conjugated Beta Actin Antibody (CABC028) |