Description
VLDLR Antibody (PACO20858)
The VLDLR Antibody (PAC020858) is a crucial tool for researchers studying the very-low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) and its role in lipid metabolism and neurological development. This polyclonal antibody, generated in rabbits, demonstrates high specificity and reactivity with human samples, making it ideal for use in Western blot applications.VLDLR is a cell surface receptor involved in the clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins from the bloodstream and is also implicated in neuronal migration and synapse formation in the brain.
Dysregulation of VLDLR function has been linked to conditions such as atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and autism spectrum disorders, highlighting the importance of studying this receptor.By utilizing the VLDLR Antibody, researchers can effectively detect and analyze VLDLR protein expression in various cell types, providing valuable insights into its physiological functions and potential therapeutic implications. This antibody is a valuable tool for investigations in lipid metabolism, neurobiology, and cardiovascular disease research.
| Antibody Name: | VLDLR Antibody (PACO20858) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO20858 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:5000, IHC:1:25-1:100 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide of human VLDLR |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
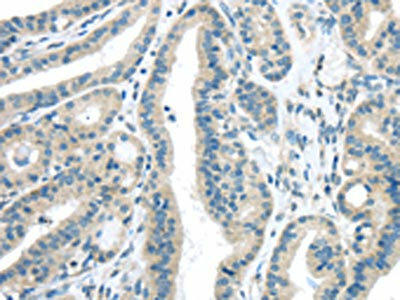 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human thyroid cancer tissue using PACO20858(VLDLR Antibody) at dilution 1/35, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
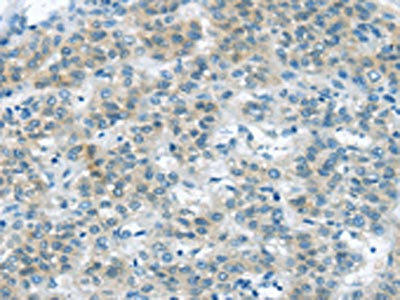 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using PACO20858(VLDLR Antibody) at dilution 1/35, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
| Background: | The low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene family consists of cell surface proteins involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis of specific ligands. This gene encodes a lipoprotein receptor that is a member of the LDLR family and plays important roles in VLDL-triglyceride metabolism and the reelin signaling pathway. Mutations in this gene cause VLDLR-associated cerebellar hypoplasia. Alternative splicing generates multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms for this gene. |
| Synonyms: | very low density lipoprotein receptor |
| UniProt Protein Function: | VLDLR: Binds VLDL and transports it into cells by endocytosis. In order to be internalized, the receptor-ligand complexes must first cluster into clathrin-coated pits. Binding to Reelin induces tyrosine phosphorylation of Dab1 and modulation of Tau phosphorylation. Defects in VLDLR are the cause of cerebellar ataxia mental retardation and dysequilibrium syndrome type 1 (CMARQ1); also known as dysequilibrium syndrome (DES) or non- progressive cerebellar disorder with mental retardation. CMARQ1 is a congenital, non-progressive cerebellar ataxia associated with disturbed equilibrium, delayed ambulation, mental retardation and cerebellar hypoplasia. Additional features include short stature, strabismus, pes planus and, rarely, seizures. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, integral; Receptor, misc. Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 9p24 Cellular Component: membrane; plasma membrane; integral to membrane; coated pit; receptor complex Molecular Function:very-low-density lipoprotein receptor activity; low-density lipoprotein receptor activity; very-low-density lipoprotein binding; protein binding; apolipoprotein binding; calcium ion binding; glycoprotein binding; calcium-dependent protein binding Biological Process: nervous system development; receptor-mediated endocytosis; cholesterol metabolic process; positive regulation of protein kinase activity; ventral spinal cord development; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; signal transduction; lipid transport; memory Disease: Cerebellar Ataxia, Mental Retardation, And Dysequilibrium Syndrome 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | The low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene family consists of cell surface proteins involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis of specific ligands. This gene encodes a lipoprotein receptor that is a member of the LDLR family and plays important roles in VLDL-triglyceride metabolism and the reelin signaling pathway. Mutations in this gene cause VLDLR-associated cerebellar hypoplasia. Alternative splicing generates multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P98155 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 65301167 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7436 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_003374.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P98155,Q5VVF6, B2RMZ7, D3DRH6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P98155 |
| Molecular Weight: | 96,098 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | very low-density lipoprotein receptor isoform a |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | very low density lipoprotein receptor |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | VLDLR |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CARMQ1; CHRMQ1; VLDLRCH |
| NCBI Protein Information: | very low-density lipoprotein receptor; VLDL-R; VLDL receptor |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Very low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| Protein Family: | Very low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | VLDLR |
| UniProt Entry Name: | VLDLR_HUMAN |
| Secondary Antibody |
| Anti-HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Antibody (CABS014) |
| Recommended Products |
| Anti-FITC Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Antibody (CABS011) |
| Anti-HRP-conjugated Beta Actin Antibody (CABC028) |














