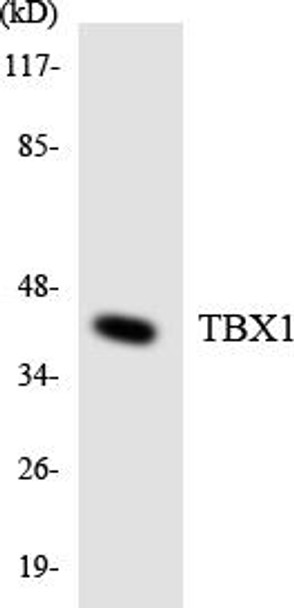
Description
TBX1 Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA
The TBX1 Colorimetric Cell Based ELISA Kit is a cutting-edge tool designed for the accurate detection of TBX1 levels in cell lysates and culture supernatants. This kit boasts high sensitivity and specificity, ensuring precise and consistent results for a variety of research applications.TBX1 is a key transcription factor that plays a vital role in embryonic development, particularly in the formation of the heart and the thymus. Dysregulation of TBX1 has been linked to several congenital disorders, including DiGeorge Syndrome.
By measuring TBX1 levels, researchers can gain valuable insights into developmental processes and potential therapeutic targets for these conditions.With its advanced technology and proven performance, the TBX1 Colorimetric Cell Based ELISA Kit is an indispensable tool for studying TBX1 function and its implications in human development and disease.
| Product Name: | TBX1 Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA |
| Product Code: | CBCAB00933 |
| ELISA Type: | Cell-Based |
| Target: | TBX1 |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Dynamic Range: | > 5000 Cells |
| Detection Method: | Colorimetric 450 nmStorage/Stability:4°C/6 Months |
| Format: | 96-Well Microplate |
The TBX1 Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit is a convenient, lysate-free, high throughput and sensitive assay kit that can detect TBX1 protein expression profile in cells. The kit can be used for measuring the relative amounts of TBX1 in cultured cells as well as screening for the effects that various treatments, inhibitors (ie siRNA or chemicals), or activators have on TBX1.
Qualitative determination of TBX1 concentration is achieved by an indirect ELISA format. In essence, TBX1 is captured by TBX1-specific primary antibodies while the HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies bind the Fc region of the primary antibody. Through this binding, the HRP enzyme conjugated to the secondary antibody can catalyze a colorimetric reaction upon substrate addition. Due to the qualitative nature of the Cell-Based ELISA, multiple normalization methods are needed:
| 1. | A monoclonal antibody specific for human GAPDH is included to serve as an internal positive control in normalizing the target absorbance values. |
| 2. | Following the colorimetric measurement of HRP activity via substrate addition, the Crystal Violet whole-cell staining method may be used to determine cell density. After staining, the results can be analysed by normalizing the absorbance values to cell amounts, by which the plating difference can be adjusted. |
| Database Information: | Gene ID: 6899, UniProt ID: O43435, OMIM: 188400/192430/217095/602054, Unigene: Hs.173984 |
| Gene Symbol: | TBX1 |
| Sub Type: | None |
| UniProt Protein Function: | TBX1: Probable transcriptional regulator involved in developmental processes. Is required for normal development of the pharyngeal arch arteries. Haploinsufficiency of the TBX1 gene is responsible for most of the physical malformations present in DiGeorge syndrome (DGS) and velocardiofacial syndrome (VCFS). DGS is characterized by the association of several malformations: hypoplastic thymus and parathyroid glands, congenital conotruncal cardiopathy, and a subtle but characteristic facial dysmorphology. VCFS is marked by the association of congenital conotruncal heart defects, cleft palate or velar insufficiency, facial dysmorpholgy and learning difficulties. It is now accepted that these two syndromes represent two forms of clinical expression of the same entity manifesting at different stages of life. Defects in TBX1 are a cause of DiGeorge syndrome (DGS). Defects in TBX1 are a cause of velocardiofacial syndrome (VCFS). Defects in TBX1 are a cause of conotruncal heart malformations (CTHM). CTHM consist of cardiac outflow tract defects, such as tetralogy of Fallot, pulmonary atresia, double-outlet right ventricle, truncus arteriosus communis, and aortic arch anomalies. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 22q11.21 Cellular Component: nucleus Molecular Function:DNA binding; protein dimerization activity; protein homodimerization activity; sequence-specific DNA binding; transcription factor activity Biological Process: angiogenesis; anterior/posterior pattern formation; artery morphogenesis; blood vessel development; blood vessel morphogenesis; blood vessel remodeling; cell fate specification; cell proliferation; determination of left/right symmetry; ear morphogenesis; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis; embryonic viscerocranium morphogenesis; epithelial cell differentiation; heart development; heart morphogenesis; inner ear morphogenesis; lymph vessel development; mesoderm development; middle ear morphogenesis; muscle cell fate commitment; muscle development; muscle morphogenesis; negative regulation of cell differentiation; neural crest cell migration; odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth; outer ear morphogenesis; parathyroid gland development; pattern specification process; pharyngeal system development; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway; semicircular canal morphogenesis; sensory perception of sound; social behavior; soft palate development; thymus development; thyroid gland development; tongue morphogenesis; transcription, DNA-dependent; vagus nerve morphogenesis Disease: Conotruncal Heart Malformations; Digeorge Syndrome; Tetralogy Of Fallot; Velocardiofacial Syndrome |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a member of a phylogenetically conserved family of genes that share a common DNA-binding domain, the T-box. T-box genes encode transcription factors involved in the regulation of developmental processes. This gene product shares 98% amino acid sequence identity with the mouse ortholog. DiGeorge syndrome (DGS)/velocardiofacial syndrome (VCFS), a common congenital disorder characterized by neural-crest-related developmental defects, has been associated with deletions of chromosome 22q11.2, where this gene has been mapped. Studies using mouse models of DiGeorge syndrome suggest a major role for this gene in the molecular etiology of DGS/VCFS. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O43435 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 6175055 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6899 |
| NCBI Accession: | O43435.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O43435,O43436, Q96RJ2, C6G493, C6G494, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O43435 |
| Molecular Weight: | 52,666 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | T-box transcription factor TBX1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | T-box 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TBX1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | DGS; TGA; VCF; CAFS; CTHM; DGCR; DORV; VCFS; TBX1C; CATCH22 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | T-box transcription factor TBX1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | T-box transcription factor TBX1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Testis-specific T-box protein |
| Protein Family: | T-box transcription factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TBX1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TBX1_HUMAN |
| Component | Quantity |
| 96-Well Cell Culture Clear-Bottom Microplate | 2 plates |
| 10X TBS | 24 mL |
| Quenching Buffer | 24 mL |
| Blocking Buffer | 50 mL |
| 15X Wash Buffer | 50 mL |
| Primary Antibody Diluent | 12 mL |
| 100x Anti-Phospho Target Antibody | 60 µL |
| 100x Anti-Target Antibody | 60 µL |
| Anti-GAPDH Antibody | 60 µL |
| HRP-Conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Antibody | 12 mL |
| HRP-Conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Antibody | 12 mL |
| SDS Solution | 12 mL |
| Stop Solution | 24 mL |
| Ready-to-Use Substrate | 12 mL |
| Crystal Violet Solution | 12 mL |
| Adhesive Plate Seals | 2 seals |
The following materials and/or equipment are NOT provided in this kit but are necessary to successfully conduct the experiment:
- Microplate reader able to measure absorbance at 450 nm and/or 595 nm for Crystal Violet Cell Staining (Optional)
- Micropipettes with capability of measuring volumes ranging from 1 µL to 1 ml
- 37% formaldehyde (Sigma Cat# F-8775) or formaldehyde from other sources
- Squirt bottle, manifold dispenser, multichannel pipette reservoir or automated microplate washer
- Graph paper or computer software capable of generating or displaying logarithmic functions
- Absorbent papers or vacuum aspirator
- Test tubes or microfuge tubes capable of storing ≥1 ml
- Poly-L-Lysine (Sigma Cat# P4832 for suspension cells)
- Orbital shaker (optional)
- Deionized or sterile water
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
| Step | Procedure |
| 1. | Seed 200 µL of 20,000 adherent cells in culture medium in each well of a 96-well plate. The plates included in the kit are sterile and treated for cell culture. For suspension cells and loosely attached cells, coat the plates with 100 µL of 10 µg/ml Poly-L-Lysine (not included) to each well of a 96-well plate for 30 minutes at 37°C prior to adding cells. |
| 2. | Incubate the cells for overnight at 37°C, 5% CO2. |
| 3. | Treat the cells as desired. |
| 4. | Remove the cell culture medium and rinse with 200 µL of 1x TBS, twice. |
| 5. | Fix the cells by incubating with 100 µL of Fixing Solution for 20 minutes at room temperature. The 4% formaldehyde is used for adherent cells and 8% formaldehyde is used for suspension cells and loosely attached cells. |
| 6. | Remove the Fixing Solution and wash the plate 3 times with 200 µL 1x Wash Buffer for five minutes each time with gentle shaking on the orbital shaker. The plate can be stored at 4°C for a week. |
| 7. | Add 100 µL of Quenching Buffer and incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature. |
| 8. | Wash the plate 3 times with 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 9. | Add 200 µL of Blocking Buffer and incubate for 1 hour at room temperature. |
| 10. | Wash 3 times with 200 µL of 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 11. | Add 50 µL of 1x primary antibodies (Anti-TBX1 Antibody and/or Anti-GAPDH Antibody) to the corresponding wells, cover with Parafilm and incubate for 16 hours (overnight) at 4°C. If the target expression is known to be high, incubate for 2 hours at room temperature. |
| 12. | Wash 3 times with 200 µL of 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 13. | Add 50 µL of 1x secondary antibodies (HRP-Conjugated AntiRabbit IgG Antibody or HRP-Conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Antibody) to corresponding wells and incubate for 1.5 hours at room temperature. |
| 14. | Wash 3 times with 200 µL of 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 15. | Add 50 µL of Ready-to-Use Substrate to each well and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature in the dark. |
| 16. | Add 50 µL of Stop Solution to each well and read OD at 450 nm immediately using the microplate reader. |
(Additional Crystal Violet staining may be performed if desired – details of this may be found in the kit technical manual.)