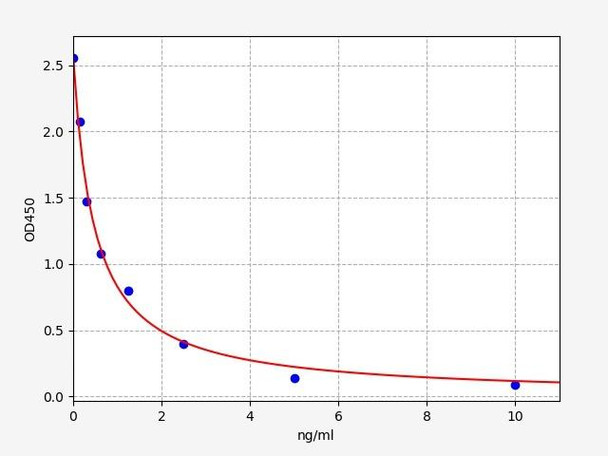
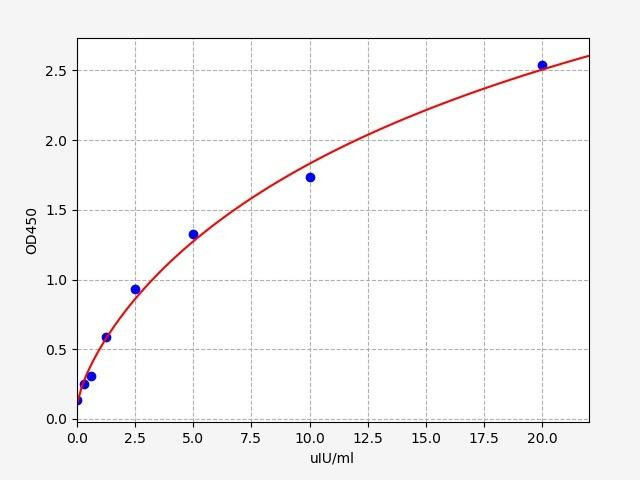
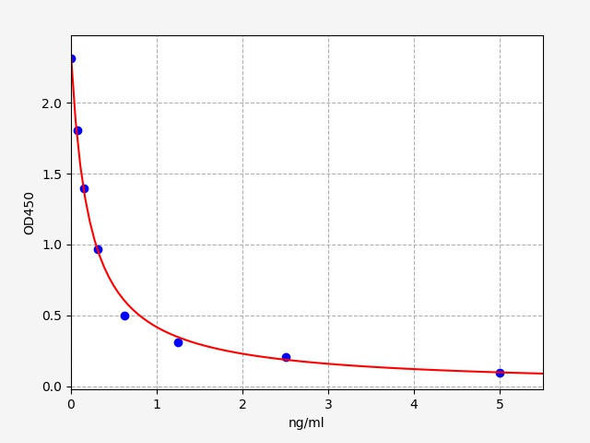
Description
T3 / Triiodothyronine ELISA Kit
The T3 ELISA Kit is designed for the quantitative measurement of triiodothyronine (T3) levels in biological samples. T3 is a vital thyroid hormone involved in metabolism, growth, and other physiological processes. This kit allows researchers to accurately assess T3 concentrations, aiding studies related to thyroid function, metabolism, and hormonal regulation.
Key Features
| Save Time | Pre-coated 96 well plate | |
| Quick Start | Kit includes all necessary reagents | |
| Publication Ready | Reproducible and reliable results |
Overview
| Product Name: | T3 (Triiodothyronine) ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | UNFI0016 |
| Size: | 96 Assays |
| Alias: | T3, Triiodothyronine |
| Detection Method: | Competitive ELISA, Coated with Antibody |
| Reactivity: | Universal |
| Sensitivity: | 0.094ng/ml |
| Range: | 0.156-10ng/ml |
| Storage: | 4°C for 6 months |
| Note: | For Research Use Only |
Additional Information
| Recovery | Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of T3 and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of T3 in samples.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Linearity: | The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of T3 and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Intra Assay | CV < 8% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Inter Assay | CV < 10% |
Kit Components
| Component | Quantity | Storage |
| ELISA Microplate (Dismountable) | 8x12 strips | 4°C for 6 months |
| Lyophilized Standard | 2 | 4°C/ -20°C |
| Sample/Standard Dlution Buffer | 20ml | 4°C |
| Biotin-labeled Antibody (Concentrated) | 120ul | 4°C (Protection from light) |
| Antibody Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate (SABC) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| SABC Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| TMB Substrate | 10ml | 4°C (Protection from light) |
| Stop Solution | 10ml | 4°C |
| Wash Buffer (25X) | 30ml | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 | - |
Other materials required:
- Microplate reader with 450 nm wavelength filter
- Multichannel Pipette, Pipette, microcentrifuge tubes and disposable pipette tips
- Incubator
- Deionized or distilled water
- Absorbent paper
- Buffer resevoir
Protocol
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
Equilibrate the TMB substrate for at least 30 min at 37°C beforeuse. When diluting samples and reagents, they must be mixed completely andevenly. It is recommended to plot a standard curve for each test.
| Step | Procedure |
| 1. | Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coatedplate respectively, and then, record their positions. It isrecommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Washplate 2 times before adding standard, sample and control (zero) wells! |
| 2. | Add Sample and Biotin-detection antibody: Add 50µL of Standard, Blank or Sample per well. The blankwell is added with Sample Dilution Buffer. Immediately add 50 µL of biotin-labelled antibody workingsolution to each well. Cover with the plate sealer provided. Gently tap the plate to ensure thoroughmixing. Incubate for 45 minutes at 37°C. (Solutions are added to the bottom of micro-ELISA platewell, avoid touching plate walls and foaming). |
| 3. | Wash: Aspirate each well and wash, repeating the process three timesWash by filling each well with Wash Buffer (approximately 350µL)using a squirt bottle, multi-channel pipette, manifold dispenser orautomated washer. Complete removal of liquid at each step is essentialto good performance. After the last wash, remove any remaining WashBuffer by aspirating or decanting. Invert the plate and pat it againstthick clean absorbent paper. |
| 4. | HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate(SABC): Add 100µL of SABC workingsolution to each well. Cover with a new Plate sealer. Incubate for30minutes at 37°C. |
| 5. | Wash: Repeat the aspiration/wash process for five times. |
| 6. | TMB Substrate: Add 90µL of TMB Substrate to each well. Coverwith a new Plate sealer. Incubate for about 10-20 minutes at 37°C.Protect from light. The reaction time can be shortened or extendedaccording to the actual color change, but not more than 30minutes.When apparent gradient appeared in standard wells, you can terminatethe reaction. |
| 7. | Stop: Add 50µL of Stop Solution to each well. Color turn toyellow immediately. The adding order of stop solution should be as thesame as the substrate solution. |
| 8. | OD Measurement: Determine the optical density (OD Value) of each wellat once, using a microplate reader set to 450 nm. You should open themicroplate reader ahead, preheat the instrument, and set the testing parameters. |
Sample Type
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clot overnight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Remove serum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |
T3 Background
Thyroid Hormone T3
Triiodothyronine, often abbreviated as T3, is one of the two main hormones produced by the thyroid gland. The other hormone is thyroxine (T4). T3 is a crucial hormone in regulating the body's metabolism, energy production, and growth.
T3 Hormone Structure:
T3 is named for its three iodine atoms. Its chemical structure consists of two benzene rings connected by an oxygen atom, with three iodine atoms attached to various positions on the rings. The chemical formula for T3 is C15H12I3NO4.
T3 Hormone Function:
The primary function of T3 is to regulate the body's metabolism. It does this by influencing the rate at which cells use energy and the synthesis of proteins. T3 affects almost every physiological process in the body, including:
- Metabolism: T3 increases the basal metabolic rate, which is the rate at which the body burns calories at rest. This helps to regulate body temperature and maintain energy balance.
- Cardiovascular System: T3 plays a role in maintaining heart rate and cardiac output, and it supports normal functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Central Nervous System: T3 is essential for proper brain development and function, particularly during fetal and early childhood development.
- Digestive System: T3 influences the digestion and absorption of nutrients from food.
- Muscle Function: T3 affects muscle contraction and strength.
T3 Clinical Significance:
The levels of T3 in the blood can have significant clinical implications. Abnormal levels of T3 can indicate various thyroid disorders:
- Hyperthyroidism: Elevated levels of T3 can be seen in conditions like Grave's disease, where the thyroid gland is overactive and produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. This can lead to symptoms such as weight loss, increased heart rate, anxiety, and heat intolerance.
- Hypothyroidism: Decreased levels of T3 can result from an underactive thyroid gland, as seen in conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and depression.
- Treatment: T3 is sometimes used in medical treatment to manage certain thyroid conditions. It's also used in combination with other thyroid medications to regulate hormone levels in patients with thyroid dysfunction.
T3 ELISA Kit FAQs
Q: What is the purpose of the T3 ELISA Kit?
The T3 ELISA Kit is designed for the quantitative measurement of triiodothyronine (T3) levels in biological samples. T3 is a vital thyroid hormone involved in metabolism, growth, and other physiological processes. This kit allows researchers to accurately assess T3 concentrations, aiding studies related to thyroid function, metabolism, and hormonal regulation.
Q: What type of samples can be used with the kit?
This kit offers universal reactivity, meaning it can be used with various sample types, including serum, plasma, and tissue extracts. However, it's essential to follow the specific sample preparation guidelines provided in the kit's manual.
Q: Is this kit for diagnostic use?
No, the T3 ELISA Kit is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic purposes. It provides reliable data for research studies, helping scientists gain insights into various physiological processes related to thyroid function.
Q: Is the kit compatible with other species besides humans?
Yes, the kit's universal reactivity makes it suitable for use with samples from various species, not just humans. However, it's advisable to verify the cross-reactivity of the kit with your specific species of interest.
Q: Where can I find additional technical support or assistance with the kit?
For any technical inquiries or assistance regarding the kit, you can reach out to our team. They will be available to answer your questions and provide the necessary guidance to ensure a successful experiment.
Related Products
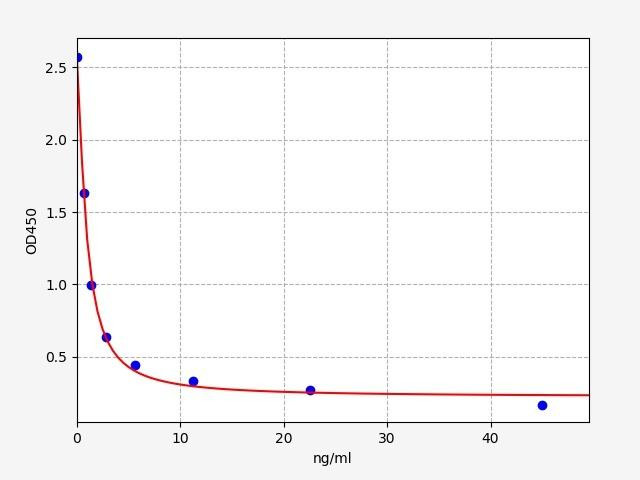
| T4 / Thyroxine ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type: | Competitive |
| Sensitivity: | 0.422ng/ml |
| Range: | 0.703-45ng/ml |
| Human Thyroglobulin ELISA Kit | |
|---|---|
| ELISA Type: | Sandwich |
| Sensitivity: | 75pg/ml |
| Range: | 125-8000pg/ml |
Citations
If you need this ask Sean G for help :)