Description
Anti-SRC Antibody (CAB18240)
The SRC Polyclonal Antibody (CAB18240) is a valuable tool for researchers studying SRC, a critical component in cell signaling pathways and cancer progression. This rabbit-derived antibody is highly specific to SRC and is validated for use in a variety of applications, including Western blotting.SRC is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation through its involvement in multiple signaling cascades. Dysregulation of SRC activity is commonly observed in various types of cancer, making it an important target for therapeutic intervention.
By using the SRC Polyclonal Antibody, researchers can detect and analyze SRC levels in different cell types, allowing for a better understanding of its role in cancer development and progression. This antibody is an essential tool for studies in oncology and cell biology, providing valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying cancer growth and metastasis.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-SRC Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB18240 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
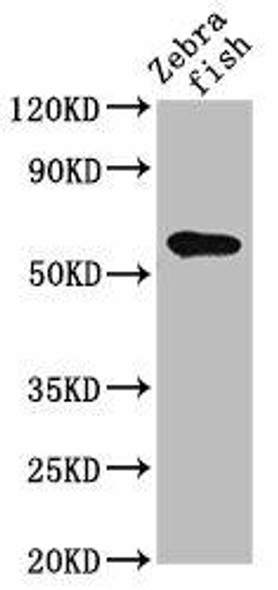
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human SRC. |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
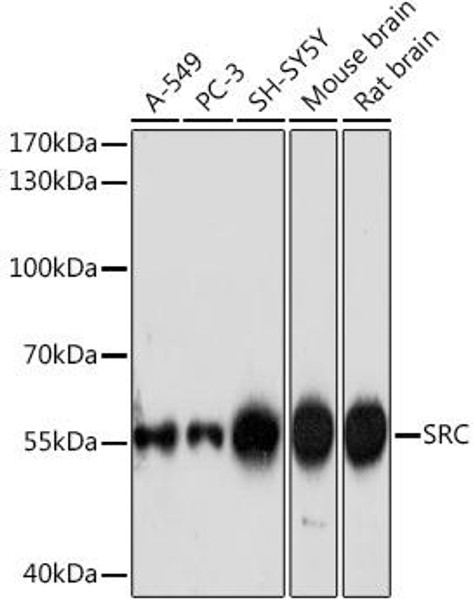
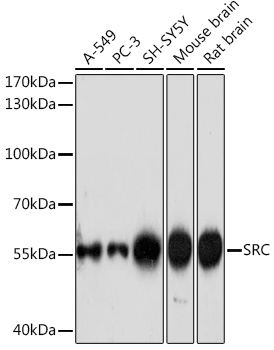
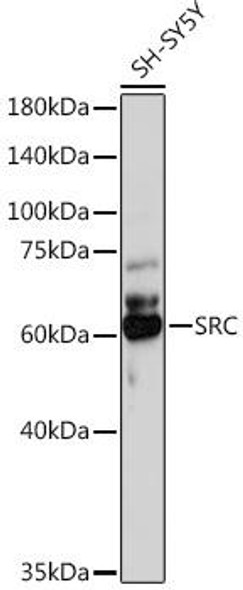
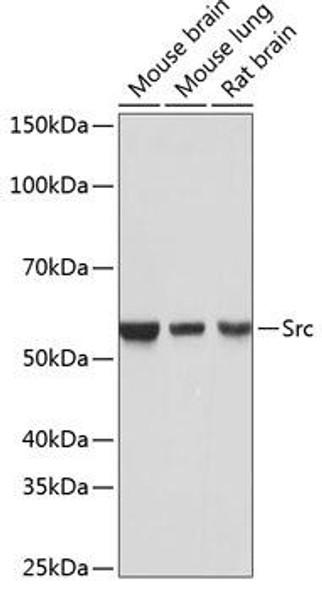
| Positive Samples: | A-549, PC-3, SH-SY5Y, Mouse brain, Rat brain |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human SRC. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 6714 |
| Uniprot: | P12931 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 59kDa |
| Observed MW: | 55kDa |
| Synonyms: | ASV, SRC1, THC6, c-SRC, p60-Src, SRC |
| Background: | This gene is highly similar to the v-src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. This proto-oncogene may play a role in the regulation of embryonic development and cell growth. The protein encoded by this gene is a tyrosine-protein kinase whose activity can be inhibited by phosphorylation by c-SRC kinase. Mutations in this gene could be involved in the malignant progression of colon cancer. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Src: proto-oncogenic cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase of the SRC family. Highly expressed in certain fully differentiated cells such as neurons, platelets and macrophages. Phosphorylation of an activation loop tyrosine activates the enzyme; phosphorylation of a tyrosine in the C-terminus by Csk inhibits the enzyme. Two alternatively spliced isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Oncoprotein; Protein kinase, tyrosine (non-receptor); Kinase, protein; EC 2.7.10.2; Protein kinase, TK; TK group; Src family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 20q12-q13 Cellular Component: neuron projection; mitochondrion; lysosome; postsynaptic density; actin filament; caveola; cytosol; extrinsic to internal side of plasma membrane; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; late endosome; mitochondrial inner membrane; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; nucleus Molecular Function:protein C-terminus binding; ephrin receptor binding; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity; phosphoprotein binding; insulin receptor binding; protein kinase activity; integrin binding; protein binding; enzyme binding; SH3/SH2 adaptor activity; protein kinase C binding; protein-tyrosine kinase activity; heme binding; estrogen receptor binding; SH2 domain binding; kinase activity; ATP binding; receptor binding; hormone receptor binding Biological Process: oogenesis; regulation of estrogen receptor signaling pathway; estrogen receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; central nervous system development; progesterone receptor signaling pathway; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; viral reproduction; regulation of cell cycle; positive regulation of apoptosis; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; uterus development; negative regulation of mitochondrial depolarization; negative regulation of protein homooligomerization; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity; cell-cell adhesion; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; response to electrical stimulus; cell adhesion; bone resorption; response to drug; platelet activation; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; activation of protein kinase B; response to virus; transcytosis; positive regulation of integrin activation; positive regulation of protein amino acid autophosphorylation; cellular response to insulin stimulus; response to mechanical stimulus; T cell costimulation; regulation of vascular permeability; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; leukocyte migration; negative regulation of apoptosis; axon guidance; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of caspase activity; signal transduction; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration; regulation of cell-cell adhesion; forebrain development; ephrin receptor signaling pathway; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; integrin-mediated signaling pathway; response to nutrient levels; regulation of bone resorption; negative regulation of focal adhesion formation; signal complex assembly; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity; response to mineralocorticoid stimulus; cell cycle; regulation of cell proliferation; cell proliferation; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; response to hydrogen peroxide; regulation of protein binding; Ras protein signal transduction; stress fiber formation; innate immune response; response to acidity; positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; blood coagulation; positive regulation of cytokine secretion |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is highly similar to the v-src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. This proto-oncogene may play a role in the regulation of embryonic development and cell growth. The protein encoded by this gene is a tyrosine-protein kinase whose activity can be inhibited by phosphorylation by c-SRC kinase. Mutations in this gene could be involved in the malignant progression of colon cancer. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P12931 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 125711 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6714 |
| NCBI Accession: | P12931.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P12931,Q76P87, Q86VB9, Q9H5A8, E1P5V4, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P12931 |
| Molecular Weight: | 60kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | SRC proto-oncogene, non-receptor tyrosine kinase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SRC |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ASV; SRC1; c-SRC; p60-Src |
| NCBI Protein Information: | proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; proto-oncogene c-Src; tyrosine kinase pp60c-src; tyrosine-protein kinase SRC-1; protooncogene SRC, Rous sarcoma; v-src avian sarcoma (Schmidt-Ruppin A-2) viral oncogene homolog |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Proto-oncogene c-Src; pp60c-src; p60-Src |
| Protein Family: | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SRC |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SRC_HUMAN |