Description
SOX3 Antibody (PACO20396)
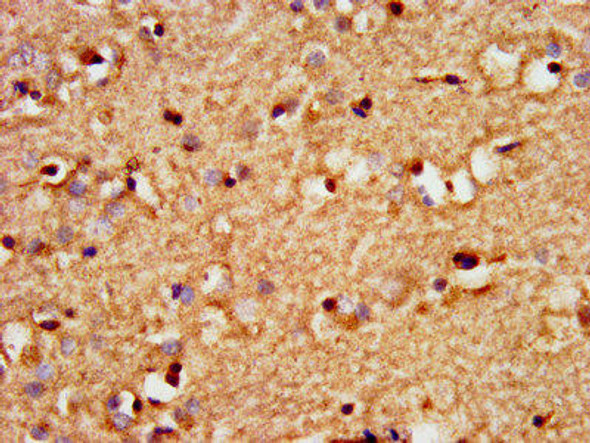
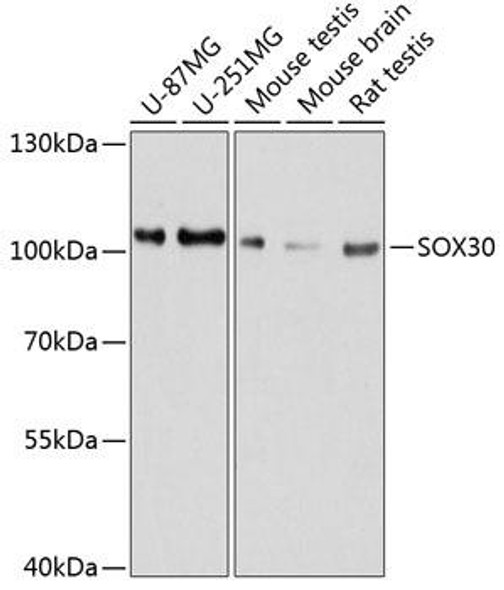
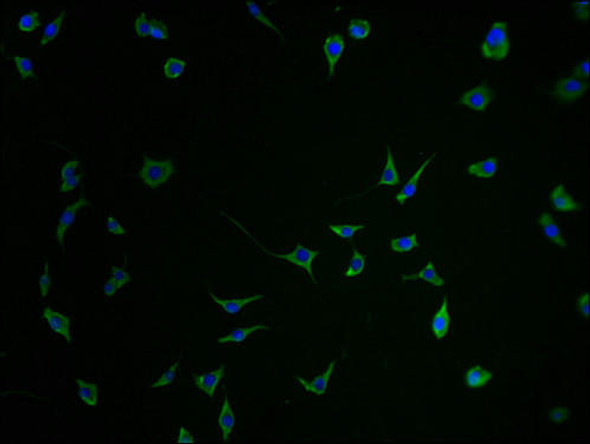
The SOX3 Polyclonal Antibody (PACO20396) is a valuable tool for research involving the SOX3 protein, a transcription factor essential for embryonic development and central nervous system function. This antibody, produced in rabbits, shows high reactivity with human samples and is validated for Western blot applications, enabling the detection and analysis of SOX3 in various cell types.SOX3, a member of the SOX (SRY-related HMG box) family of transcription factors, plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression during development and in the adult brain. Dysfunction of SOX3 has been implicated in developmental disorders, neurological diseases, and brain tumors, underscoring its importance in both normal physiology and pathology.
By using the SOX3 Polyclonal Antibody, researchers can explore the function and regulation of SOX3 in different biological contexts, advancing our understanding of its role in development, neurobiology, and disease. This antibody is a valuable tool for studies in developmental biology, neuroscience, and cancer research, providing insights that may lead to the development of new therapeutic approaches.
| Antibody Name: | SOX3 Antibody (PACO20396) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO20396 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:5000, WB:1:500-1:2000 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide of human SOX2 |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
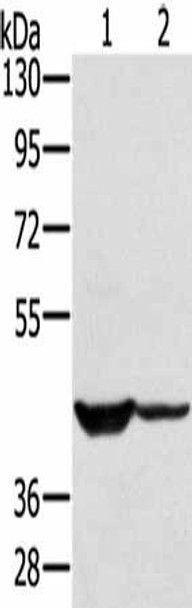
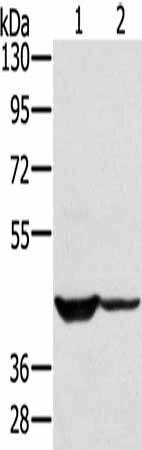 | Gel: 8%SDS-PAGE, Lysate: 40 µg, Lane 1-2: 231 cells, hela cells, Primary antibody: PACO20396(SOX2 Antibody) at dilution 1/300, Secondary antibody: Goat anti rabbit IgG at 1/8000 dilution, Exposure time: 20 seconds. |
| Background: | This intronless gene encodes a member of the SRY-related HMG-box (SOX) family of transcription factors involved in the regulation of embryonic development and in the determination of cell fate. The product of this gene is required for stem-cell maintenance in the central nervous system, and also regulates gene expression in the stomach. Mutations in this gene have been associated with optic nerve hypoplasia and with syndromic microphthalmia, a severe form of structural eye malformation. |
| Synonyms: | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 2 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SOX3: Transcription factor required during the formation of the hypothalamo-pituitary axis. May function as a switch in neuronal development. Keeps neural cells undifferentiated by counteracting the activity of proneural proteins and suppresses neuronal differentiation. Required also within the pharyngeal epithelia for craniofacial morphogenesis. Controls a genetic switch in male development. Is necessary for initiating male sex determination by directing the development of supporting cell precursors (pre-Sertoli cells) as Sertoli rather than granulosa cells. Defects in SOX3 are a cause of panhypopituitarism X- linked (PHPX). Affected individuals have absent infundibulum, anterior pituitary hypoplasia, and ectopic posterior pituitary. Defects in SOX3 are the cause of mental retardation X- linked with isolated growth hormone deficiency (MRXGH). Defects in SOX3 are the cause of 46,XX sex reversal type 3 (SRXX3). A condition in which male gonads develop in a genetic female (female to male sex reversal). Copy number variations (CNV) encompassing or in close proximity to SOX3 are responsible for XX male reversal. These variations include two duplications of approximately 123 kb and 85 kb, the former of which spans the entire SOX3 gene; a 343 kb deletion immediately upstream of SOX3 that is probably responsible of altered regulation (and not increased dosage) of SOX3; a large (approximately 6 Mb) duplication that encompasses SOX3 and at least 18 additional distally located genes. Its proximal breakpoint falls within the SOX3 regulatory region. This large rearrangement has been found in a patient with XX male reversal and a complex phenotype that also includes a scrotal hypoplasia, microcephaly, developmental delay, and growth retardation. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding; Nuclear receptor co-regulator; Transcription factor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xq27.1 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm Molecular Function:DNA binding Biological Process: central nervous system development; hypothalamus development; negative regulation of neuron differentiation; pituitary gland development; sensory organ development; sex determination Disease: Mental Retardation, X-linked, With Panhypopituitarism; Panhypopituitarism, X-linked |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) family of transcription factors involved in the regulation of embryonic development and in the determination of the cell fate. The encoded protein may act as a transcriptional regulator after forming a protein complex with other proteins. Mutations in this gene have been associated with X-linked mental retardation with growth hormone deficiency. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P41225 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 48429228 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6658 |
| NCBI Accession: | P41225.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P41225,P35714, Q5JWI3, Q9NP49, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P41225 |
| Molecular Weight: | 45,210 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Transcription factor SOX-3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | SRY-box 3 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SOX3 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PHP; GHDX; MRGH; PHPX; SOXB |
| NCBI Protein Information: | transcription factor SOX-3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Transcription factor SOX-3 |
| Protein Family: | Transcription factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SOX3 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SOX3_HUMAN |