Description
Anti-SMYD1 Antibody (CAB2340)
The SMYD1 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB2340) is formulated for research involving SMYD1, a protein involved in the regulation of muscle development and function. This antibody, generated in rabbits, exhibits high specificity and reactivity towards SMYD1 in human samples, making it a reliable tool for Western blot applications. By binding to the SMYD1 protein, this antibody enables accurate detection and analysis in a variety of cell types, rendering it ideal for investigations in the fields of muscle biology and disease research.SMYD1, also known as SET and MYND domain-containing protein 1, is a key player in myogenesis, the process by which muscle cells differentiate and mature. Its crucial role in muscle formation and maintenance makes it a valuable target for studies on muscular disorders, cardiac diseases, and muscular dystrophies.
Understanding the function of SMYD1 is essential for developing therapeutic strategies that can enhance muscle regeneration and prevent muscle-related disorders.Overall, the SMYD1 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB2340) serves as a valuable tool for researchers seeking to explore the biological functions and mechanisms of SMYD1 in various physiological and pathological contexts. Its high specificity and sensitivity make it an indispensable asset in advancing our understanding of muscle biology and developing targeted therapies for muscle-related conditions.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-SMYD1 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB2340 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
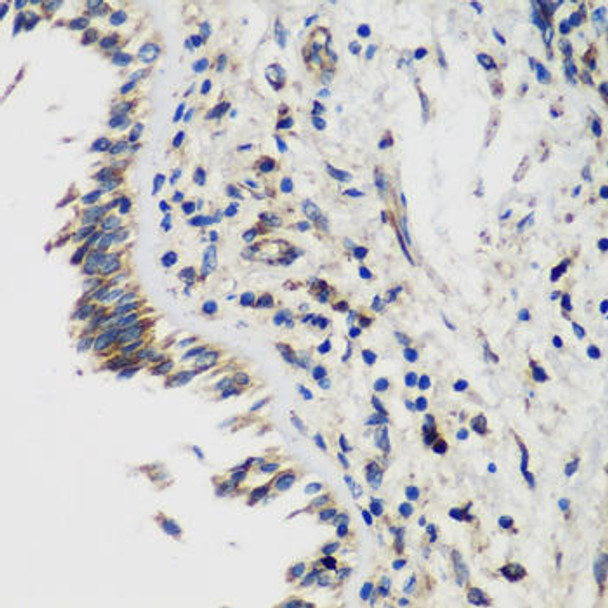
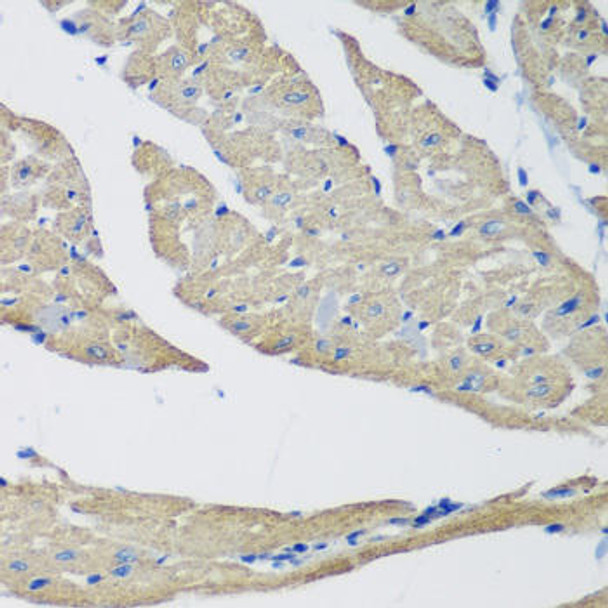
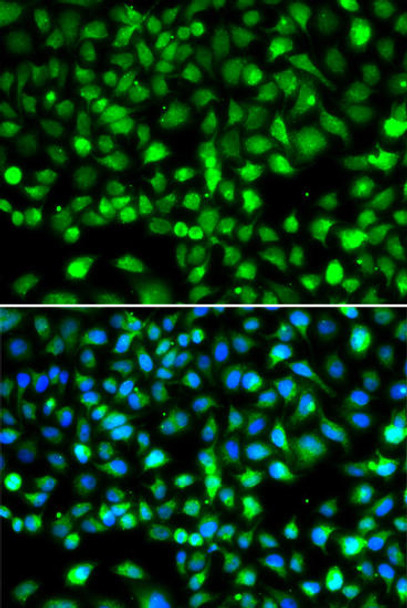
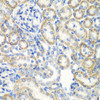
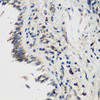
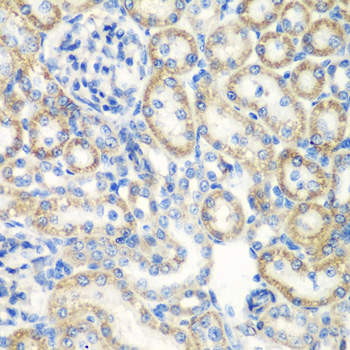
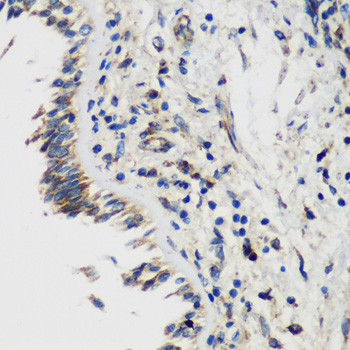
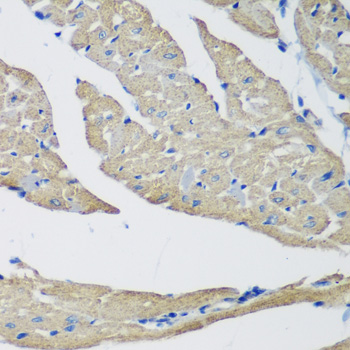
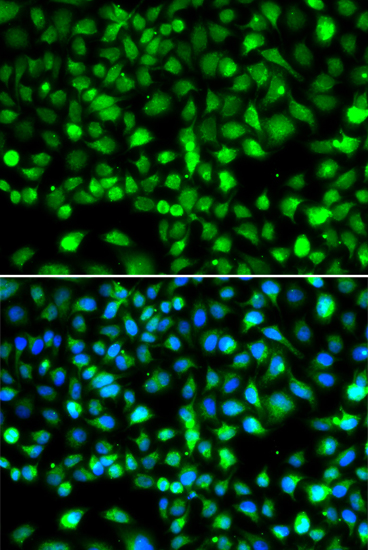
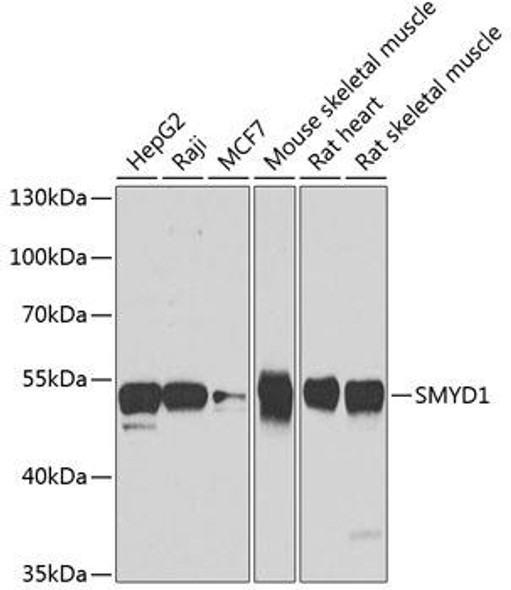
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-350 of human SMYD1 (NP_938015.1). |
| Application: | WB IHC IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:200 - 1:2000 IHC 1:20 - 1:200 IF 1:20 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
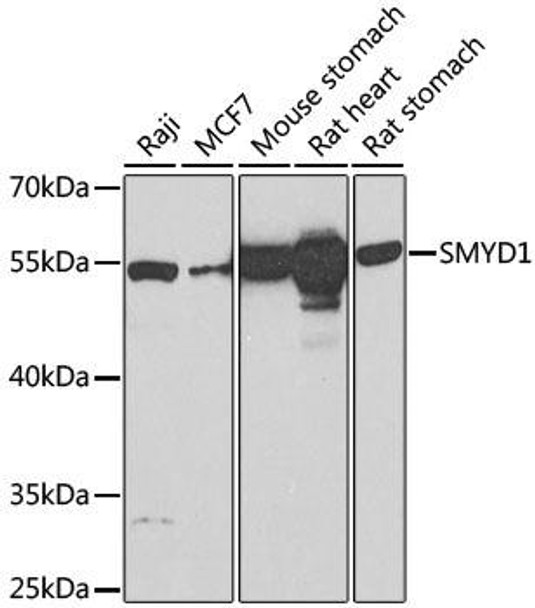
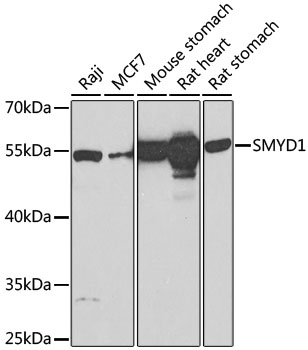
| Positive Samples: | Raji, MCF7, Mouse stomach, Rat heart, Rat stomach |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-350 of human SMYD1 (NP_938015.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MTIG RMEN VEVF TAEG KGRG LKAT KEFW AADI IFAE RAYS AVVF DSLV NFVC HTCF KRQE KLHR CGQC KFAH YCDR TCQK DAWL NHKN ECSA IKRY GKVP NENI RLAA RIMW RVER EGTG LTEG CLVS VDDL QNHV EHFG EEEQ KDLR VDVD TFLQ YWPP QSQQ FSMQ YISH IFGV INCN GFTL SDQR GLQA VGVG IFPN LGLV NHDC WPNC TVIF NNGN HEAV KSMF HTQM RIEL RALG KISE GEEL TVSY IDFL NVSE ERKR QLKK QYYF DCTC EHCQ KKLK DDLF LGVK DNPK PSQE VVKE MIQF SKDT LEKI DKAR SEGL YHEV VKLC RECL EKQE PVFA DTNI YM |
| Gene ID: | 150572 |
| Uniprot: | Q8NB12 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 56kDa |
| Observed MW: | 57kDa |
| Synonyms: | SMYD1, BOP, KMT3D, ZMYND18, ZMYND22 |
| Background: |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SMYD1: Acts as a transcriptional repressor. Essential for cardiomyocyte differentiation and cardiac morphogenesis. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Methyltransferase, protein lysine; Transcription, coactivator/corepressor; EC 2.1.1.43 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2p11.2 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding; DNA binding; metal ion binding; histone-lysine N-methyltransferase activity; transcription corepressor activity Biological Process: chromatin remodeling; transcription, DNA-dependent; heart development; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of myoblast differentiation |
| UniProt Code: | Q8NB12 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 34925329 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 150572 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q8NB12.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q8NB12,A0AV30, A6NE13, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q8NB12 |
| Molecular Weight: | 490 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SMYD1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | SET and MYND domain containing 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SMYD1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BOP; KMT3D; ZMYND18; ZMYND22 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SMYD1; CD8 beta opposite; zinc finger, MYND domain containing 18; SET and MYND domain-containing protein 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SMYD1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | SET and MYND domain-containing protein 1 |
| Protein Family: | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SMYD1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SMYD1_HUMAN |