SHISA5 Antibody (PACO37914)
- SKU:
- PACO37914
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Applications:
- ELISA
- IHC
- IF
- IP
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Conjugation:
- Unconjugated
Frequently bought together:
Description
| Antibody Name: | SHISA5 Antibody (PACO37914) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO37914 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IHC, IF, IP |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:10000, IHC:1:20-1:200, IF:1:50-1:500, IP:1:200-1:2000 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant Human Protein shisa-5 protein (56-137AA) |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300 Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, PH 7.4 |
| Purification Method: | >95%, Protein G purified |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
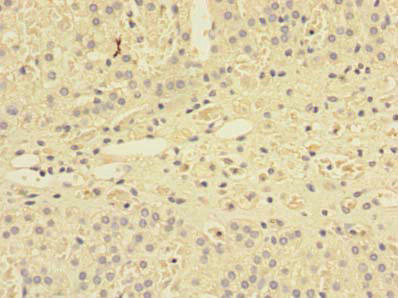 | Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human adrenal gland tissue using PACO37914 at dilution of 1:100. |
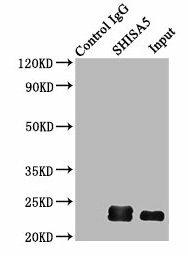 | Immunoprecipitating SHISA5 in HepG2 whole cell lysate. Lane 1: Rabbit control IgG (1µg) instead of PACO37914 in HepG2 whole cell lysate.For western blotting, a HRP-conjugated Protein G antibody was used as the secondary antibody (1/2000). Lane 2: PACO37914 (6µg) + HepG2 whole cell lysate (500µg). Lane 3: HepG2 whole cell lysate (10µg). |
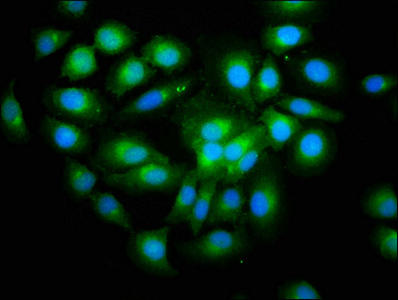 | Immunofluorescence staining of A549 cells with PACO37914 at 1:200, counter-stained with DAPI. The cells were fixed in 4% formaldehyde, permeabilized using 0.2% Triton X-100 and blocked in 10% normal Goat Serum. The cells were then incubated with the antibody overnight at 4°C. The secondary antibody was Alexa Fluor 488-congugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L). |
| Background: | Can induce apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner and plays a role in p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis. |
| Synonyms: | Protein shisa-5 (Putative NF-kappa-B-activating protein 120) (Scotin), SHISA5, SCOTIN |
| UniProt Protein Function: | SCOTIN: Can induce apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner and plays a role in p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis. Belongs to the shisa family. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing.Protein type: Apoptosis; Membrane protein, integralChromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 3p21.31Molecular Function: protein binding; signal transducer activityBiological Process: positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade |
| UniProt Protein Details: | |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the shisa family. The encoded protein is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum, and together with p53 induces apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Related pseudogenes of this gene are found on chromosome X. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016] |
| UniProt Code: | Q8N114 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 74714697 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 51246 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q8N114.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q8N114,Q69YY9, Q7Z433, Q8NHL9, Q96MW8, Q9BV58, B3KW99 F8W9N8 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q8N114 |
| Molecular Weight: | 24,855 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Protein shisa-5 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | shisa family member 5 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | SHISA5 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SCOTIN |
| NCBI Protein Information: | protein shisa-5 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Protein shisa-5 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Putative NF-kappa-B-activating protein 120; Scotin |
| Protein Family: | Protein shisa |
| UniProt Gene Name: | SHISA5 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | SHSA5_HUMAN |






