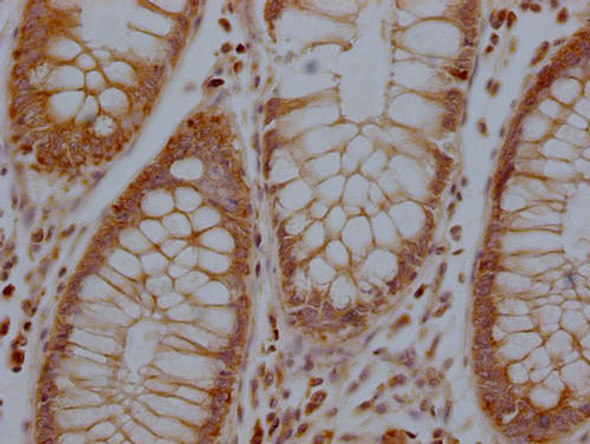
Description
RHBDF2 Antibody (PACO64915)
The RHBDF2 Polyclonal Antibody (PAC064915) is a valuable tool for researchers studying RHBDF2, a protein involved in the regulation of cell growth and proliferation. This antibody, generated in rabbits, has high specificity for human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications. By binding to the RHBDF2 protein, this antibody allows for the detection and analysis of RHBDF2 in different cell types, making it an excellent choice for studies in cancer research and cell biology.
RHBDF2, also known as a regulator of cell proliferation and migration, plays a crucial role in modulating cell signaling pathways involved in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Its importance in these processes makes it a promising target for research into cancer therapy and personalized medicine. Investigating the function of RHBDF2 can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying cancer development and progression, leading to the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
| Product Name: | RHBDF2 Antibody |
| Product Code: | PACO64915 |
| Size: | 50µL |
| Target Names: | RHBDF2 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Antigen Species: | Human |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, IF; Recommended dilution: IF:1:100-1:500 |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Clone ID: | N/A |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Antigen: | Recombinant Human Inactive rhomboid protein 2 protein (1-200aa) |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Buffer: | Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300 Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 |
| Purification Method: | >95%, Protein G purified |
| Storage: | Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze. |
| Aliases: | Inactive rhomboid protein 2 (iRhom2) (Rhomboid 5 homolog 2) (Rhomboid family member 2) (Rhomboid veinlet-like protein 5) (Rhomboid veinlet-like protein 6), RHBDF2, IRHOM2 RHBDL5 RHBDL6 |
| Uniprot ID: | Q6PJF5 |
| Background: | Rhomboid protease-like protein which has no protease activity but regulates the secretion of several ligands of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Indirectly activates the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway and may thereby regulate sleep, cell survival, proliferation and migration (By similarity). |
| Research Area: | Signal Transduction |