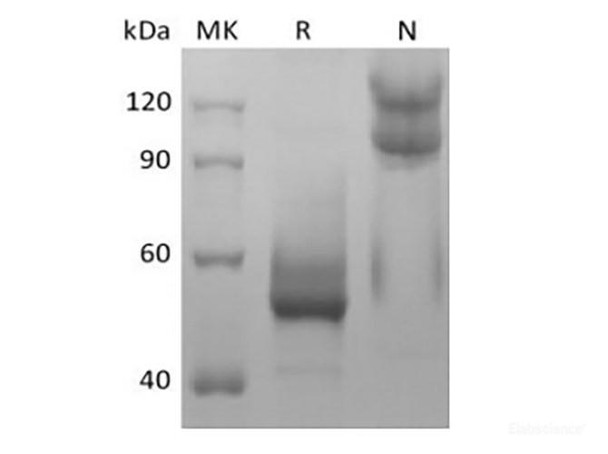
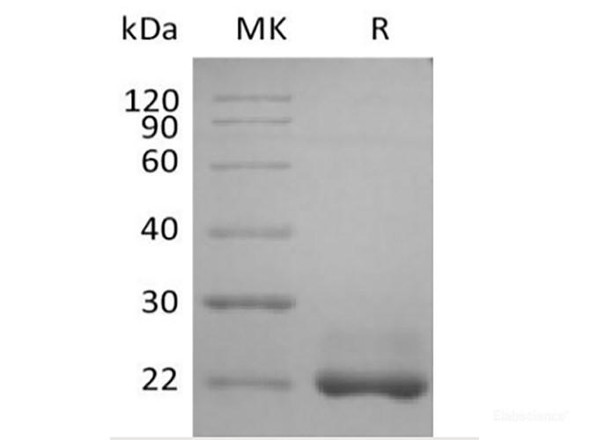
| Background: | TNFSF13B/TNFSF20 belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family. It abundantly is expressed in peripheral blood Leukocytes and is specifically expressed in monocytes and macrophages. Also found in the spleen, lymph node, bone marrow, T-cells and dendritic cells. A lower expression seen in placenta, heart, lung, fetal liver, thymus, and pancreas. Isoform 2 is expressed in many myeloid cell lines. A third B-cell specific BAFF-receptor (BAFFR/BR3) promotes the survival of mature B-cells and the B-cell response. Isoform 2 seems to inhibit isoform 1 secretion and bioactivity. Isoform 3 acts as a transcription factor for its own parent gene, in association with NF-kappa-B p50 subunit, at least in autoimmune and proliferative B-cell diseases. The presence of Delta4BAFF is essential for soluble BAFF release by IFNG/IFN-gamma-stimulated monocytes and for B-cell survival. It can directly or indirectly regulate the differential expression of a large number of genes involved in the innate immune response and the regulation of apoptosis. Isoform 2 heteromultimerizes with isoform 1, probably limiting the amount of functional isoform 1 on the cell surface. Isoform 3 is unlikely form trimers or bind to BAFF receptors. Mature human BAFF consists of a 46 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic domain, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 218 aa extracellular domain (ECD) with a stalk region and one TNF-like domain. Within aa 134-285 of the ECD, human BAFF shares 72% aa sequence identity with mouse BAFF. |