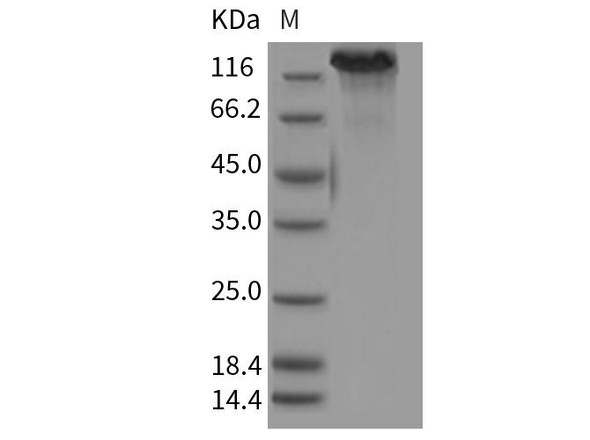
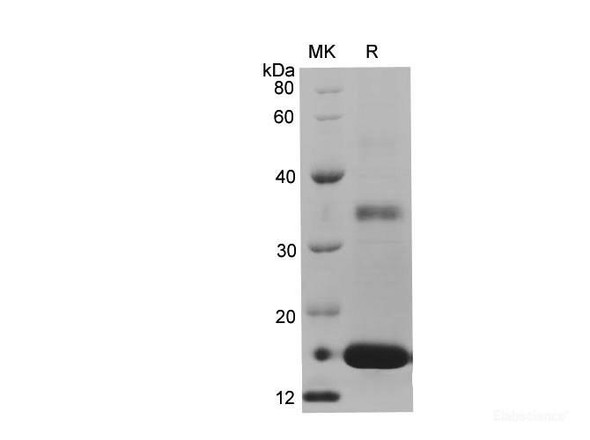
The IL-7 receptor (IL-7R) is comprised of two protein subunits, CD127/IL-7Rα (IL-7Ralpha) and the common gamma chain (CD132), which is the major signaling component for several cytokines including IL-2, IL-4, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21. CD127/IL-7Rα is a transmembrane protein belonging to the cytokine receptor homology class 1 (CRH1) and is expressed by a wide variety of cells including immature B cells, thymic natural killer cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and T cells. On its own, CD127/IL-7Rα functions as a receptor for two cytokine receptor complex signaling cascades: IL-7 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). IL-7 signaling contributes to T cell development and homeostasis whereas TSLP receptor signaling contributes to dendritic cell activation and B cell development. IL-7 signaling is an essential component in regulating the homeostasis of naive and memory T cells as differential expression of CD127/IL-7Rα is observed on naive and activated T cells, which occurs following TCR activation. Specifically, CD127/IL-7Rα expression is downregulated on activated T cells and the subsequent re-expression of CD127/IL-7Rα on these cells is indicative of cells that will differentiate into memory T cells.