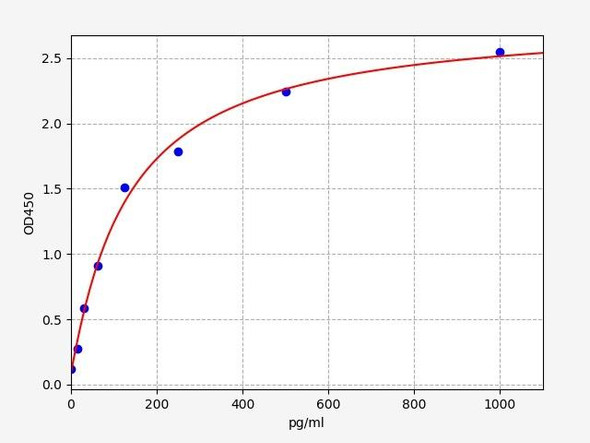
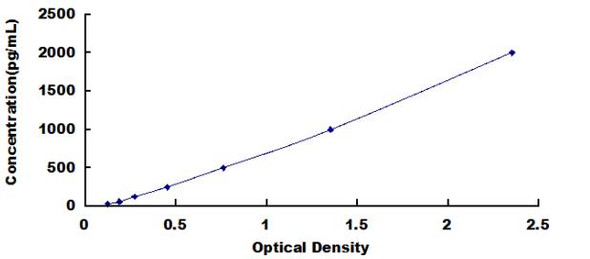
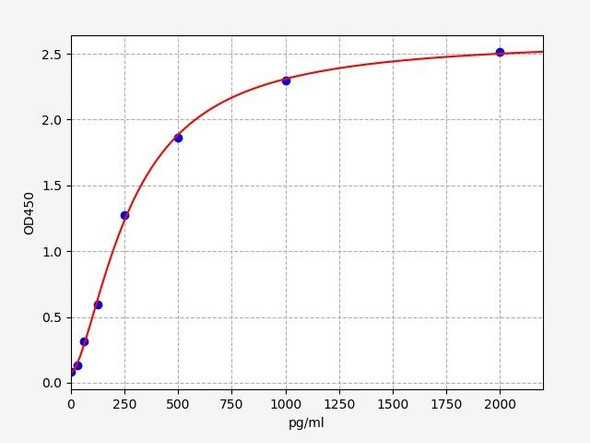
Rat PDGFB ELISA Kit (RTFI00084)
- SKU:
- RTFI00084
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Uniprot:
- Q05028
- Sensitivity:
- 18.75pg/ml
- Range:
- 31.25-2000pg/ml
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Synonyms:
- PDGFB, B chain, Becaplermin, FLJ12858, PDGF subunit B, PDGF2, PDGF-2, platelet-derived growth factor 2, Platelet-derived growth factor beta polypeptide, platelet-derived growth factor subunit B, platelet-derived growth factor, B chain
- Reactivity:
- Rat
Description
Rat PDGFB ELISA Kit
The Rat PDGFB ELISA Kit is specially designed for the precise measurement of PDGFB levels in rat serum, plasma, and tissue culture supernatants. With its high sensitivity and specificity, this kit delivers accurate and consistent results, making it perfect for various research purposes.PDGFB, or Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB, is a key growth factor involved in cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation. It plays a critical role in various physiological processes, such as wound healing, embryonic development, and tissue repair.
Dysregulation of PDGFB is associated with conditions like fibrotic diseases, certain cancers, and vascular disorders, highlighting its importance as a biomarker for studying these diseases and exploring potential therapeutic interventions.Get reliable and insightful data with the Rat PDGFB ELISA Kit, a valuable tool for advancing your research in the field of cell biology, molecular biology, and beyond.
| Product Name: | Rat PDGFB ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | RTFI00084 |
| Size: | 96 Assays |
| Target: | Rat PDGFB |
| Alias: | PDGFB, B chain, Becaplermin, FLJ12858, PDGF subunit B, PDGF2, PDGF-2, platelet-derived growth factor 2, Platelet-derived growth factor beta polypeptide, platelet-derived growth factor subunit B, platelet-derived growth factor, B chain |
| Reactivity: | Rat |
| Detection Method: | Sandwich ELISA, Double Antibody |
| Sensitivity: | 18.75pg/ml |
| Range: | 31.25-2000pg/ml |
| Storage: | 4°C for 6 months |
| Note: | For Research Use Only |
| Recovery: | Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Rat PDGFB and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Rat PDGFB in samples. | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Linearity: | The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Rat PDGFB and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected. | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Intra-Assay: | CV <8% | ||||||||||||||||
| Inter-Assay: | CV <10% |
| Uniprot: | Q05028 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PDGFB: Growth factor that plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell migration, survival and chemotaxis. Potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin. Required for normal proliferation and recruitment of pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells in the central nervous system, skin, lung, heart and placenta. Required for normal blood vessel development, and for normal development of kidney glomeruli. Plays an important role in wound healing. Signaling is modulated by the formation of heterodimers with PDGFA. A chromosomal aberration involving PDGFB is found in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Translocation t(17;22)(q22;q13) with PDGFB. Belongs to the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Oncoprotein; Secreted, signal peptide; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis Cellular Component: basolateral plasma membrane; cell soma; cell surface; cytoplasm; dendrite; extracellular space; intracellular; membrane Molecular Function:chemoattractant activity; collagen binding; growth factor activity; identical protein binding; platelet-derived growth factor binding; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding; protein heterodimerization activity; protein homodimerization activity; receptor binding; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity Biological Process: actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; activation of protein kinase activity; activation of protein kinase B; blood vessel morphogenesis; cell growth; cell projection biogenesis; DNA replication; embryonic placenta development; eye photoreceptor cell development; glial cell development; heart development; hemopoiesis; monocyte chemotaxis; negative regulation of cell migration; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process; negative regulation of protein binding; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; neuron remodeling; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive chemotaxis; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration; positive regulation of cell migration; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of chemotaxis; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process; positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; positive regulation of DNA replication; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation; positive regulation of glomerular filtration; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity; positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade; positive regulation of mitosis; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle, embryonic; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade; positive regulation of protein amino acid autophosphorylation; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of cell proliferation; regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; response to axon injury; response to drug; response to estradiol stimulus; response to estrogen stimulus; response to hypoxia; response to insulin stimulus; response to organic cyclic substance; response to organic substance; response to wounding; retina development in camera-type eye; substrate-bound cell migration; synaptogenesis; wound healing |
| NCBI Summary: | may play a role in carotid artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal formation in response to balloon catheter injury [RGD, Feb 2006] |
| UniProt Code: | Q05028 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 158081747 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 24628 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_113712.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q05028 |
| Molecular Weight: | 25,603 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | platelet-derived growth factor subunit B |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | platelet derived growth factor subunit B |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | Pdgfb |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SIS; c-sis |
| NCBI Protein Information: | platelet-derived growth factor subunit B |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Platelet-derived growth factor subunit B |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | PDGF-2; Platelet-derived growth factor B chain; Platelet-derived growth factor beta polypeptide |
| Protein Family: | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | Pdgfb |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PDGFB_RAT |
| Step | Procedure |
| 1. | Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate respectively, and then, record their positions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Wash plate 2 times before adding standard, sample and control (zero) wells! |
| 2. | Aliquot 0.1ml standard solutions into the standard wells. |
| 3. | Add 0.1 ml of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well. |
| 4. | Add 0.1 ml of properly diluted sample ( Human serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and other biological fluids.) into test sample wells. |
| 5. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37°C for 90 min. |
| 6. | Remove the cover and discard the plate content, clap the plate on the absorbent filter papers or other absorbent material. Do NOT let the wells completely dry at any time. Wash plate X2. |
| 7. | Add 0.1 ml of Biotin- detection antibody working solution into the above wells (standard, test sample & zero wells). Add the solution at the bottom of each well without touching the side wall. |
| 8. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37°C for 60 min. |
| 9. | Remove the cover, and wash plate 3 times with Wash buffer. Let wash buffer rest in wells for 1 min between each wash. |
| 10. | Add 0.1 ml of SABC working solution into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37°C for 30 min. |
| 11. | Remove the cover and wash plate 5 times with Wash buffer, and each time let the wash buffer stay in the wells for 1-2 min. |
| 12. | Add 90 µL of TMB substrate into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37°C in dark within 10-20 min. (Note: This incubation time is for reference use only, the optimal time should be determined by end user.) And the shades of blue can be seen in the first 3-4 wells (with most concentrated standard solutions), the other wells show no obvious color. |
| 13. | Add 50 µL of Stop solution into each well and mix thoroughly. The color changes into yellow immediately. |
| 14. | Read the O.D. absorbance at 450 nm in a microplate reader immediately after adding the stop solution. |
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum: | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clotovernight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Removeserum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at-80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma: | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anti-coagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles.Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid: | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell Culture Supernatant: | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell Lysates: | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20°C. |
| Tissue Homogenates: | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenizein 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or-80°C. |
| Tissue Lysates: | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Breast Milk: | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |