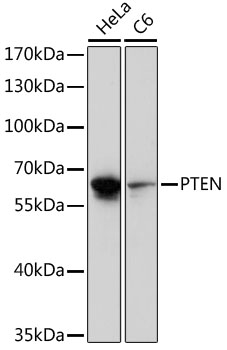
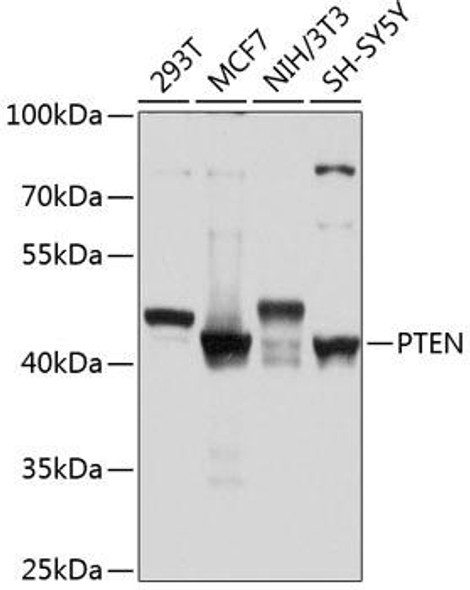
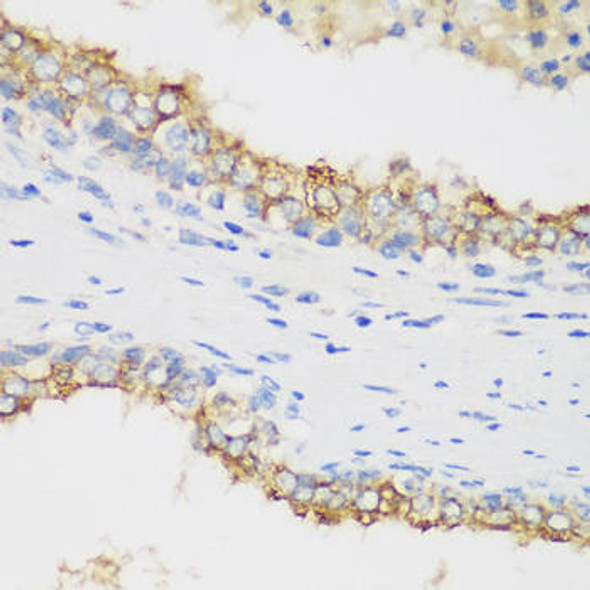
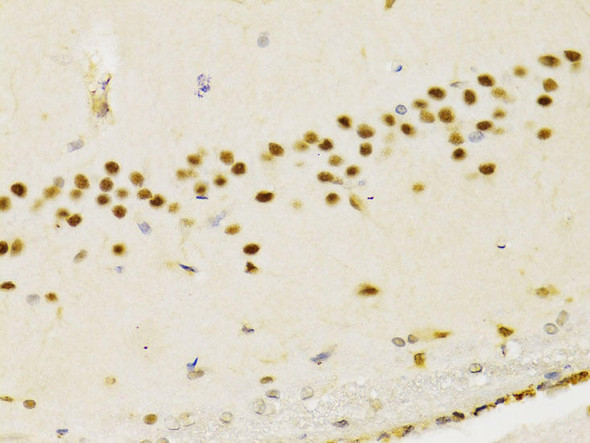
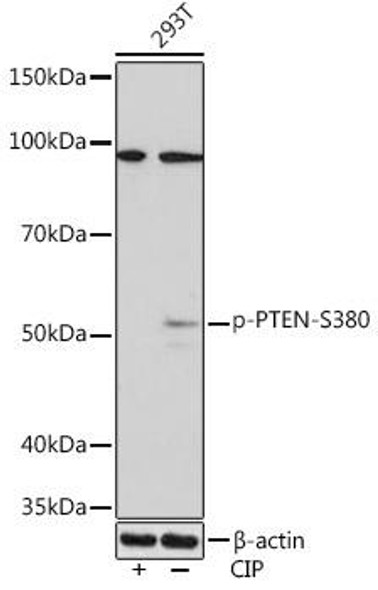
Description
Anti-PTEN Antibody (CAB16965)
The PTEN Polyclonal Antibody (CAB16965) is a valuable tool for research involving PTEN, a tumor suppressor gene known for its role in regulating cell growth and division. This antibody, generated in rabbits, is highly specific to PTEN and is validated for use in Western blotting applications with human samples.PTEN, or phosphatase and tensin homolog, is a critical regulator of cell signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation, survival, and metabolism. Loss of PTEN function is commonly observed in various cancers, making it a promising target for cancer research and therapy development.
The PTEN Polyclonal Antibody allows for the detection and analysis of PTEN protein levels in different cell types, aiding in the investigation of its role in cancer progression and tumorigenesis.With its high reactivity and specificity, the PTEN Polyclonal Antibody is an essential tool for studying PTEN biology in both basic and clinical research settings. Its ability to detect PTEN protein expression provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying cancer development and progression, as well as potential therapeutic strategies targeting PTEN signaling pathways.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-PTEN Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB16965 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human PTEN. |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Positive Samples: |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant protein of human PTEN. |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 5728 |
| Uniprot: | P60484 |
| Cellular Location: | |
| Calculated MW: | 47kDa |
| Observed MW: | Refer to figures |
| Synonyms: | 10q23del, BZS, CWS1, DEC, GLM2, MHAM, MMAC1, PTEN1, TEP1, PTEN, PTENbeta |
| Background: | This gene was identified as a tumor suppressor that is mutated in a large number of cancers at high frequency. The protein encoded by this gene is a phosphatidylinositol-3, 4, 5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase. It contains a tensin like domain as well as a catalytic domain similar to that of the dual specificity protein tyrosine phosphatases. Unlike most of the protein tyrosine phosphatases, this protein preferentially dephosphorylates phosphoinositide substrates. It negatively regulates intracellular levels of phosphatidylinositol-3, 4, 5-trisphosphate in cells and functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating AKT/PKB signaling pathway. The use of a non-canonical (CUG) upstream initiation site produces a longer isoform that initiates translation with a leucine, and is thought to be preferentially associated with the mitochondrial inner membrane. This longer isoform may help regulate energy metabolism in the mitochondria. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 9. Alternative splicing and the use of multiple translation start codons results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PTEN: a phosphoinositide 3-phosphatase (PIP3) and a tumor suppressor implicated in a wide variety of human cancers. Dephosphorylates inositol phospholipids generated by the activation of the phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K). A major negative regulator of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Possesses a C-terminal regulatory domain that contains three phosphorylation sites which may regulate its stability. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Carbohydrate Metabolism - inositol phosphate; EC 3.1.3.48; Phosphatase, lipid; Nuclear receptor co-regulator; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; EC 3.1.3.16; EC 3.1.3.67; Tumor suppressor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 10q23.3 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; postsynaptic membrane; PML body; internal side of plasma membrane; neuron projection; cell projection; mitochondrion; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; extracellular region; dendritic spine; cytosol; nucleus Molecular Function:phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphatase activity; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase activity; inositol-1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate 3-phosphatase activity; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding; magnesium ion binding; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity; protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity; protein kinase binding; PDZ domain binding; protein binding; enzyme binding; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate 3-phosphatase activity; protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity; lipid binding Biological Process: central nervous system development; male mating behavior; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; prepulse inhibition; response to arsenic; regulation of cellular component size; heart development; anaphase-promoting complex activation during mitotic cell cycle; Wnt receptor signaling pathway through beta-catenin; T cell receptor signaling pathway; regulation of B cell apoptosis; myelin maintenance in the central nervous system; response to glucose stimulus; negative regulation of axonogenesis; response to drug; rhythmic synaptic transmission; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; dentate gyrus development; negative regulation of myelination; social behavior; forebrain morphogenesis; negative regulation of organ growth; response to ethanol; response to zinc ion; inositol phosphate dephosphorylation; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process; endothelial cell migration; positive regulation of transcription factor activity; multicellular organismal response to stress; negative regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of phagocytosis; synapse maturation; inositol phosphate metabolic process; apoptosis; regulation of protein stability; locomotory behavior; negative regulation of cell size; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway; protein amino acid dephosphorylation; regulation of myeloid cell apoptosis; response to estradiol stimulus; negative regulation of cell proliferation; locomotor rhythm; learning and/or memory; synaptogenesis; negative regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; phospholipid metabolic process; positive regulation of cell proliferation; brain morphogenesis; protein kinase B signaling cascade; nerve-nerve synaptic transmission; angiogenesis; negative regulation of cell migration; response to nutrient; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; aging; cardiac muscle development; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; cell migration; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; protein stabilization; central nervous system neuron axonogenesis; maternal behavior; negative regulation of focal adhesion formation; response to ATP; memory; cell proliferation; G1/S-specific negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; innate immune response; phosphoinositide dephosphorylation; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; negative regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade Disease: Meningioma, Familial, Susceptibility To; Thyroid Carcinoma, Follicular; Melanoma, Cutaneous Malignant, Susceptibility To, 1; Bannayan-riley-ruvalcaba Syndrome; Cowden Syndrome 1; Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Head And Neck; Prostate Cancer; Glioma Susceptibility 2; Vacterl Association With Hydrocephalus; Endometrial Cancer; Macrocephaly/autism Syndrome |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene was identified as a tumor suppressor that is mutated in a large number of cancers at high frequency. The protein encoded this gene is a phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase. It contains a tensin like domain as well as a catalytic domain similar to that of the dual specificity protein tyrosine phosphatases. Unlike most of the protein tyrosine phosphatases, this protein preferentially dephosphorylates phosphoinositide substrates. It negatively regulates intracellular levels of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in cells and functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating AKT/PKB signaling pathway. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P60484 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 42560209 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5728 |
| NCBI Accession: | P60484.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P60484,O00633, O02679, Q6ICT7, B2R904, F2YHV0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P60484 |
| Molecular Weight: | 19,796 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase PTEN |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PTEN |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | BZS; DEC; CWS1; GLM2; MHAM; TEP1; MMAC1; PTEN1; 10q23del |
| NCBI Protein Information: | phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase PTEN; mitochondrial PTENalpha; phosphatase and tensin-like protein; mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1; mitochondrial phosphatase and tensin protein alpha; MMAC1 phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase PTEN |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase PTEN |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Mutated in multiple advanced cancers 1; Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| Protein Family: | Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase and dual-specificity protein phosphatase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PTEN |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PTEN_HUMAN |