PRPS1/PRPS2/PRPS1L1 Antibody (PACO18615)
- SKU:
- PACO18615
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Applications:
- ELISA
- WB
- IHC
- Antibody Type:
- Polyclonal Antibody
- Conjugation:
- Unconjugated
Description
PRPS1/PRPS2/PRPS1L1 Antibody (PACO18615)
The PRPS1/PRPS2/PRPS1L1 Antibody (PAC018615) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the PRPS1, PRPS2, and PRPS1L1 proteins, which are key enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of purine nucleotides. This polyclonal antibody, generated in rabbits, exhibits high specificity and sensitivity for detecting these proteins in human samples. Validated for use in Western blot applications, the PRPS1/PRPS2/PRPS1L1 Antibody allows for the detection and analysis of these enzymes in various cell types, making it an essential tool for studies in biochemistry, molecular biology, and cancer research.
PRPS1, PRPS2, and PRPS1L1 play crucial roles in nucleotide metabolism, and dysregulation of their activity has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer and metabolic disorders. Understanding the function and regulation of these enzymes is vital for the development of targeted therapies and diagnostic tools for these conditions. By using the PRPS1/PRPS2/PRPS1L1 Antibody, researchers can gain valuable insights into the roles of these enzymes in cellular processes and disease pathogenesis, ultimately advancing our knowledge and potential treatments for associated disorders.
| Antibody Name: | PRPS1/PRPS2/PRPS1L1 Antibody (PACO18615) |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO18615 |
| Size: | 50ul |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| Recommended Dilutions: | ELISA:1:2000-1:5000, WB:1:500-1:2000, IHC:1:25-1:100 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide of human PRPS1/2/1L1 |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | -20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol |
| Purification Method: | Antigen affinity purification |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
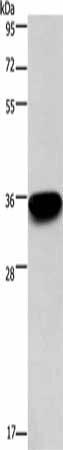 | Gel: 8%SDS-PAGE, Lysate: 40 μg, Lane: 293T cells, Primary antibody: PACO18615(PRPS1/2/1L1 Antibody) at dilution 1/400, Secondary antibody: Goat anti rabbit IgG at 1/8000 dilution, Exposure time: 1 minute. |
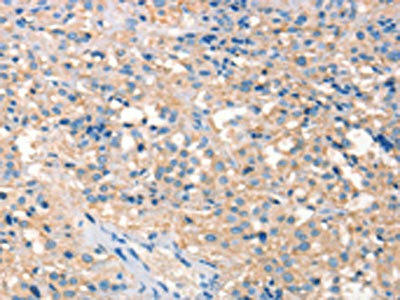 | The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human thyroid cancer tissue using PACO18615(PRPS1/2/1L1 Antibody) at dilution 1/30, on the right is treated with synthetic peptide. (Original magnification: x200). |
| Background: | PRPS (phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase) proteins catalyze the synthesis of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP). Three human PRPS isoforms exist and are encoded by three different genes. PRPS1 and PRPS2 (also known as PRS1 and PRS2, respectively) are ubiquitously expressed, while PRPS3 (also known as PRPS1L1) is specific to the testis. PRPP is an important substrate synthesized from MgATP and ribose-5-phosphate in a reaction that requires inorganic phosphate and magnesium as a cofactor. PRPP is essential in the synthesis of nearly all nucleotides, implying that PRPS1/2 play an important role in nucleotide biosynthesis and purine metabolism. A mutation in the gene encoding PRPS1 may result in PRPS superactivity, a disease characterized by gout and the overproduction of purine nucleotides, uric acid, and PRPP. PRPS1 mutations can also lead to a reduction in PRPS1 activity resulting in ARTS syndrome or CMTX5 (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease X-linked recessive type 5). |
| Synonyms: | phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1/2/1-like 1 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | PRPS1: Catalyzes the synthesis of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP) that is essential for nucleotide synthesis. Defects in PRPS1 are the cause of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase superactivity (PRPS1 superactivity); also known as PRPS-related gout. It is a familial disorder characterized by excessive purine production, gout and uric acid urolithiasis. Defects in PRPS1 are the cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease X-linked recessive type 5 (CMTX5); also known as optic atrophy-polyneuropathy-deafness or Rosenberg-Chutorian syndrome. CMTX5 is a form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, the most common inherited disorder of the peripheral nervous system. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is classified in two main groups on the basis of electrophysiologic properties and histopathology: primary peripheral demyelinating neuropathies characterized by severely reduced motor nerve conduction velocities (NCVs) (less than 38m/s) and segmental demyelination and remyelination, and primary peripheral axonal neuropathies characterized by normal or mildly reduced NCVs and chronic axonal degeneration and regeneration on nerve biopsy. Defects in PRPS1 are the cause of ARTS syndrome (ARTS); also known as fatal ataxia X-linked with deafness and loss of vision. ARTS is a disorder characterized by mental retardation, early-onset hypotonia, ataxia, delayed motor development, hearing impairment, and optic atrophy. Susceptibility to infections, especially of the upper respiratory tract, can result in early death. Defects in PRPS1 are the cause of deafness X-linked type 1 (DFNX1); also known as congenital sensorineural deafness X-linked 2 (DFN2). It is a form of deafness characterized by progressive, severe-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss in males. Females manifest mild to moderate hearing loss. Belongs to the ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Nucleotide Metabolism - purine; Kinase, other; Carbohydrate Metabolism - pentose phosphate pathway; EC 2.7.6.1 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xq22.3 Cellular Component: cytosol Molecular Function:ATP binding; protein binding; protein homodimerization activity; ribose phosphate diphosphokinase activity Biological Process: 5-phosphoribose 1-diphosphate biosynthetic process; hypoxanthine biosynthetic process; nervous system development; purine base metabolic process; purine nucleotide biosynthetic process Disease: Arts Syndrome; Charcot-marie-tooth Disease, X-linked Recessive, 5; Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate Synthetase Superactivity |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the phosphoribosylation of ribose 5-phosphate to 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate, which is necessary for purine metabolism and nucleotide biosynthesis. Defects in this gene are a cause of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase superactivity, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease X-linked recessive type 5 and Arts Syndrome. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011] |
| UniProt Code: | P60891 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 46397477 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5631 |
| NCBI Accession: | P60891.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P60891,P09329, B1ALA8, B2R6T7, B4DNL6, D3DUX6, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P60891 |
| Molecular Weight: | 27,526 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PRPS1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ARTS; DFN2; PRSI; CMTX5; DFNX1; PRS-I; PPRibP |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | PPRibP; Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthase I; PRS-I |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PRPS1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PRPS1_HUMAN |