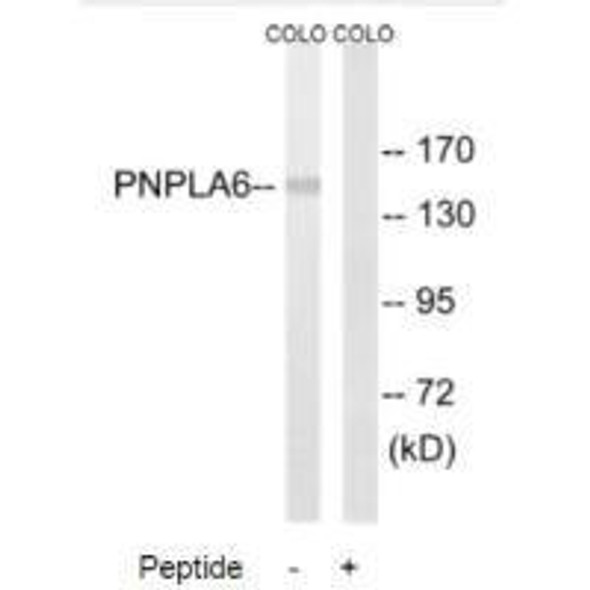
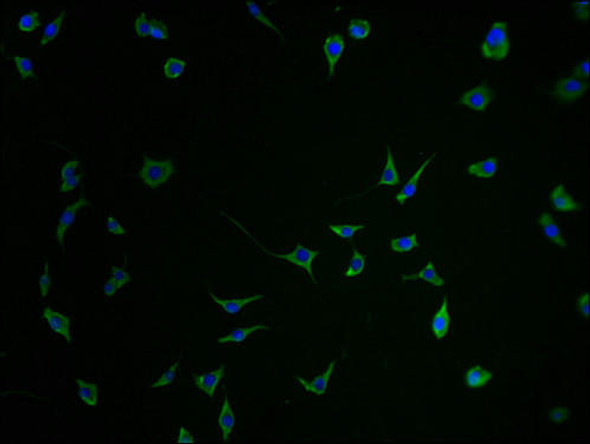
Description
PNPLA6 Antibody (PACO02379)
The PNPLA6 Polyclonal Antibody (PACO02379) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the PNPLA6 protein, which is involved in lipid metabolism and neurological functions. This antibody is raised in rabbits and is highly specific to human samples, making it ideal for Western blot applications. By binding to the PNPLA6 protein, this antibody enables accurate detection and analysis in a variety of cell types, facilitating research in neuroscience and metabolic disorders.PNPLA6, also known as neuropathy target esterase (NTE), plays a critical role in lipid droplet metabolism and the nervous system. Dysregulation of PNPLA6 has been linked to neurodegenerative disorders and metabolic diseases, making it a promising target for therapeutic interventions.
By studying the function and regulation of PNPLA6, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms underlying these conditions and potentially develop new treatment strategies.Overall, the PACO02379 antibody is a reliable tool for investigating the role of PNPLA6 in health and disease. Its high specificity and sensitivity make it a valuable asset for researchers aiming to uncover the biological functions of PNPLA6 and its potential implications for human health.
| Antibody Name: | PNPLA6 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | PACO02379 |
| Size: | 50ug |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Tested Applications: | ELISA, WB |
| Recommended Dilutions: | WB:1:500-1:2000 |
| Species Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen: | synthesized peptide derived from the N-terminal region of human NTE. |
| Form: | Liquid |
| Storage Buffer: | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide. |
| Purification Method: | The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen. |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Conjugate: | Non-conjugated |
| Synonyms: | PNPLA6; NTE; Neuropathy target esterase; Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 6 |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NTE: Phospholipase B that deacylates intracellular phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho), generating glycerophosphocholine (GroPtdCho). This deacylation occurs at both sn-2 and sn-1 positions of PtdCho. Its specific chemical modification by certain organophosphorus (OP) compounds leads to distal axonopathy. Defects in PNPLA6 are the cause of spastic paraplegia autosomal recessive type 39 (SPG39); also known as NTE-related motor neuron disorder (NTEMND). Spastic paraplegia is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. SPG39 is associated with a motor axonopathy affecting upper and lower limbs and resulting in progressive wasting of distal upper and lower extremity muscles. Belongs to the NTE family. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, integral; Hydrolase; EC 3.1.1.5 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 19p13.2 Cellular Component: endoplasmic reticulum; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; membrane Molecular Function:lysophospholipase activity Biological Process: developmental process; glycerophospholipid catabolic process Disease: Boucher-neuhauser Syndrome; Laurence-moon Syndrome; Oliver-mcfarlane Syndrome; Spastic Paraplegia 39, Autosomal Recessive |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a phospholipase that deacetylates intracellular phosphatidylcholine to produce glycerophosphocholine. It is thought to function in neurite outgrowth and process elongation during neuronal differentiation. The protein is anchored to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum in both neurons and non-neuronal cells. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia, and the protein is the target for neurodegeneration induced by organophosphorus compounds and chemical warfare agents. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | Q8IY17 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 150403921 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 10908 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q8IY17.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q8IY17,O60859, Q86W58, Q9UG58, A6NGQ0, B4DFB9, B7Z7T2 F5H5K9, J3KQS3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q8IY17 |
| Molecular Weight: | 143,351 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Neuropathy target esterase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | patatin like phospholipase domain containing 6 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PNPLA6 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | NTE; sws; BNHS; LNMS; OMCS; SPG39; NTEMND; iPLA2delta |
| NCBI Protein Information: | neuropathy target esterase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Neuropathy target esterase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 6 |
| Protein Family: | Neuropathy target esterase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PNPLA6 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PLPL6_HUMAN |