Anti-Phospho-FLNA-S2152 pAb Antibody (CABP0783)
- SKU:
- CABP0783
- Product Type:
- Antibody
- Applications:
- WB
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
Anti-Phospho-FLNA-S2152 pAb Antibody (CABP0783)
The Phospho-FLNA (S2152) Polyclonal Antibody (CABP0783) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the phosphorylation of Filamin A (FLNA) at serine 2152. FLNA is a widely expressed actin-binding protein involved in various cellular processes, including cell motility, adhesion, and signaling.This antibody, raised in rabbits, exhibits high reactivity with human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications to detect and quantify the phosphorylation of FLNA at serine 2152. By specifically binding to the phosphorylated form of FLNA, researchers can gain insights into the signaling pathways and cellular functions regulated by this post-translational modification.The phosphorylation of FLNA at serine 2152 has been implicated in various cellular processes, such as cytoskeletal organization, cell migration, and adhesion dynamics.
Dysregulation of FLNA phosphorylation has also been associated with diseases like cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurological conditions. Therefore, studying the phosphorylation status of FLNA can provide important clues for understanding disease mechanisms and developing targeted therapies.Overall, the Phospho-FLNA (S2152) Polyclonal Antibody is a valuable tool for researchers interested in exploring the role of FLNA phosphorylation in cellular physiology and disease pathogenesis. Its high specificity and sensitivity make it an ideal choice for studies in cell biology, signal transduction, and disease research.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-FLNA-S2152 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0783 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S2152 of human FLNA (NP_001104026.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
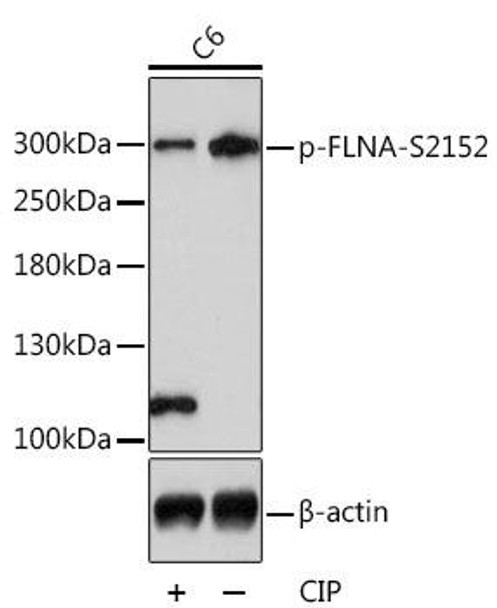
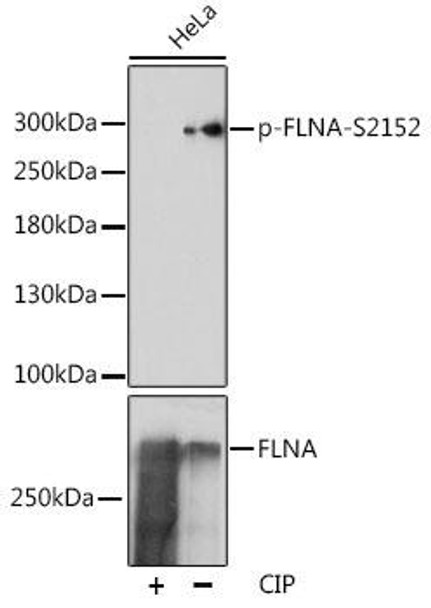
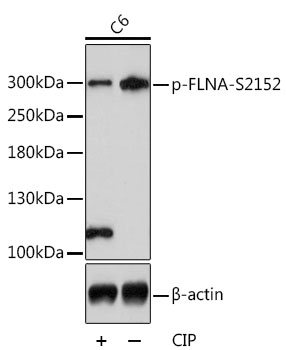
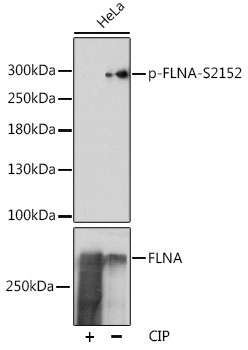
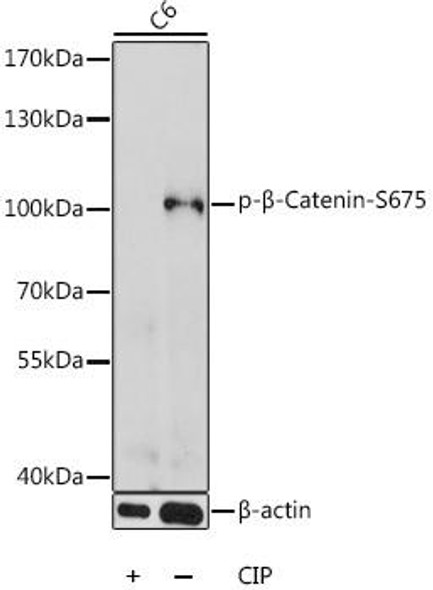
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, C6 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S2152 of human FLNA (NP_001104026.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | APSV A |
| Gene ID: | 2316 |
| Uniprot: | P21333 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, cell cortex, cytoskeleton |
| Calculated MW: | 280kDa |
| Observed MW: | 300kDa |
| Synonyms: | FLNA, ABP-280, ABPX, CSBS, CVD1, FLN, FLN-A, FLN1, FMD, MNS, NHBP, OPD, OPD1, OPD2, XLVD, XMVD, filamin-A |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is an actin-binding protein that crosslinks actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins. The encoded protein is involved in remodeling the cytoskeleton to effect changes in cell shape and migration. This protein interacts with integrins, transmembrane receptor complexes, and second messengers. Defects in this gene are a cause of several syndromes, including periventricular nodular heterotopias (PVNH1, PVNH4), otopalatodigital syndromes (OPD1, OPD2), frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD), Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS), and X-linked congenital idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction (CIIPX). Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | FLNA: a ubiquitous cytoskeletal protein that promotes orthogonal branching of actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins. Plays an essential role in embryonic cell migration. Anchors various transmembrane proteins to the actin cytoskeleton and serves as a scaffold for a wide range of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Interactions with filamin A may allow neuroblast migration from the ventricular zone into the cortical plate. Tethers cell surface-localized furin, modulates its rate of internalization and directs its intracellular trafficking. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Actin-binding; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Nuclear receptor co-regulator Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xq28 Cellular Component: cortical cytoskeleton; focal adhesion; extracellular region; actin filament; trans-Golgi network; cytosol; actin cytoskeleton; cell soma; membrane; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; dendritic shaft; nucleus Molecular Function:Rho GTPase binding; protein homodimerization activity; Rac GTPase binding; Ral GTPase binding; transcription factor binding; actin filament binding; small GTPase binding; signal transducer activity; protein binding; protein kinase C binding; mu-type opioid receptor binding; glycoprotein binding; SMAD binding Biological Process: actin crosslink formation; platelet activation; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; protein stabilization; negative regulation of transcription factor activity; mRNA transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; receptor clustering; dopamine receptor, adenylate cyclase inhibiting pathway; establishment of protein localization; platelet degranulation; early endosome to late endosome transport; actin cytoskeleton reorganization; positive regulation of transcription factor import into nucleus; cytoplasmic sequestering of protein; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; cilium biogenesis; negative regulation of protein catabolic process; blood coagulation Disease: Terminal Osseous Dysplasia; Fg Syndrome 2; Cardiac Valvular Dysplasia, X-linked; Frontometaphyseal Dysplasia; Melnick-needles Syndrome; Heterotopia, Periventricular, Ehlers-danlos Variant; Intestinal Pseudoobstruction, Neuronal, Chronic Idiopathic, X-linked; Heterotopia, Periventricular, X-linked Dominant; Otopalatodigital Syndrome, Type Ii; Otopalatodigital Syndrome, Type I |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is an actin-binding protein that crosslinks actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins. The encoded protein is involved in remodeling the cytoskeleton to effect changes in cell shape and migration. This protein interacts with integrins, transmembrane receptor complexes, and second messengers. Defects in this gene are a cause of several syndromes, including periventricular nodular heterotopias (PVNH1, PVNH4), otopalatodigital syndromes (OPD1, OPD2), frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD), Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS), and X-linked congenital idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction (CIIPX). Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P21333 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 116241365 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2316 |
| NCBI Accession: | P21333.4 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P21333,Q5HY53, Q5HY55, Q8NF52, E9KL45, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P21333 |
| Molecular Weight: | 280,739 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Filamin-A |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | filamin A, alpha |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FLNA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | FLN; FMD; MNS; OPD; ABPX; CSBS; CVD1; FLN1; NHBP; OPD1; OPD2; XLVD; XMVD; FLN-A; ABP-280 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | filamin-A; filamin-1; alpha-filamin; non-muscle filamin; actin binding protein 280; endothelial actin-binding protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Filamin-A |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Actin-binding protein 280; ABP-280; Alpha-filamin; Endothelial actin-binding protein; Filamin-1; Non-muscle filamin |
| Protein Family: | Filamin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FLNA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FLNA_HUMAN |