Description
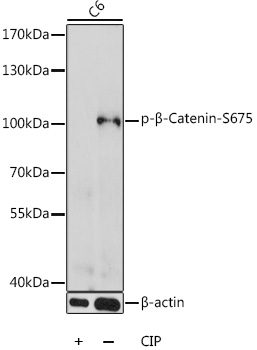
Anti-Phospho-CTNNB1-S675 pAb Antibody (CABP0795)
The Phospho-CTNNB1 (S675) Polyclonal Antibody (CABP0795) offered by Assaygenie is a highly specific research tool for studying the phosphorylation of CTNNB1 at serine 675. This antibody, generated in rabbits, is ideal for Western blotting applications with human samples, providing reliable and reproducible results.CTNNB1, also known as beta-catenin, is a key player in the Wnt signaling pathway, regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and stem cell maintenance. Phosphorylation of CTNNB1 at serine 675 is a critical post-translational modification that influences its stability and activity, impacting various cellular processes.The Phospho-CTNNB1 (S675) Polyclonal Antibody enables researchers to investigate the role of CTNNB1 phosphorylation in signal transduction pathways, gene expression, and tumorigenesis.
By targeting this specific phosphorylation site, scientists can gain insights into the mechanisms underlying cancer development and progression, as well as potential therapeutic targets for intervention.Overall, this antibody is a valuable tool for studying the complex regulation of CTNNB1 and its implications in cancer biology, stem cell biology, and developmental processes. Its high specificity and sensitivity make it a reliable choice for researchers seeking to unravel the intricacies of CTNNB1 phosphorylation in both normal and pathological conditions.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-Phospho-CTNNB1-S675 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CABP0795 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S675 of human beta Catenin (NP_001091679.1). |
| Application: | WB |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
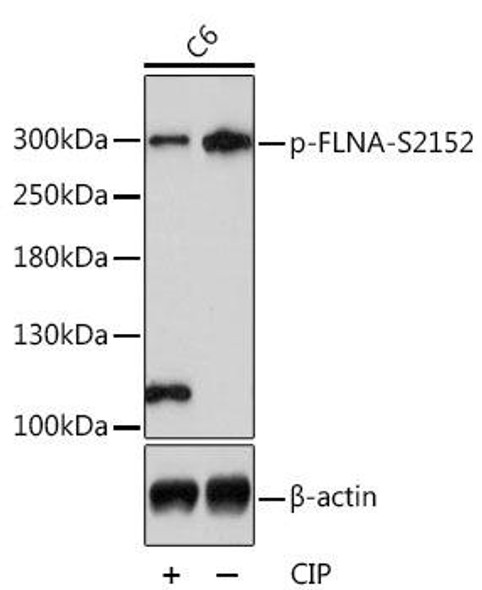
| Positive Samples: | C6 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S675 of human beta Catenin (NP_001091679.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | RLSV E |
| Gene ID: | 1499 |
| Uniprot: | P35222 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell junction, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus, adherens junction, centrosome, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, spindle pole |
| Calculated MW: | 9kDa/85kDa |
| Observed MW: | 100kDa |
| Synonyms: | CTNNB, MRD19, armadillo, beta Catenin, CTNNB1 |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex of proteins that constitute adherens junctions (AJs). AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion between cells. The encoded protein also anchors the actin cytoskeleton and may be responsible for transmitting the contact inhibition signal that causes cells to stop dividing once the epithelial sheet is complete. Finally, this protein binds to the product of the APC gene, which is mutated in adenomatous polyposis of the colon. Mutations in this gene are a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC), pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma (MDB), and ovarian cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | CTNNB1: a regulator of cell adhesion and a key downstream effector in the Wnt signaling pathway. Implicated early embryonic development and tumorigenesis. Phosphorylated and destabilized by CK1 and GSK-3beta. Stabilized cytoplasmic beta-catenin is a hallmark of a variety of cancers. Stabilized beta-catenin translocates to the nucleus, where it acts as a transcriptional activator of T-cell factor (TCF)-regulated genes. Interacts with the PDZ domain of TAX1BP3, inhibiting its transcriptional activity. Two alternatively spliced human isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Transcription factor; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Cell adhesion; Oncoprotein; Nuclear receptor co-regulator; Actin-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 3p21 Cellular Component: centrosome; basolateral plasma membrane; intercellular junction; fascia adherens; cytosol; beta-catenin destruction complex; transcription factor complex; cell-cell adherens junction; membrane; lamellipodium; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; cytoplasm; synapse; dendritic shaft; lateral plasma membrane; spindle pole; focal adhesion; tight junction; catenin complex; cell cortex; Z disc; nucleoplasm; adherens junction; microvillus membrane; apical part of cell; plasma membrane; nucleus; cell junction Molecular Function:protein C-terminus binding; transcription coactivator activity; transcription factor binding; protein phosphatase binding; ionotropic glutamate receptor binding; protein binding; signal transducer activity; enzyme binding; androgen receptor binding; cadherin binding; double-stranded DNA binding; protein complex binding; estrogen receptor binding; nitric-oxide synthase binding; SMAD binding; transcription factor activity; kinase binding; alpha-catenin binding; nuclear hormone receptor binding Biological Process: regulation of myelination; regulation of centriole-centriole cohesion; positive regulation of apoptosis; protein heterooligomerization; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; regulation of fibroblast proliferation; cell maturation; negative regulation of chondrocyte differentiation; T cell differentiation in the thymus; positive regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; osteoclast differentiation; Wnt receptor signaling pathway through beta-catenin; cell-cell adhesion; positive regulation of endothelial cell differentiation; regulation of cell fate specification; embryonic foregut morphogenesis; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation; male genitalia development; ectoderm development; synapse organization and biogenesis; cell adhesion; bone resorption; response to drug; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation; transcription, DNA-dependent; hair cell differentiation; negative regulation of protein sumoylation; patterning of blood vessels; genitalia morphogenesis; muscle cell differentiation; midgut development; smooth muscle cell differentiation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; embryonic digit morphogenesis; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; oocyte development; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis; negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation; glial cell fate determination; endodermal cell fate commitment; apoptosis; cell-matrix adhesion; neuron migration; dorsal/ventral axis specification; cell fate specification; positive regulation of histone H3-K4 methylation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis; response to estradiol stimulus; negative regulation of cell proliferation; central nervous system vasculogenesis; positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade; pancreas development; positive regulation of interferon type I production; fallopian tube development; proximal/distal pattern formation; layer formation in the cerebral cortex; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle, embryonic; cell structure disassembly during apoptosis; Wnt receptor signaling pathway; hair follicle morphogenesis; thymus development; in utero embryonic development; regulation of T cell proliferation; neural plate development; stem cell maintenance; embryonic axis specification; synaptic vesicle transport; gastrulation with mouth forming second; liver development; regulation of angiogenesis; odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth; myoblast differentiation; negative regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation; Schwann cell proliferation; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation; response to cadmium ion; ureteric bud branching; response to cytokine stimulus; androgen receptor signaling pathway; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; positive regulation of muscle cell differentiation; embryonic heart tube development; innate immune response; lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye; anterior/posterior axis specification Disease: Pilomatrixoma; Mental Retardation, Autosomal Dominant 19; Ovarian Cancer; Colorectal Cancer; Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex of proteins that constitute adherens junctions (AJs). AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion between cells. The encoded protein also anchors the actin cytoskeleton and may be responsible for transmitting the contact inhibition signal that causes cells to stop dividing once the epithelial sheet is complete. Finally, this protein binds to the product of the APC gene, which is mutated in adenomatous polyposis of the colon. Mutations in this gene are a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC), pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma (MDB), and ovarian cancer. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P35222 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 461854 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1499 |
| NCBI Accession: | P35222.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P35222,Q8NEW9, Q8NI94, Q9H391, A8K1L7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P35222 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Catenin beta-1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CTNNB1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CTNNB; MRD19; armadillo |
| NCBI Protein Information: | catenin beta-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Catenin beta-1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Beta-catenin |
| Protein Family: | Catenin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CTNNB1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CTNB1_HUMAN |