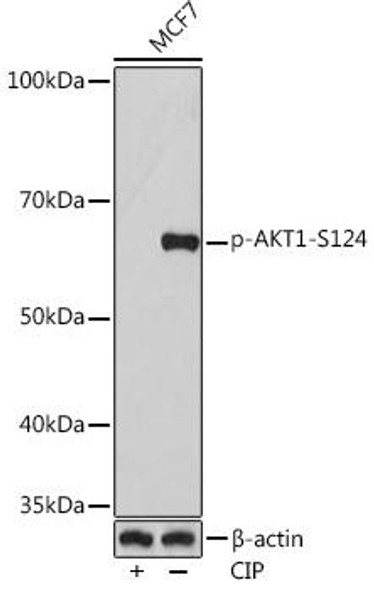
Description
Phospho-AKT1-S473 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (CABP0637)
The Phospho-Akt1 (S473) Monoclonal Antibody (CABP0637) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the Akt1 signaling pathway, a key regulator of cell proliferation, survival, and metabolism. This antibody specifically targets the phosphorylated form of Akt1 at Ser473, which plays a crucial role in Akt1 activation and downstream signaling.Raised in mice, this monoclonal antibody is highly specific to human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications, enabling researchers to detect and analyze phosphorylated Akt1 in various cell types. By targeting the phosphorylated form of Akt1, researchers can gain insights into the activation status of this critical signaling molecule and its role in cell growth, survival, and metabolism.
The Akt1 signaling pathway is dysregulated in various diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular disorders, making it a prime target for drug development and personalized medicine. Understanding the phosphorylation status of Akt1 at Ser473 is essential for unraveling the complex signaling networks that govern cell behavior and identifying potential therapeutic targets for disease intervention. The Phospho-Akt1 (S473) Monoclonal Antibody (CABP0637) is a valuable tool for researchers seeking to elucidate the role of Akt1 signaling in health and disease.
| Product Name: | Phospho-AKT1-S473 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| SKU: | CABP0637 |
| Size: | 20uL, 100uL |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Reactivity: | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S473 of human Akt1 (P31749). |
| Sequence: | QFSY S |
| Tested Applications: | WB IHC-P ELISA |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB,1:500 - 1:2000 IHC-P,1:50 - 1:200 |
| Synonyms: | AKT; PKB; RAC; PRKBA; PKB-ALPHA; RAC-ALPHA; Phospho-AKT1-S473 |
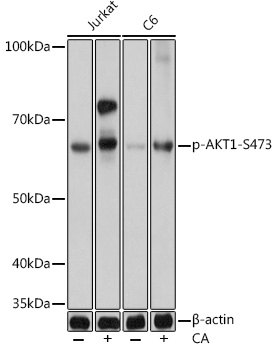
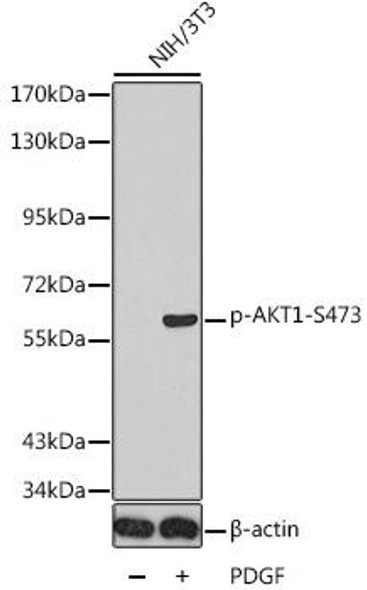
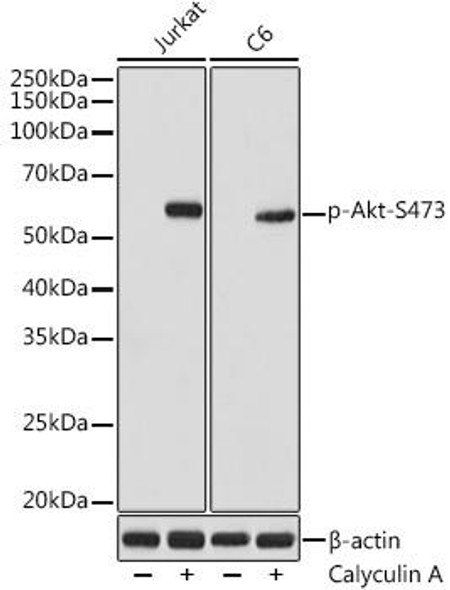
| Positive Sample: | Jurkat+Calyculin A,NIH/3T3+Calyculin A,C6+Calyculin A |
| Conjugate: | Unconjugated |
| Cellular Localization: | Cell membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleus. |
| Calculated MW: | 56kDa |
| Observed MW: | 60kDa |
This gene encodes one of the three members of the human AKT serine-threonine protein kinase family which are often referred to as protein kinase B alpha, beta, and gamma. These highly similar AKT proteins all have an N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain, a serine/threonine-specific kinase domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain. These proteins are phosphorylated by phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). AKT/PI3K forms a key component of many signalling pathways that involve the binding of membrane-bound ligands such as receptor tyrosine kinases, G-protein coupled receptors, and integrin-linked kinase. These AKT proteins therefore regulate a wide variety of cellular functions including cell proliferation, survival, metabolism, and angiogenesis in both normal and malignant cells. AKT proteins are recruited to the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) after phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) by PI3K. Subsequent phosphorylation of both threonine residue 308 and serine residue 473 is required for full activation of the AKT1 protein encoded by this gene. Phosphorylation of additional residues also occurs, for example, in response to insulin growth factor-1 and epidermal growth factor. Protein phosphatases act as negative regulators of AKT proteins by dephosphorylating AKT or PIP3. The PI3K/AKT signalling pathway is crucial for tumor cell survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating AKT1 which then phosphorylates and inactivates components of the apoptotic machinery. AKT proteins also participate in the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway which controls the assembly of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4F (eIF4E) complex and this pathway, in addition to responding to extracellular signals from growth factors and cytokines, is disregulated in many cancers. Mutations in this gene are associated with multiple types of cancer and excessive tissue growth including Proteus syndrome and Cowden syndrome 6, and breast, colorectal, and ovarian cancers. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Gene ID: | 207 |
| Clone Number: | ARC0169 |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20℃. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide,0.05% BSA,50% glycerol,pH7.3. |