Description
p53 scFv Monoclonal Antibody (CPAB0475)
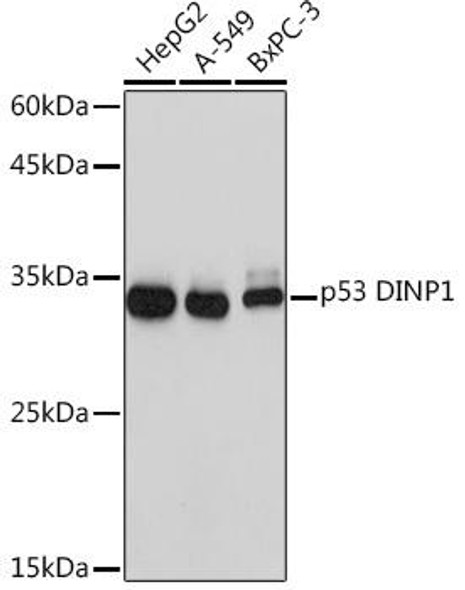
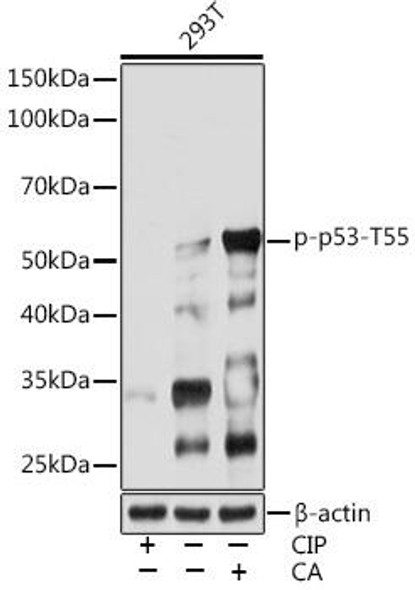
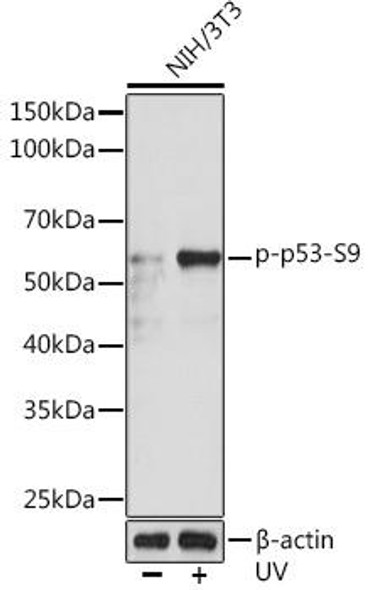
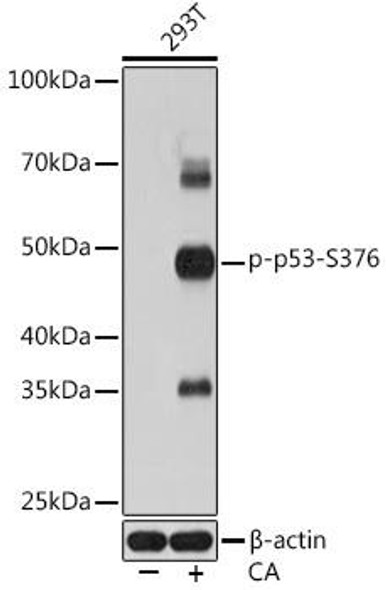
The p53 scFv Antibody (CPAB0475) is a cutting-edge tool for research involving p53, a key tumor suppressor protein that plays a crucial role in cell cycle regulation and DNA repair. This antibody, derived from a single-chain variable fragment (scFv), is highly specific and sensitive in detecting p53 protein levels in various biological samples.The p53 scFv Antibody has been extensively validated for use in immunofluorescence, immunoprecipitation, and flow cytometry applications, providing researchers with a versatile tool for studying p53 expression and function in different cellular contexts.
Its high affinity binding to p53 allows for precise and reliable detection, making it an essential reagent for cancer research and studies on the molecular mechanisms of tumorigenesis.The p53 scFv Antibody holds great potential for advancing our understanding of p53 biology and its role in cancer development, progression, and therapeutic response. By enabling accurate and specific detection of p53, this antibody opens up new opportunities for investigating the complex signaling pathways and interactions involving p53, paving the way for innovative discoveries in the field of oncology.
| Product Name: | p53 scFv antibody |
| Product Sku: | CPAB0475 |
| Size: | 2μg |
| Host Species: | |
| Immunogen: | |
| Clone: | |
| Reactivity: | Other bodies |
| Applications: |
| Purification Method: | |
| Isotype: | |
| Background: | Tumor protein p53, a nuclear protein, plays an essential role in the regulation of cell cycle, specifically in the transition from G0 to G1. It is found in very low levels in normal cells, however, in a variety of transformed cell lines, it is expressed in high amounts, and believed to contribute to transformation and malignancy. p53 is a DNA-binding protein containing DNA-binding, oligomerization and transcription activation domains. It is postulated to bind as a tetramer to a p53-binding site and activate expression of downstream genes that inhibit growth and/or invasion, and thus function as a tumor suppressor. Mutants of p53 that frequently occur in a number of different human cancers fail to bind the consensus DNA binding site, and hence cause the loss of tumor suppressor activity. Alterations of the TP53 gene occur not only as somatic mutations in human malignancies, but also as germline mutations in some cancer-prone families with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. |
| Synonyms: | LFS1, TRP53, TP53, p53. |
| Storage Buffer: |