Description
Notch1 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB21516)
The Notch1 Polyclonal Antibody (CAB21516) is a research tool specifically designed for studying Notch1, a transmembrane receptor involved in various cellular processes, including cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. This antibody, raised in rabbits, is highly specific to human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications.Notch1 is a key regulator of development and tissue homeostasis, with dysregulation of its signaling pathway implicated in numerous diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurological conditions. By targeting the Notch1 protein, researchers can investigate its role in various cellular functions and disease processes.
This antibody enables detection and analysis of Notch1 expression in different cell types, making it a valuable tool for studies in developmental biology, oncology, and regenerative medicine.Understanding the molecular mechanisms of Notch1 signaling is essential for developing targeted therapies that modulate its activity in disease settings. The Notch1 Polyclonal Antibody provides researchers with a reliable tool to further explore the functions of Notch1 and its potential as a therapeutic target in various pathologies.
| Product Name: | Notch1 Polyclonal Antibody |
| Product Code: | CAB21516 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Applications: | Immunofluorescence |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Tested Applications: | IF/ICC, ELISA |
| Key Applications: | Immunofluorescence |
| Recommended Dilution: | IF/ICC 1:50-1:200 |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.Buffer: PBS with 0.01% thimerosal, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Nucleus, Single-pass type I membrane protein |
This gene encodes a member of the NOTCH family of proteins. Members of this Type I transmembrane protein family share structural characteristics including an extracellular domain consisting of multiple epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats, and an intracellular domain consisting of multiple different domain types. Notch signaling is an evolutionarily conserved intercellular signaling pathway that regulates interactions between physically adjacent cells through binding of Notch family receptors to their cognate ligands. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed in the trans-Golgi network to generate two polypeptide chains that heterodimerize to form the mature cell-surface receptor. This receptor plays a role in the development of numerous cell and tissue types. Mutations in this gene are associated with aortic valve disease, Adams-Oliver syndrome, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 2456-2555 of human Notch1 (NP_060087.3). |
| Sequence: | ILPQE SPALP TSLPS SLVPP VTAAQ FLTPP SQHSY SSPVD NTPSH QLQVP EHPFL TPSPE SPDQW SSSSP HSNVS DWSEG VSSPP TSMQS QIARI PEAFK |
| Synonyms: | hN1, AOS5, TAN1, AOVD1 |
| Calculated MW: | 273kDa |
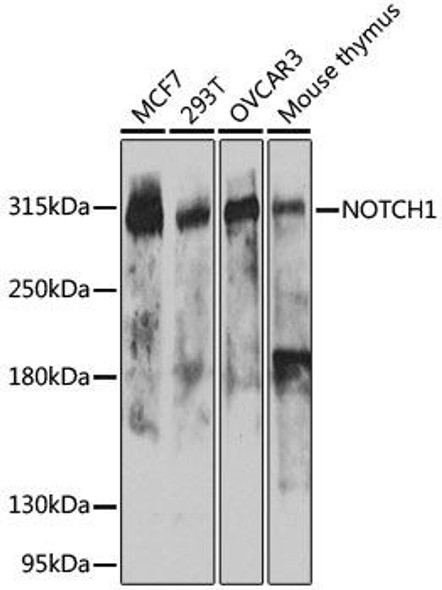
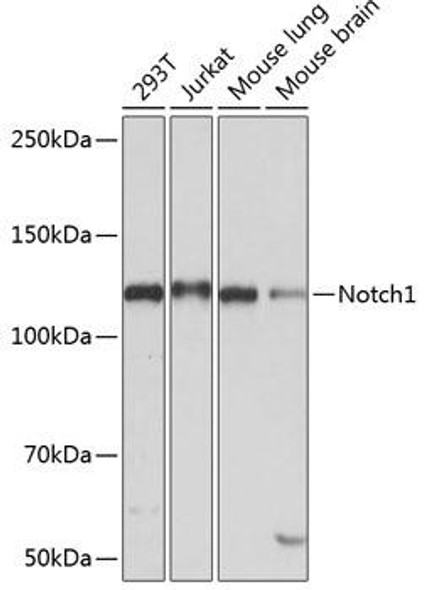
| Observed MW: | Refer to figures |