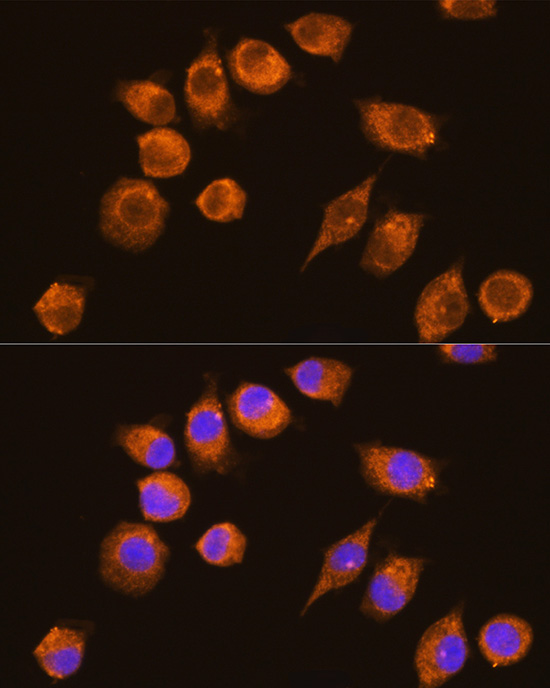
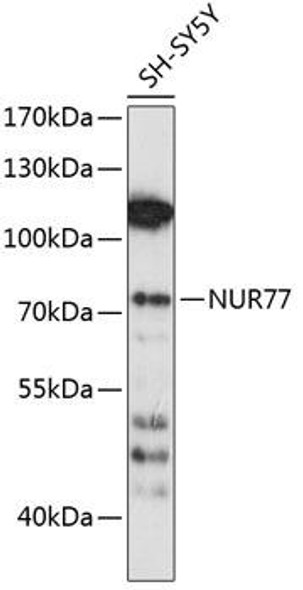
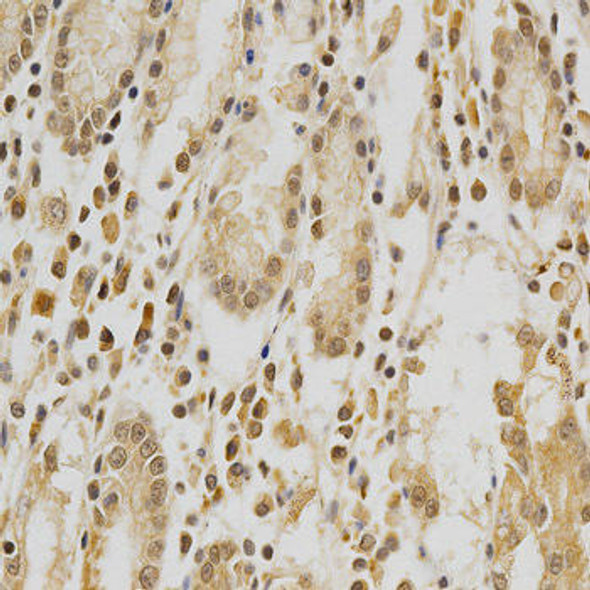
Description
Anti-NAGA Antibody (CAB9942)
The NAGA Polyclonal Antibody (CAB9942) is a valuable tool for researchers studying NAGA, an enzyme involved in the breakdown of glycosphingolipids. This antibody, produced in rabbits, exhibits high reactivity with human samples and has been validated for use in various applications, including Western blotting. By binding to the NAGA protein, this antibody enables precise detection and analysis in a range of cell types, making it ideal for studies in biochemistry and metabolism.NAGA, or alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase, plays a crucial role in lysosomal degradation pathways and is implicated in several metabolic disorders.
Research into the function and regulation of NAGA is important for understanding its role in glycosphingolipid metabolism and its potential as a therapeutic target for lysosomal storage diseases. The NAGA Polyclonal Antibody offers researchers a reliable tool for investigating NAGA in both normal and diseased states, facilitating advancements in the field of lysosomal biology.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-NAGA Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB9942 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
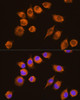
| Application: | WB IF |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 312-411 of human NAGA (NP_000253.1). |
| Application: | WB IF |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IF 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
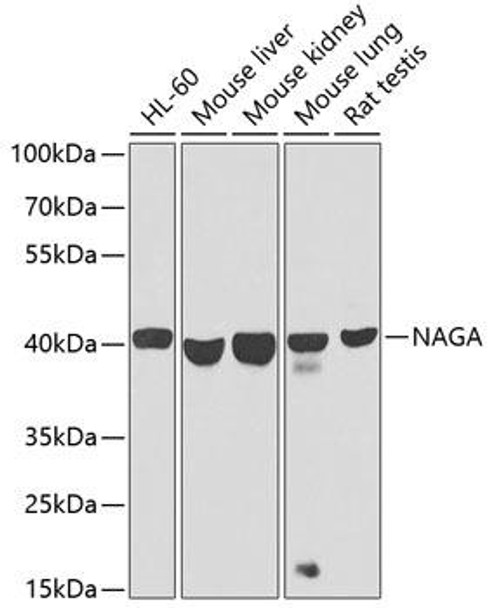
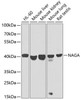
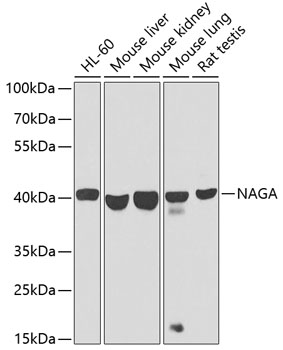
| Positive Samples: | HL-60, Mouse liver, Mouse kidney, Mouse lung, Rat testis |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 312-411 of human NAGA (NP_000253.1). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | IQGR RIHK EKSL IEVY MRPL SNKA SALV FFSC RTDM PYRY HSSL GQLN FTGS VIYE AQDV YSGD IISG LRDE TNFT VIIN PSGV VMWY LYPI KNLE MSQQ |
| Gene ID: | 4668 |
| Uniprot: | P17050 |
| Cellular Location: | Lysosome |
| Calculated MW: | 46kDa |
| Observed MW: | 46kDa |
| Synonyms: | NAGA, D22S674, GALB |
| Background: | NAGA encodes the lysosomal enzyme alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase, which cleaves alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyl moieties from glycoconjugates. Mutations in NAGA have been identified as the cause of Schindler disease types I and II (type II also known as Kanzaki disease). |
| UniProt Protein Function: | NAGA: Removes terminal alpha-N-acetylgalactosamine residues from glycolipids and glycopeptides. Required for the breakdown of glycolipids. Defects in NAGA are the cause of Schindler disease (SCHIND). Schindler disease is a form of NAGA deficiency characterized by early onset neuroaxonal dystrophy and neurological signs (convulsion during fever, epilepsy, psychomotor retardation and hypotonia). NAGA deficiency is typically classified in three main phenotypes: NAGA deficiency type I (Schindler disease or Schindler disease type I) with severe manifestations; NAGA deficiency type II (Kanzazi disease or Schindler disease type II) which is mild; NAGA deficiency type III (Schindler disease type III) characterized by mild-to-moderate neurologic manifestations. NAGA deficiency results in the increased urinary excretion of glycopeptides and oligosaccharides containing alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyl moieties. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. Defects in NAGA are the cause of Kanzaki disease (KANZD); also known as NAGA deficiency type II or Schindler disease type II. Kanzaki disease is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by late onset, angiokeratoma corporis diffusum and mild intellectual impairment. Belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase 27 family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Glycan Metabolism - glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - globo series; Hydrolase; EC 3.2.1.49 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 22q11 Cellular Component: lysosome; cytoplasm Molecular Function:protein homodimerization activity; alpha-galactosidase activity; alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase activity Biological Process: glycolipid catabolic process; carbohydrate catabolic process; glycoside catabolic process; glycosylceramide catabolic process; oligosaccharide metabolic process Disease: Schindler Disease, Type I; Kanzaki Disease |
| NCBI Summary: | NAGA encodes the lysosomal enzyme alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase, which cleaves alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyl moieties from glycoconjugates. Mutations in NAGA have been identified as the cause of Schindler disease types I and II (type II also known as Kanzaki disease). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P17050 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 4557781 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4668 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_000253.1 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P17050 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46,565 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | N-acetylgalactosaminidase, alpha- |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | NAGA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | GALB; D22S674 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase; alpha-galactosidase B; Acetylgalactosaminidase, alpha-N- (alpha-galactosidase B) |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Alpha-galactosidase B |
| Protein Family: | Alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | NAGA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | NAGAB_HUMAN |