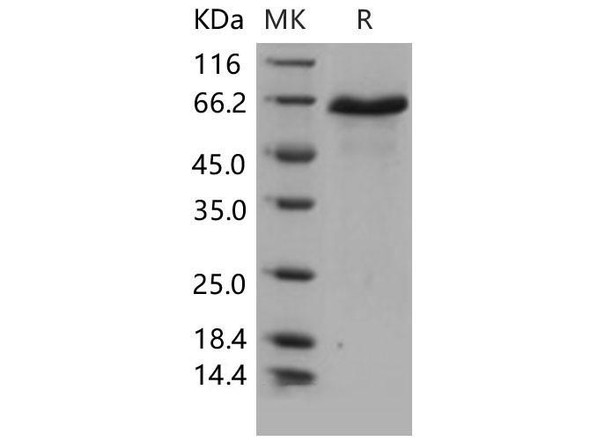
Description
Mouse Delta-like protein 1 (Dll1) ELISA Kit
The Mouse Delta-Like Protein 1 (DLL1) ELISA Kit is a reliable and sensitive tool for detecting levels of DLL1 in mouse serum, plasma, and cell culture supernatants. This kit provides accurate and reproducible results, making it suitable for a variety of research applications.DLL1 is a key protein involved in Notch signaling pathway, playing a crucial role in cell differentiation and development.
Dysregulation of DLL1 has been linked to various diseases and disorders, making it a valuable biomarker for studying and potentially treating these conditions.Order your Mouse DLL1 ELISA Kit from AssayGenie today and enhance your research on Notch signaling pathway and related diseases.
| Product Name: | Mouse Delta-like protein 1 (Dll1) ELISA Kit |
| SKU: | MOEB1230 |
| Size: | 96T |
| Target: | Mouse Delta-like protein 1 (Dll1) |
| Synonyms: | Drosophila Delta homolog 1, Delta1 |
| Assay Type: | Sandwich |
| Detection Method: | ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Detection Range: | 31.2-2000pg/mL |
| Sensitivity: | 15.62pg/mL |
| Intra CV: | 6.3% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Inter CV: | 8.2% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Linearity: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Recovery: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Function: | Transmembrane ligand protein of NOTCH1, NOTCH2 and NOTCH3 receptors that binds the extracellular domain (ECD) of Notch receptor in a cis and trans fashion manner (PubMed:21985982, PubMed:10958687). Following transinteraction, ligand cells produce mechanical force that depends of a clathrin-mediated endocytosis, requiring ligand ubiquitination, EPN1 interaction, and actin polymerisation; these events promote Notch receptor extracellular domain (NECD) transendocytosis and triggers Notch signaling through induction of cleavage, hyperphosphorylation, and nuclear accumulation of the intracellular domain of Notch receptors (NICD) (PubMed:10958687, PubMed:18676613). Is required for embryonic development and maintenance of adult stem cells in many different tissues and immune systeme; the DLL1-induced Notch signaling is mediated through an intercellular communication that regulates cell lineage, cell specification, cell patterning and morphogenesis through effects on differentiation and proliferation (PubMed:17194759, PubMed:19562077, PubMed:18997111, PubMed:23695674, PubMed:16495313, PubMed:21238454, PubMed:22282195, PubMed:7671806, PubMed:17960184, PubMed:22529374, PubMed:19389377, PubMed:23699523, PubMed:19144989, PubMed:23688253, PubMed:23806616, PubMed:26114479, PubMed:22940113, PubMed:25220152, PubMed:20081190, PubMed:21572390, PubMed:22096075). Plays a role in brain development at different level, namely by regulating neuronal differentiation of neural precursor cells via cell-cell interaction, most likely through the lateral inhibitory system in an endogenous level dependent-manner (PubMed:7671806, PubMed:18997111). During neocortex development, Dll1-Notch signaling transmission is mediated by dynamic interactions between intermediate neurogenic progenitors and radial glia; the cell-cell interactions are mediated via dynamic and transient elongation processes, likely to reactivate/maintain Notch activity in neighboring progenitors, and coordinate progenitor cell division and differentiation across radial and zonal boundaries (PubMed:23699523). During cerebellar development, regulates Bergmann glial monolayer formation and its morphological maturation through a Notch signaling pathway (PubMed:23688253). At the retina and spinal cord level, regulates neurogenesis by preventing the premature differentiation of neural progenitors and also by maintaining progenitors in spinal cord through Notch signaling pathway (PubMed:19389377, PubMed:26114479). Also controls neurogenesis of the neural tube in a progenitor domain-specific fashion along the dorsoventral axis (PubMed:20081190). Maintains quiescence of neural stem cells and plays a role as a fate determinant that segregates asymmetrically to one daughter cell during neural stem cells mitosis, resulting in neuronal differentiation in Dll1-inheriting cell (PubMed:23695674). Plays a role in immune systeme development, namely the development of all T-cells and marginal zone (MZ) B cells (PubMed:15146182, PubMed:19217325). Blocks the differentiation of progenitor cells into the B-cell lineage while promoting the emergence of a population of cells with the characteristics of a T-cell/NK-cell precursor (By similarity). Upon MMP14 cleavage, negatively regulates Notch signaling in haematopoietic progenitor cells to specifically maintain normal B-cell development in bone marrow (PubMed:21572390). Also plays a role during muscle development. During early development, inhibits myoblasts differentiation from the medial dermomyotomal lip and later regulates progenitor cell differentiation (PubMed:17194759). Directly modulates cell adhesion and basal lamina formation in satellite cells through Notch signaling. Maintains myogenic progenitors pool by suppressing differentiation through down-regulation of MYOD1 and is required for satellite cell homing and PAX7 expression (PubMed:22940113). During craniofacial and trunk myogenesis suppresses differentiation of cranial mesoderm-derived and somite-derived muscle via MYOD1 regulation but in cranial mesoderm-derived progenitors, is neither required for satellite cell homing nor for PAX7 expression (PubMed:25220152). Also plays a role during pancreatic cell development. During type B pancreatic cell development, may be involved in the initiation of proximodistal patterning in the early pancreatic epithelium (PubMed:22529374). Stimulates multipotent pancreatic progenitor cells proliferation and pancreatic growth by maintaining HES1 expression and PTF1A protein levels (PubMed:22096075). During fetal stages of development, is required to maintain arterial identity and the responsiveness of arterial endothelial cells for VEGFA through regulation of KDR activation and NRP1 expression (PubMed:19144989). Controls sprouting angiogenesis and subsequent vertical branch formation througth regulation on tip cell differentiation (PubMed:22282195). Negatively regulates goblet cell differentiation in intestine and controls secretory fat commitment through lateral inhibition in small intestine (PubMed:21238454, PubMed:21915337). Plays a role during inner ear development; negatively regulates auditory hair cell differentiation (PubMed:16495313). Plays a role during nephron development through Notch signaling pathway (PubMed:23806616). Regulates growth, blood pressure and energy homeostasis (PubMed:19562077). |
| Uniprot: | Q61483 |
| Sample Type: | Serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids |
| Specificity: | Natural and recombinant mouse Delta-like protein 1 |
| Sub Unit: | Homodimer (PubMed:12794186). Interacts with TJP1 (PubMed:24715457). Interacts with MMP14; inhibits DLL1-induced Notch signaling (PubMed:21572390). Interacts with MAGI1 (via PDZ domain); forms a complex with CTNNB1 and CDH2 and promotes recruitment to the adherens junction and stabilization on the cell surface (PubMed:15908431). Interacts with PSEN1; undergoes a presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase cleavage that releases a Dll1-intracellular form (PubMed:12794186). Interacts with MFAP5 (PubMed:15788413). Interacts with MIB1 (PubMed:21985982). Interacts with NEURL1B; leads to ubiquitination (PubMed:17003037, PubMed:19723503). Interacts with NEURL1 (PubMed:19723503). Interacts with SYNJ2BP; enhances DLL1 protein stability, and promotes Notch signaling in endothelial cells (By similarity). Interacts with MAGI1, MAGI2, MAGI3 and MPDZ (By similarity). Interacts (via ubiquitin) with EPN1 (via IUM domain); binding with NOTCH1 attached to neighboring cell, promotes ligand ubiquitination and EPN1 interaction, leading to NECD transendocytosis and Notch signaling. |
| Research Area: | Development Biology |
| Subcellular Location: | Dll1-intracellular form Nucleus |
| Storage: | Please see kit components below for exact storage details |
| Note: | For research use only |
| UniProt Protein Function: | DLL1: Acts as a ligand for Notch receptors. Blocks the differentiation of progenitor cells into the B-cell lineage while promoting the emergence of a population of cells with the characteristics of a T-cell/NK-cell precursor. Interacts with Notch receptors. Expressed in heart and pancreas, with lower expression in brain and muscle and almost no expression in placenta, lung, liver and kidney.Protein type: Membrane protein, integral; Cell development/differentiation; Motility/polarity/chemotaxisCellular Component: membrane; plasma membrane; integral to membrane; cytoplasmic vesicleMolecular Function: protein binding; calcium ion binding; Notch bindingBiological Process: negative regulation of interleukin-10 production; multicellular organismal development; auditory receptor cell differentiation; compartment specification; somite specification; regulation of neurogenesis; cell-cell signaling; cell communication; heart looping; cell differentiation; inner ear development; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway; nervous system development; Notch signaling pathway; inner ear morphogenesis; somitogenesis; negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation; in utero embryonic development; odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth; negative regulation of neuron differentiation; negative regulation of cell differentiation; organ morphogenesis; negative regulation of auditory receptor cell differentiation; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; determination of left/right symmetry; auditory receptor cell fate commitment |
| UniProt Protein Details: | |
| NCBI Summary: | |
| UniProt Code: | Q61483 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 40789272 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 13388 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_031891.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q61483,Q6PFV7 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q61483 |
| Molecular Weight: | 78,449 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | delta-like protein 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | delta-like 1 (Drosophila) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | Dll1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | Delta1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | delta-like protein 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Delta-like protein 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Drosophila Delta homolog 1; Delta1 |
| Protein Family: | Delta-like protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | Dll1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | DLL1_MOUSE |
| Component | Quantity (96 Assays) | Storage |
| ELISA Microplate (Dismountable) | 8×12 strips | -20°C |
| Lyophilized Standard | 2 | -20°C |
| Sample Diluent | 20ml | -20°C |
| Assay Diluent A | 10mL | -20°C |
| Assay Diluent B | 10mL | -20°C |
| Detection Reagent A | 120µL | -20°C |
| Detection Reagent B | 120µL | -20°C |
| Wash Buffer | 30mL | 4°C |
| Substrate | 10mL | 4°C |
| Stop Solution | 10mL | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 | - |
Other materials and equipment required:
- Microplate reader with 450 nm wavelength filter
- Multichannel Pipette, Pipette, microcentrifuge tubes and disposable pipette tips
- Incubator
- Deionized or distilled water
- Absorbent paper
- Buffer resevoir
*Note: The below protocol is a sample protocol. Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
Allow all reagents to reach room temperature (Please do not dissolve the reagents at 37°C directly). All the reagents should be mixed thoroughly by gently swirling before pipetting. Avoid foaming. Keep appropriate numbers of strips for 1 experiment and remove extra strips from microtiter plate. Removed strips should be resealed and stored at -20°C until the kits expiry date. Prepare all reagents, working standards and samples as directed in the previous sections. Please predict the concentration before assaying. If values for these are not within the range of the standard curve, users must determine the optimal sample dilutions for their experiments. We recommend running all samples in duplicate.
| Step | |
| 1. | Add Sample: Add 100µL of Standard, Blank, or Sample per well. The blank well is added with Sample diluent. Solutions are added to the bottom of micro ELISA plate well, avoid inside wall touching and foaming as possible. Mix it gently. Cover the plate with sealer we provided. Incubate for 120 minutes at 37°C. |
| 2. | Remove the liquid from each well, don't wash. Add 100µL of Detection Reagent A working solution to each well. Cover with the Plate sealer. Gently tap the plate to ensure thorough mixing. Incubate for 1 hour at 37°C. Note: if Detection Reagent A appears cloudy warm to room temperature until solution is uniform. |
| 3. | Aspirate each well and wash, repeating the process three times. Wash by filling each well with Wash Buffer (approximately 400µL) (a squirt bottle, multi-channel pipette,manifold dispenser or automated washer are needed). Complete removal of liquid at each step is essential. After the last wash, completely remove remaining Wash Buffer by aspirating or decanting. Invert the plate and pat it against thick clean absorbent paper. |
| 4. | Add 100µL of Detection Reagent B working solution to each well. Cover with the Plate sealer. Incubate for 60 minutes at 37°C. |
| 5. | Repeat the wash process for five times as conducted in step 3. |
| 6. | Add 90µL of Substrate Solution to each well. Cover with a new Plate sealer and incubate for 10-20 minutes at 37°C. Protect the plate from light. The reaction time can be shortened or extended according to the actual color change, but this should not exceed more than 30 minutes. When apparent gradient appears in standard wells, user should terminatethe reaction. |
| 7. | Add 50µL of Stop Solution to each well. If color change does not appear uniform, gently tap the plate to ensure thorough mixing. |
| 8. | Determine the optical density (OD value) of each well at once, using a micro-plate reader set to 450 nm. User should open the micro-plate reader in advance, preheat the instrument, and set the testing parameters. |
| 9. | After experiment, store all reagents according to the specified storage temperature respectively until their expiry. |
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clot overnight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Remove serum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |