Mouse CTNNb1 (Catenin, Beta 1) ELISA Kit (MOES00818)
- SKU:
- MOES00818
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Uniprot:
- Q02248
- Sensitivity:
- 0.09ng/mL
- Range:
- 0.16-10ng/mL
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Synonyms:
- CTNNB1 , CTNNB, MRD19, armadillo,beta-catenin
- Reactivity:
- Mouse
- Sample Type:
- Serum, plasma and other biological fluids
- Research Area:
- Cell Biology
Description
Mouse CTNNb1 (Catenin, Beta 1) ELISA Kit
The Mouse CTNNB1 (Catenin beta-1) ELISA Kit is a highly sensitive and specific assay designed for the accurate detection of catenin beta-1 levels in mouse serum, plasma, and cell culture supernatants. This kit ensures reliable and reproducible results, making it an ideal tool for various research applications.Catenin beta-1 is a key protein involved in cell adhesion and signaling pathways, playing a critical role in embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and disease progression. Dysregulation of catenin beta-1 has been implicated in various diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and neurological conditions, making it a valuable biomarker for studying these diseases and potential therapeutic interventions.
The Mouse CTNNB1 ELISA Kit from Assay Genie provides researchers with a precise and efficient method for quantifying catenin beta-1 levels in biological samples, enabling further exploration of its biological functions and potential clinical applications.
| Assay type: | Sandwich |
| Format: | 96T |
| Assay time: | 4.5h |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Detection Method: | Colormetric |
| Detection Range: | 0.16-10 ng/mL |
| Sensitivity: | 0.10 ng/mL |
| Sample Volume Required Per Well: | 100µL |
| Sample Type: | Serum, plasma and other biological fluids |
| Specificity: | This kit recognizes Mouse CTNNb1 in samples. No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Mouse CTNNb1 and analogues was observed. |
This ELISA kit uses Sandwich-ELISA as the method. The micro ELISA plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Mouse CTNNb1. Standards or samples are added to the appropriate micro ELISA plate wells and combined with the specific antibody. Then a biotinylated detection antibody specific for Mouse CTNNb1 and Avidin-Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugate are added to each micro plate well successively and incubated. Free components are washed away. The substrate solution is added to each well. Only those wells that contain Mouse CTNNb1, biotinylated detection antibody and Avidin-HRP conjugate will appear blue in color. The enzyme-substrate reaction is terminated by adding Stop Solution and the color turns yellow. The optical density (OD) is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 450 nm ± 2 nm. The OD value is proportional to the concentration of Mouse CTNNb1. The concentration of Mouse CTNNb1 in samples can be calculated by comparing the OD of the samples to the standard curve.
| UniProt Protein Function: | CTNNB1: a regulator of cell adhesion and a key downstream effector in the Wnt signaling pathway. Implicated early embryonic development and tumorigenesis. Phosphorylated and destabilized by CK1 and GSK-3beta. Stabilized cytoplasmic beta-catenin is a hallmark of a variety of cancers. Stabilized beta-catenin translocates to the nucleus, where it acts as a transcriptional activator of T-cell factor (TCF)-regulated genes. Interacts with the PDZ domain of TAX1BP3, inhibiting its transcriptional activity. Two alternatively spliced human isoforms have been described. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Actin-binding; Cell adhesion; Transcription factor; Oncoprotein; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Nuclear receptor co-regulator Cellular Component: adherens junction; apical junction complex; apical part of cell; basolateral plasma membrane; beta-catenin destruction complex; catenin complex; cell cortex; cell junction; cell projection membrane; cell-cell adherens junction; centrosome; cytoplasm; cytoskeleton; cytosol; dendritic shaft; fascia adherens; flotillin complex; focal adhesion; intercellular junction; lamellipodium; lateral plasma membrane; membrane; microvillus membrane; neuron projection; nucleus; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; plasma membrane; protein complex; synapse; tight junction; transcription factor complex; Z disc Molecular Function:alpha-catenin binding; cadherin binding; chromatin binding; DNA binding; double-stranded DNA binding; enzyme binding; estrogen receptor binding; ionotropic glutamate receptor binding; kinase binding; nitric-oxide synthase binding; nuclear hormone receptor binding; protein binding; protein C-terminus binding; protein complex binding; protein kinase binding; protein phosphatase binding; signal transducer activity; SMAD binding; transcription coactivator activity; transcription factor activity; transcription factor binding Biological Process: anterior/posterior axis specification; bone resorption; cardiac muscle cell proliferation; cell adhesion; cell differentiation; cell fate determination; cell fate specification; cell maturation; cell proliferation; cell-cell adhesion; cell-matrix adhesion; cellular morphogenesis during differentiation; cellular process; central nervous system vasculogenesis; chromatin-mediated maintenance of transcription; dorsal/ventral axis specification; dorsal/ventral pattern formation; ectoderm development; embryonic axis specification; embryonic digit morphogenesis; embryonic foregut morphogenesis; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis; embryonic heart tube development; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis; endoderm formation; endodermal cell fate commitment; fallopian tube development; forebrain development; gastrulation with mouth forming second; genitalia morphogenesis; glial cell fate determination; hair cycle process; hair follicle morphogenesis; heart development; hemopoiesis; hindbrain development; in utero embryonic development; kidney development; layer formation in the cerebral cortex; lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye; limb development; lung development; male genitalia development; midbrain development; morphogenesis of embryonic epithelium; negative regulation of cell differentiation; negative regulation of cell proliferation; negative regulation of chondrocyte differentiation; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle, embryonic; negative regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation; negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation; negative regulation of protein sumoylation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; nervous system development; neural plate development; neuron differentiation; neuron migration; odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth; oocyte development; organ development; osteoclast differentiation; pancreas development; patterning of blood vessels; positive regulation of apoptosis; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of endothelial cell differentiation; positive regulation of epithelial cell differentiation; positive regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation; positive regulation of neuron apoptosis; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation; positive regulation of skeletal muscle development; positive regulation of telomerase activity; positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase; positive regulation of transcription factor activity; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; protein heterooligomerization; proximal/distal pattern formation; regulation of apoptosis; regulation of cell differentiation; regulation of cell proliferation; regulation of centriole-centriole cohesion; regulation of epithelial cell differentiation; regulation of gene expression; regulation of histone H3-K4 methylation; regulation of myelination; regulation of osteoblast differentiation; regulation of osteoclast differentiation; regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation; regulation of T cell proliferation; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; response to cytokine stimulus; response to estradiol stimulus; response to estrogen stimulus; Schwann cell proliferation; skeletal development; skin development; smooth muscle cell differentiation; stem cell maintenance; synapse organization and biogenesis; synaptic transmission; synaptic vesicle transport; T cell differentiation; T cell differentiation in the thymus; thymus development; transcription, DNA-dependent; ureteric bud branching; vasculature development; vasculogenesis; Wnt receptor signaling pathway; Wnt receptor signaling pathway through beta-catenin |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes not only an important cytoplasmic component of the classical cadherin adhesion complex that forms the adherens junction in epithelia and mediates cell-cell adhesion in many other tissues but also a key signaling molecule in the canonical Wnt signaling pathway that controls cell growth and differentiation during both normal development and tumorigenesis. The gene product contains a central armadillo-repeat containing domain through which it binds the cytoplasmic tail of classical cadherins; meanwhile, it also binds alpha-catenin, which further links the cadherin complex to the actin cytoskeleton either directly or indirectly. Beta-catenin is therefore necessary for the adhesive function of classical cadherins. Another key function of this protein is to mediate the canonical Wnt signaling pathway and regulate gene transcription. Without Wnt signal, cytoplasmic beta-catenin that is not associated with the cadherin complex is quickly phosphorylated at the N-terminal Ser/Thr residues by the so called degradation complex containing axin, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), casein kinase I, and GSK3B, then ubiquitylated by beta-TrCP, and degraded by the proteasome. However, in the presence of Wnt signal, the degradation complex is disrupted and the stabilized cytoplasmic beta-catenin translocates into the nucleus, where it binds various transcription factors and, together with these factors, regulates the transcription of many downstream genes. Mutations of this gene have been linked with various types of tumors. Alternatively spliced variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | Q02248 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 399310 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 12387 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q02248. 1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q02248,Q922W1, Q9D335, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q02248 |
| Molecular Weight: | 85,471 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Catenin beta-1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | catenin (cadherin associated protein), beta 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | Ctnnb1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | Bfc; Mesc; Catnb |
| NCBI Protein Information: | catenin beta-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Catenin beta-1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Beta-catenin |
| Protein Family: | Beta-catenin-like protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | Ctnnb1 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CTNB1_MOUSE |
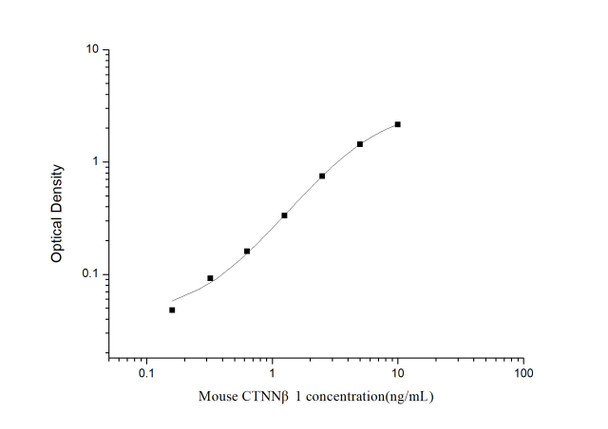
As the OD values of the standard curve may vary according to the conditions of the actual assay performance (e. g. operator, pipetting technique, washing technique or temperature effects), the operator should establish a standard curve for each test. Typical standard curve and data is provided below for reference only.
| Concentration (ng/mL) | O.D | Average | Corrected |
| 10 | 2.197 2.235 | 2.216 | 2.155 |
| 5 | 1.475 1.529 | 1.502 | 1.441 |
| 2.5 | 0.827 0.791 | 0.809 | 0.748 |
| 1.25 | 0.386 0.404 | 0.395 | 0.334 |
| 0.63 | 0.229 0.213 | 0.221 | 0.16 |
| 0.32 | 0.157 0.149 | 0.153 | 0.092 |
| 0.16 | 0.101 0.117 | 0.109 | 0.048 |
| 0 | 0.055 0.067 | 0.061 | -- |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Mouse CTNNb1 were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, mid range and high level Mouse CTNNb1 were tested on 3 different plates, 20 replicates in each plate.
| Intra-assay Precision | Inter-assay Precision | |||||
| Sample | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| n | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Mean (ng/mL) | 0.55 | 1.35 | 3.81 | 0.55 | 1.46 | 4.11 |
| Standard deviation | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.21 |
| C V (%) | 5.45 | 4.44 | 3.15 | 5.45 | 4.11 | 5.11 |
Recovery
The recovery of Mouse CTNNb1 spiked at three different levels in samples throughout the range of the assay was evaluated in various matrices.
| Sample Type | Range (%) | Average Recovery (%) |
| Serum (n=5) | 88-100 | 93 |
| EDTA plasma (n=5) | 90-102 | 95 |
| Cell culture media (n=5) | 89-105 | 97 |
Linearity
Samples were spiked with high concentrations of Mouse CTNNb1 and diluted with Reference Standard & Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the range of the assay.
| Serum (n=5) | EDTA plasma (n=5) | Cell culture media (n=5) | ||
| 1:2 | Range (%) | 96-109 | 89-101 | 95-109 |
| Average (%) | 102 | 94 | 103 | |
| 1:4 | Range (%) | 87-102 | 79-93 | 84-95 |
| Average (%) | 94 | 85 | 90 | |
| 1:8 | Range (%) | 90-107 | 84-99 | 86-100 |
| Average (%) | 98 | 91 | 92 | |
| 1:16 | Range (%) | 87-102 | 80-93 | 82-96 |
| Average (%) | 94 | 86 | 88 |
An unopened kit can be stored at 4°C for 1 month. If the kit is not used within 1 month, store the items separately according to the following conditions once the kit is received.
| Item | Specifications | Storage |
| Micro ELISA Plate(Dismountable) | 8 wells ×12 strips | -20°C, 6 months |
| Reference Standard | 2 vials | |
| Concentrated Biotinylated Detection Ab (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | |
| Concentrated HRP Conjugate (100×) | 1 vial, 120 µL | -20°C(shading light), 6 months |
| Reference Standard & Sample Diluent | 1 vial, 20 mL | 4°C, 6 months |
| Biotinylated Detection Ab Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| HRP Conjugate Diluent | 1 vial, 14 mL | |
| Concentrated Wash Buffer (25×) | 1 vial, 30 mL | |
| Substrate Reagent | 1 vial, 10 mL | 4°C(shading light) |
| Stop Solution | 1 vial, 10 mL | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 pieces | |
| Product Description | 1 copy | |
| Certificate of Analysis | 1 copy |
- Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate and record theirpositions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Note: addall solutions to the bottom of the plate wells while avoiding contact with the well walls. Ensuresolutions do not foam when adding to the wells.
- Aliquot 100µl of standard solutions into the standard wells.
- Add 100µl of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well.
- Add 100µl of properly diluted sample (serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and otherbiological fluids) into test sample wells.
- Cover the plate with the sealer provided in the kit and incubate for 90 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate the liquid from each well, do not wash. Immediately add 100µL of BiotinylatedDetection Ab working solution to each well. Cover the plate with a plate seal and gently mix. Incubate for 1 hour at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from the plate and add 350µL of wash buffer to each welland incubate for 1-2 minutes at room temperature. Aspirate the solution from each well andclap the plate on absorbent filter paper to dry. Repeat this process 3 times. Note: a microplatewasher can be used in this step and other wash steps.
- Add 100µL of HRP Conjugate working solution to each well. Cover with a plate seal andincubate for 30 min at 37°C.
- Aspirate or decant the solution from each well. Repeat the wash process for five times asconducted in step 7.
- Add 90µL of Substrate Reagent to each well. Cover with a new plate seal and incubate forapproximately 15 min at 37°C. Protect the plate from light. Note: the reaction time can beshortened or extended according to the actual color change, but not by more than 30min.
- Add 50 µL of Stop Solution to each well. Note: Adding the stop solution should be done inthe same order as the substrate solution.
- Determine the optical density (OD value) of each well immediately with a microplate readerset at 450 nm.