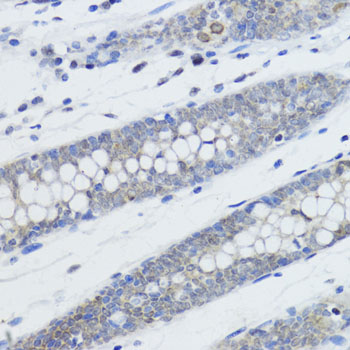
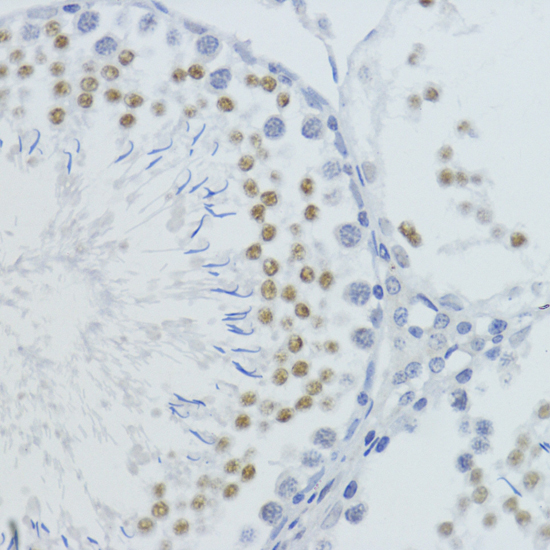
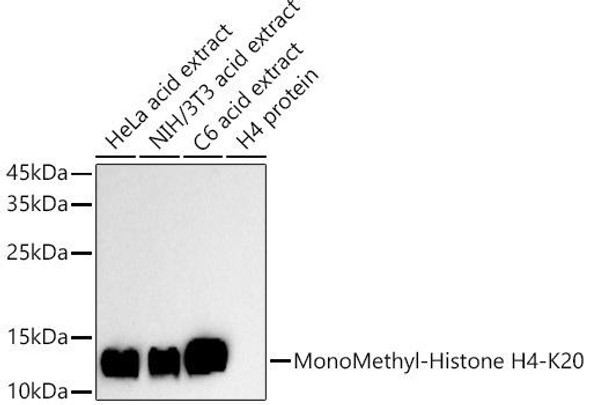
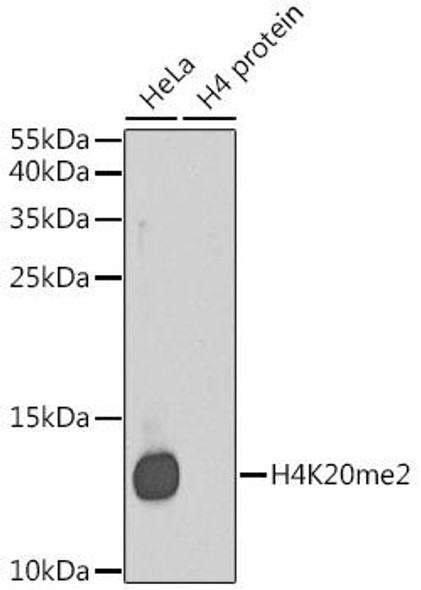
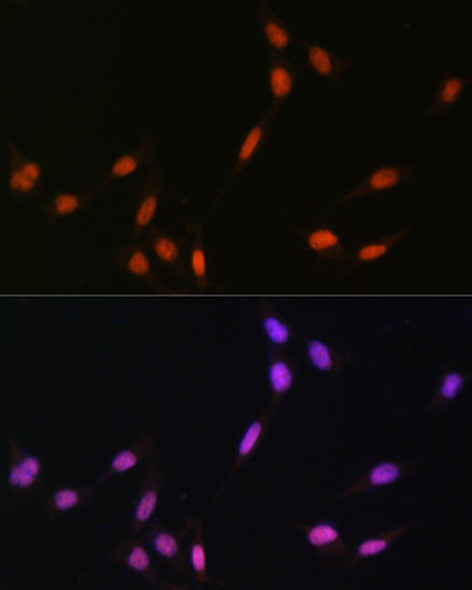
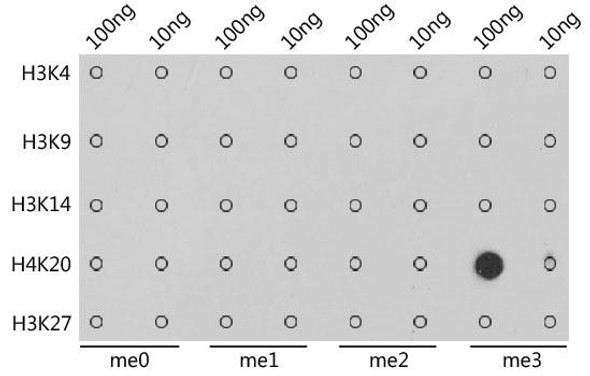
Description
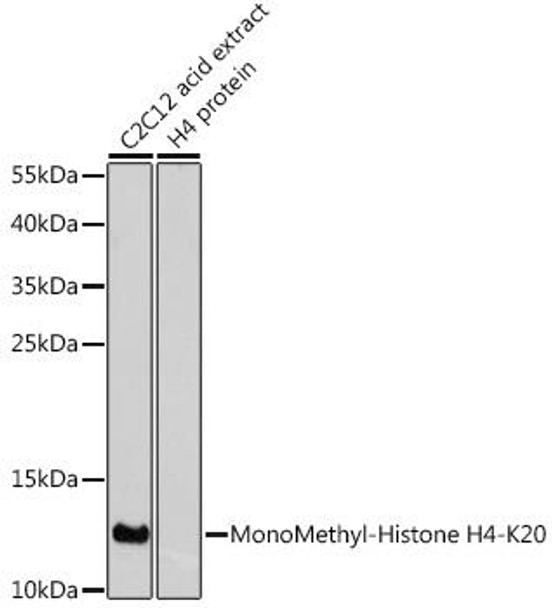
Anti-MonoMethyl-Histone H4-K20 Antibody (CAB2370)
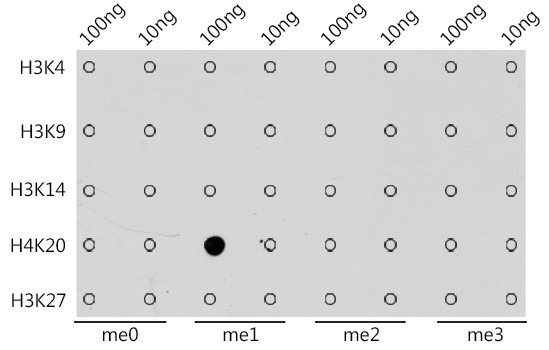
The Monomethyl Histone H4 (K20) Polyclonal Antibody (CAB2370) is a valuable tool for researchers studying epigenetic regulation and chromatin structure. This antibody, produced in rabbits, has high reactivity with human samples and is optimized for use in immunoprecipitation and ChIP applications. By binding specifically to the monomethylated form of Histone H4 at lysine 20, this antibody enables precise detection and analysis of this histone modification in a variety of cell types.Histone H4 monomethylation at lysine 20 is a key epigenetic mark associated with transcriptional regulation and DNA repair processes. Dysregulation of this modification has been linked to various diseases, including cancer and neurological disorders.
By studying the dynamics of Histone H4 monomethylation, researchers can gain insights into gene expression patterns and cellular responses to environmental stimuli.The Monomethyl Histone H4 (K20) Polyclonal Antibody is an essential tool for investigating the role of histone modifications in chromatin remodeling and gene regulation. Its specificity and sensitivity make it ideal for exploring the complex interplay between epigenetic marks and cellular function. Researchers in the fields of molecular biology, genetics, and epigenetics will find this antibody invaluable for their studies on chromatin biology and epigenetic mechanisms.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-MonoMethyl-Histone H4-K20 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB2370 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
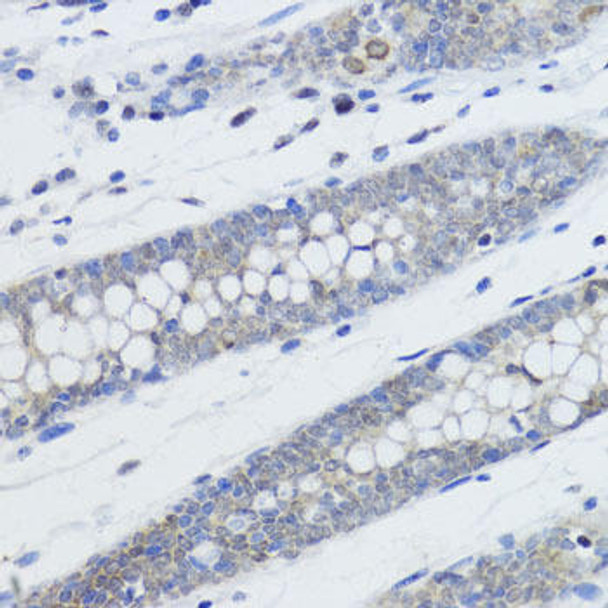
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP ChIP ChIPseq |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Other (Wide Range) |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human MonoMethyl-Histone H4-K20 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP ChIP ChIPseq |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 IP 1:50 - 1:200 ChIP 1:20 - 1:100 ChIPseq 1:20 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Other (Wide Range) |
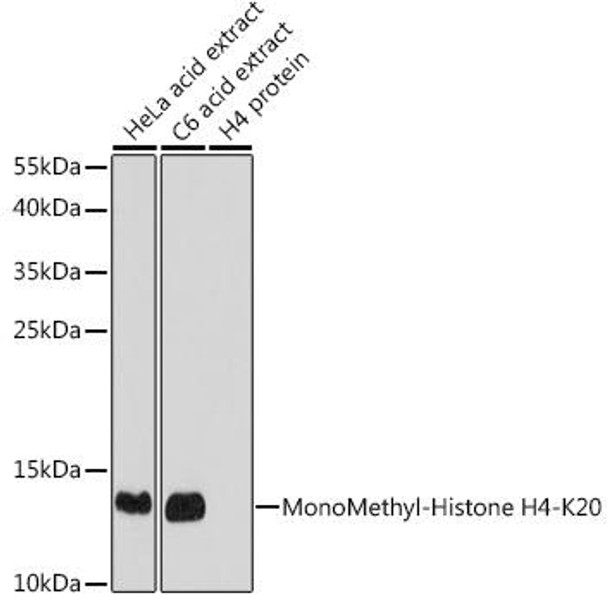
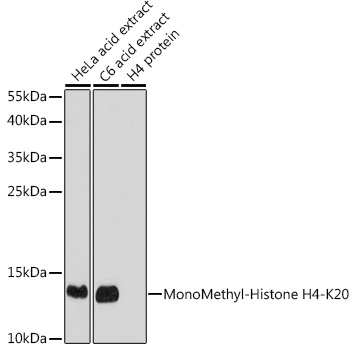
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, C2C12, C6 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human MonoMethyl-Histone H4-K20 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 8370 |
| Uniprot: | P62805 |
| Cellular Location: | Chromosome, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 11kDa |
| Observed MW: | 11kDa |
| Synonyms: | FO108, H4, H4/n, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, Histone H4, HIST1H4A, HIST2H4A |
| Background: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. This structure consists of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a nucleosome, an octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a replication-dependent histone that is a member of the histone H4 family. Transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails; instead, they contain a palindromic termination element. This gene is found in a histone cluster on chromosome 1. This gene is one of four histone genes in the cluster that are duplicated; this record represents the centromeric copy. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | Function: Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Subunit structure: The nucleosome is a histone octamer containing two molecules each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 assembled in one H3-H4 heterotetramer and two H2A-H2B heterodimers. The octamer wraps approximately 147 bp of DNA. Subcellular location: Nucleus. Chromosome. Post-translational modification: Acetylation at Lys-6 (H4K5ac), Lys-9 (H4K8ac), Lys-13 (H4K12ac) and Lys-17 (H4K16ac) occurs in coding regions of the genome but not in heterochromatin.Citrullination at Arg-4 (H4R3ci) by PADI4 impairs methylation.Monomethylation and asymmetric dimethylation at Arg-4 (H4R3me1 and H4R3me2a, respectively) by PRMT1 favors acetylation at Lys-9 (H4K8ac) and Lys-13 (H4K12ac). Demethylation is performed by JMJD6. Symmetric dimethylation on Arg-4 (H4R3me2s) by the PRDM1/PRMT5 complex may play a crucial role in the germ-cell lineage.Monomethylated, dimethylated or trimethylated at Lys-21 (H4K20me1, H4K20me2, H4K20me3). Monomethylation is performed by SET8. Trimethylation is performed by SUV420H1 and SUV420H2 and induces gene silencing. Ref.19 Ref.20 Ref.21 Ref.23 Ref.24 Ref.28Phosphorylated by PAK2 at Ser-48 (H4S47ph). This phosphorylation increases the association of H3.3-H4 with the histone chaperone HIRA, thus promoting nucleosome assembly of H3.3-H4 and inhibiting nucleosome assembly of H3.1-H4. Ref.28 Ref.36Ubiquitinated by the CUL4-DDB-RBX1 complex in response to ultraviolet irradiation. This may weaken the interaction between histones and DNA and facilitate DNA accessibility to repair proteins. Monoubiquitinated at Lys-92 of histone H4 (H4K91ub1) in response to DNA damage. The exact role of H4K91ub1 in DNA damage response is still unclear but it may function as a licensing signal for additional histone H4 post-translational modifications such as H4 Lys-21 methylation (H4K20me). Ref.27 Ref.30Sumoylated, which is associated with transcriptional repression. Ref.22Crotonylation (Kcr) is specifically present in male germ cells and marks testis-specific genes in post-meiotic cells, including X-linked genes that escape sex chromosome inactivation in haploid cells. Crotonylation marks active promoters and enhancers and confers resistance to transcriptional repressors. It is also associated with post-meiotically activated genes on autosomes. Ref.35 Sequence similarities: Belongs to the histone H4 family. Sequence caution: The sequence AAI28106.1 differs from that shown. Reason: Frameshift at position 3. |
| NCBI Summary: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. This structure consists of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a nucleosome, an octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H4 family. Transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails; instead, they contain a palindromic termination element. This gene is found in a histone cluster on chromosome 1. This gene is one of four histone genes in the cluster that are duplicated; this record represents the telomeric copy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P62805 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 77539758 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 554313 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_001029249.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P62805,P02304, P02305, Q6DRA9, Q6FGB8, Q6NWP7, A2VCL0 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P62805 |
| Molecular Weight: | 11,367 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | histone H4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | histone cluster 2, H4b |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HIST2H4B |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | H4/o |
| NCBI Protein Information: | histone H4; histone 2, H4b |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Histone H4 |
| Protein Family: | Histone |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HIST1H4A |
| UniProt Entry Name: | H4_HUMAN |