Description
Anti-MonoMethyl-Histone H3-K36 Antibody (CAB2364)
The Monomethyl Histone H3 (K36) Polyclonal Antibody (CAB2364) is a valuable tool for researchers studying epigenetic modifications and their impact on gene expression. Histone H3 lysine 36 monomethylation is a crucial modification involved in transcriptional activation and elongation processes. This antibody, raised in rabbits, specifically targets the monomethylated form of histone H3 at lysine 36 and is highly reactive in human samples.Validated for use in Western blot applications, the Monomethyl Histone H3 (K36) Polyclonal Antibody (CAB2364) allows for the detection and analysis of this epigenetic mark in various cell types. Its specificity and sensitivity make it an ideal tool for research in the fields of epigenetics, chromatin biology, and gene regulation.
Understanding the role of histone H3 lysine 36 monomethylation is essential for unraveling the complex network of epigenetic mechanisms that control gene expression. This antibody provides researchers with a reliable means to investigate the functions of this modification in normal cellular processes and diseases such as cancer, developmental disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions. Unlocking the secrets of histone H3 lysine 36 monomethylation could lead to new therapeutic strategies targeting epigenetic pathways for the treatment of various diseases.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-MonoMethyl-Histone H3-K36 Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB2364 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP ChIP ChIPseq |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Other (Wide Range) |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic methylated peptide corresponding to residues surrounding K36 of human histone H3 |
| Application: | WB IHC IF IP ChIP ChIPseq |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 IF 1:50 - 1:200 IP 1:50 - 1:200 ChIP 1:20 - 1:100 ChIPseq 1:20 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Other (Wide Range) |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa, NIH/3T3, C6 |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic methylated peptide corresponding to residues surrounding K36 of human histone H3 |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20'C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 8290 |
| Uniprot: | Q16695 |
| Cellular Location: | Chromosome, Nucleus |
| Calculated MW: | 15kDa |
| Observed MW: | 17KDa |
| Synonyms: | H3.4, H3/g, H3FT, H3t, HIST3H3, Histone H3, HIST1H3A |
| Background: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a replication-dependent histone that is a member of the histone H3 family. Transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails; instead, they contain a palindromic termination element. This gene is located separately from the other H3 genes that are in the histone gene cluster on chromosome 6p22-p21.3. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | HIST3H3: Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. The nucleosome is a histone octamer containing two molecules each of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 assembled in one H3-H4 heterotetramer and two H2A-H2B heterodimers. The octamer wraps approximately 147 bp of DNA. Expressed in testicular cells. Belongs to the histone H3 family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:DNA-binding Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1q42 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding; DNA binding; histone binding; protein heterodimerization activity Biological Process: nucleosome assembly; negative regulation of protein oligomerization; protein heterotetramerization; telomere maintenance |
| NCBI Summary: | Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H3 family. Transcripts from this gene lack polyA tails; instead, they contain a palindromic termination element. This gene is located separately from the other H3 genes that are in the histone gene cluster on chromosome 6p22-p21.3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q16695 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 18202512 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 8290 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q16695.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q16695,Q6FGU4, B2R5K3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q16695 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | Histone H3.1t |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | histone cluster 3, H3 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | HIST3H3 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | H3t; H3.4; H3/g; H3FT |
| NCBI Protein Information: | histone H3.1t; H3/t; histone 3, H3; H3 histone family, member T |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Histone H3.1t |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | H3/g |
| UniProt Gene Name: | HIST3H3 |
| UniProt Entry Name: | H31T_HUMAN |
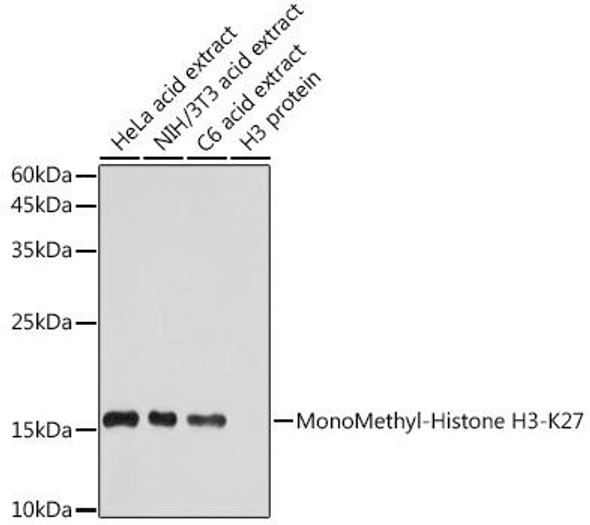
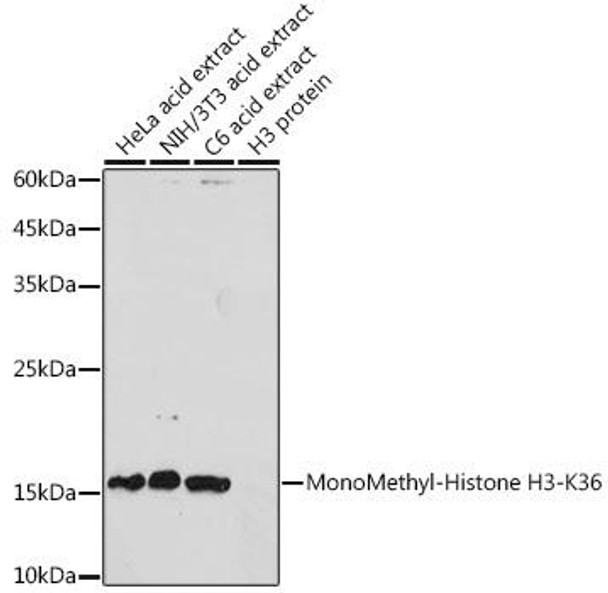
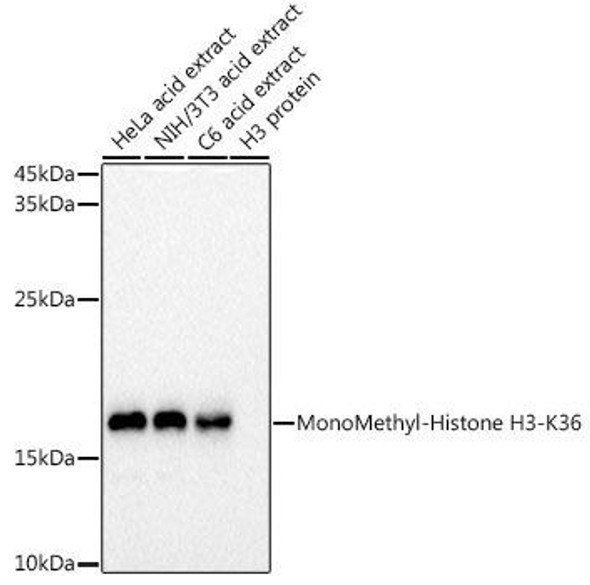
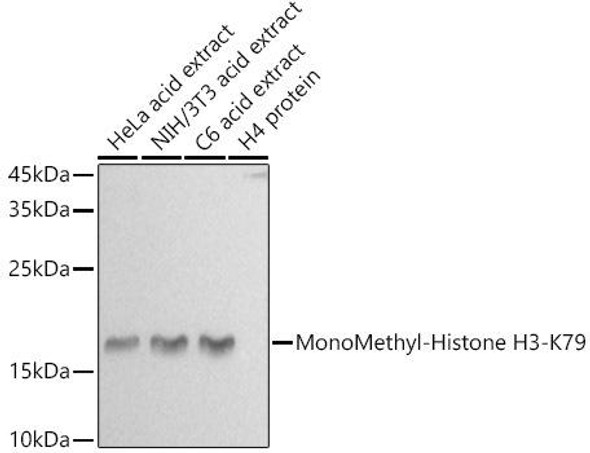
 | Western blot analysis of extracts of various cell lines, using MonoMethyl-Histone H3-K36 antibody at 1:1000 dilution. Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) at 1:10000 dilution. Lysates/proteins: 25ug per lane. Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST. Detection: ECL Basic Kit. Exposure time: 180s. |
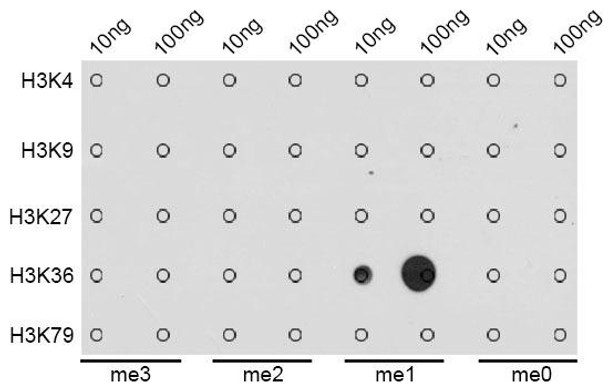
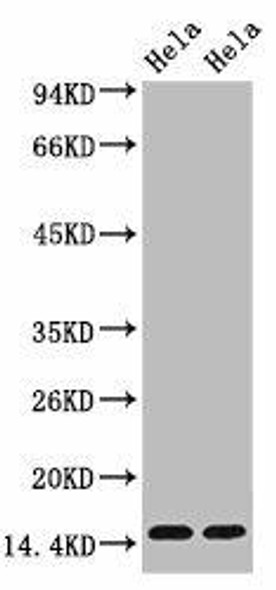
 | Dot-blot analysis of all sorts of methylation peptides using MonoMethyl-Histone H3-K36 antibody (A2364). |
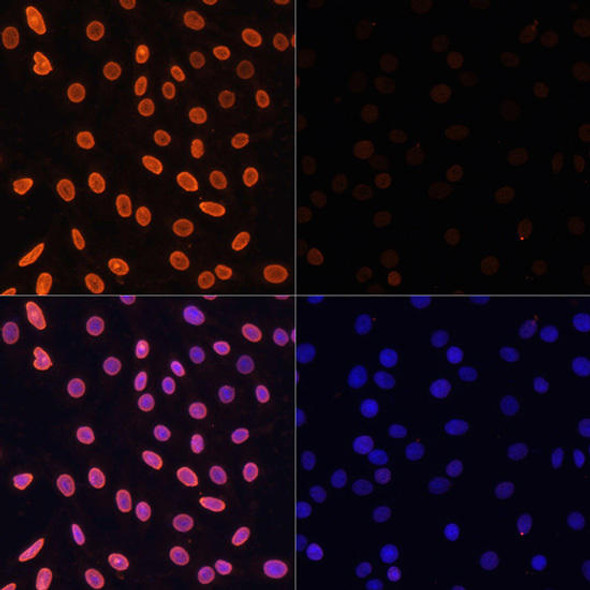
 | Immunofluorescence analysis of 293T cells using MonoMethyl-Histone H3-K36 antibody (A2364). Blue: DAPI for nuclear staining. |
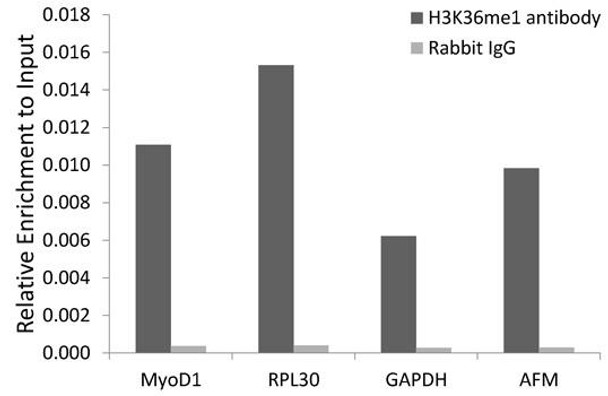
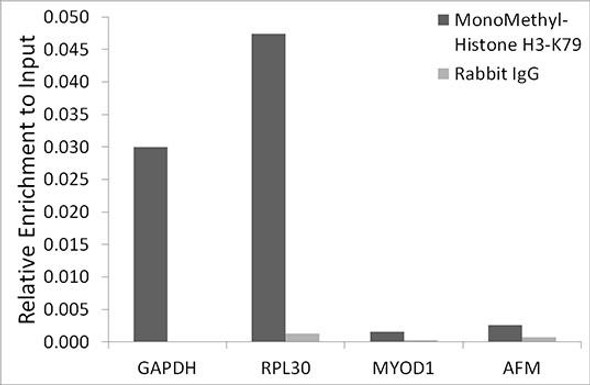
 | Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of extracts of HeLa cells, using MonoMethyl-Histone H3-K36 antibody and rabbit IgG. The amount of immunoprecipitated DNA was checked by quantitative PCR. Histogram was constructed by the ratios of the immunoprecipitated DNA to the input. |