Description
Anti-IDH1 Antibody (CAB18023)[KO Validated]
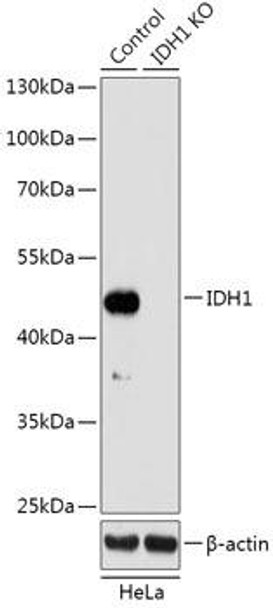
The KO Validated IDH1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (CAB18023) is a valuable tool for researchers studying the IDH1 protein, which plays a key role in cellular metabolism and is frequently mutated in various types of cancer. This antibody, specifically raised in rabbits, demonstrates high reactivity with human samples and has been validated for use in Western blot applications.IDH1, an enzyme involved in the citric acid cycle, is known to be mutated in a variety of cancers, leading to altered metabolic pathways and potential oncogenic properties. The KO Validated IDH1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody targets the IDH1 protein, allowing for the detection and analysis of this important molecule in different cell types.
By using this antibody, researchers can further investigate the role of IDH1 in cancer development and progression, potentially leading to insights into novel therapeutic approaches targeting this pathway. The antibody's specificity and reliability make it an essential tool for studies in cancer biology and metabolism research, providing valuable data for understanding the mechanisms underlying oncogenesis and potential therapeutic interventions.
| Antibody Name: | Anti-IDH1 Antibody [KO Validated] |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB18023 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
| Application: | WB IP |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-414 of human IDH1 (NP_005887.2). |
| Application: | WB IP |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IP 1:50 - 1:100 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | HeLa |
| Immunogen: | Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 1-414 of human IDH1 (NP_005887.2). |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | MSKK ISGG SVVE MQGD EMTR IIWE LIKE KLIF PYVE LDLH SYDL GIEN RDAT NDQV TKDA AEAI KKHN VGVK CATI TPDE KRVE EFKL KQMW KSPN GTIR NILG GTVF REAI ICKN IPRL VSGW VKPI IIGR HAYG DQYR ATDF VVPG PGKV EITY TPSD GTQK VTYL VHNF EEGG GVAM GMYN QDKS IEDF AHSS FQMA LSKG WPLY LSTK NTIL KKYD GRFK DIFQ EIYD KQYK SQFE AQKI WYEH RLID DMVA QAMK SEGG FIWA CKNY DGDV QSDS VAQG YGSL GMMT SVLV CPDG KTVE AEAA HGTV TRHY RMYQ KGQE TSTN PIAS IFAW TRGL AHRA KLDN NKEL AFFA NALE EVSI ETIE AGFM TKDL AACI KGLP NVQR SDYL NTFE FMDK LGEN LKIK LAQA KL |
| Gene ID: | 3417 |
| Uniprot: | O75874 |
| Cellular Location: | Cytoplasm, Peroxisome |
| Calculated MW: | 46kDa |
| Observed MW: | 45kDa |
| Synonyms: | IDH1, HEL-216, HEL-S-26, IDCD, IDH, IDP, IDPC, PICD |
| Background: | Isocitrate dehydrogenases catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to 2-oxoglutarate. These enzymes belong to two distinct subclasses, one of which utilizes NAD(+) as the electron acceptor and the other NADP(+). Five isocitrate dehydrogenases have been reported: three NAD(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, which localize to the mitochondrial matrix, and two NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, one of which is mitochondrial and the other predominantly cytosolic. Each NADP(+)-dependent isozyme is a homodimer. The protein encoded by this gene is the NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase found in the cytoplasm and peroxisomes. It contains the PTS-1 peroxisomal targeting signal sequence. The presence of this enzyme in peroxisomes suggests roles in the regeneration of NADPH for intraperoxisomal reductions, such as the conversion of 2, 4-dienoyl-CoAs to 3-enoyl-CoAs, as well as in peroxisomal reactions that consume 2-oxoglutarate, namely the alpha-hydroxylation of phytanic acid. The cytoplasmic enzyme serves a significant role in cytoplasmic NADPH production. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | IDH1: an oxidoreductase that catalyzes the third step of the TCA cycle: the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate, consuming NADP(+), and producing alpha-ketoglutarate (alpha-KG) and CO2. Alpha-KG is an activator the dioxygenases that hydroxylate the transcription factor HIF and lead to its degradation by VHL. Since HIF turns on oncogenic pathways, IDH1 has apparent tumor suppressor activity. Homo-dimerization is required for activity. Each subunit binds 1 magnesium or manganese ion. IDH1 is located in the cytosol and peroxisomes. Somatic mutations affecting arginine 132 (R132) are found in 80% of grade II?III gliomas and secondary glioblastomas in humans, and cause disease in a tissue-specific fashion. Only a single copy of the gene has been found to be mutated in tumours. Mutations of R132 to H, C, S, G, V, or L have been reported to be neomorphic, abolishing the conversion of isocitrate to alpha-KG. Instead, alpha-KG is converted to R(-)-2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG). Elevated levels of 2HG correlate with an elevated risk of malignant brain tumors. Neomorphic mutations in IDH1 and IDH2 convert alpha-KG to 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) occur in a high percentage of patients with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia (AML). |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Carbohydrate Metabolism - citrate (TCA) cycle; EC 1.1.1.42; Other Amino Acids Metabolism - glutathione; Oxidoreductase Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2q34 Cellular Component: cell-cell adherens junction; cytoplasm; cytosol; peroxisomal matrix; peroxisome Molecular Function:(R)-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase activity; isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity; magnesium ion binding; protein homodimerization activity; receptor binding Biological Process: 2-oxoglutarate metabolic process; isocitrate metabolic process; NADPH regeneration Disease: Glioma Susceptibility 1 |
| NCBI Summary: | Isocitrate dehydrogenases catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to 2-oxoglutarate. These enzymes belong to two distinct subclasses, one of which utilizes NAD(+) as the electron acceptor and the other NADP(+). Five isocitrate dehydrogenases have been reported: three NAD(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, which localize to the mitochondrial matrix, and two NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, one of which is mitochondrial and the other predominantly cytosolic. Each NADP(+)-dependent isozyme is a homodimer. The protein encoded by this gene is the NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase found in the cytoplasm and peroxisomes. It contains the PTS-1 peroxisomal targeting signal sequence. The presence of this enzyme in peroxisomes suggests roles in the regeneration of NADPH for intraperoxisomal reductions, such as the conversion of 2, 4-dienoyl-CoAs to 3-enoyl-CoAs, as well as in peroxisomal reactions that consume 2-oxoglutarate, namely the alpha-hydroxylation of phytanic acid. The cytoplasmic enzyme serves a significant role in cytoplasmic NADPH production. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013] |
| UniProt Code: | O75874 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 21903432 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3417 |
| NCBI Accession: | O75874.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O75874,Q567U4, Q6FHQ6, Q7Z3V0, Q93090, Q9NTJ9, Q9UKW8 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O75874 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46,659 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP(+)) 1, cytosolic |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | IDH1 |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | IDH; IDP; IDCD; IDPC; PICD; HEL-216; HEL-S-26 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cytosolic NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase; IDP; NADP(+)-specific ICDH; Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase |
| Protein Family: | Isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | IDH1 |

![Anti-IDH1 Antibody [KO Validated] (CAB18023)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-h68l9z2lnx/product_images/u/194/A18023_1__51621.jpg)