Description
IKK-alpha (Phospho-Thr23)Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit
The IKK alpha Phospho-Thr23 Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit is a cutting-edge tool for the precise measurement of IKK alpha phosphorylation at Thr23 in cell lysates. This kit offers exceptional sensitivity and specificity, guaranteeing accurate and consistent results, making it ideal for a variety of research applications.IKK alpha is a key regulator of the NF-kB signaling pathway, playing a vital role in inflammation, immune response, and cell survival. Phosphorylation of IKK alpha at Thr23 is crucial for its activation and downstream signaling, making it a crucial target for studying various cellular processes and potential therapeutic interventions.
With the IKK alpha Phospho-Thr23 Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit, researchers can uncover valuable insights into the intricate mechanisms of NF-kB signaling and its implications in various diseases, including cancer, inflammatory disorders, and autoimmune conditions. This kit is a valuable asset for scientists seeking to advance their understanding of cellular signaling pathways and develop innovative therapeutic strategies.
| Product Name: | IKK-alpha (Phospho-Thr23) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA |
| Product Code: | CBCAB01548 |
| ELISA Type: | Cell-Based |
| Target: | IKK-alpha (Phospho-Thr23) |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Dynamic Range: | > 5000 Cells |
| Detection Method: | Colorimetric 450 nm |
| Format: | 2 x 96-Well Microplates |
The IKK-alpha (Phospho-Thr23) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit is a convenient, lysate-free, high throughput and sensitive assay kit that can detect IKK-alpha protein phosphorylation and expression profile in cells. The kit can be used for measuring the relative amounts of phosphorylated IKK-alpha in cultured cells as well as screening for the effects that various treatments, inhibitors (ie. siRNA or chemicals), or activators have on IKK-alpha phosphorylation.
Qualitative determination of IKK-alpha (Phospho-Thr23) concentration is achieved by an indirect ELISA format. In essence, IKK-alpha (Phospho-Thr23) is captured by IKK-alpha (Phospho-Thr23)-specific primary (1ø) antibodies while the HRP-conjugated secondary (2ø) antibodies bind the Fc region of the 1ø antibody. Through this binding, the HRP enzyme conjugated to the 2ø antibody can catalyze a colorimetric reaction upon substrate addition. Due to the qualitative nature of the Cell-Based ELISA, multiple normalization methods are needed:
| 1. | A monoclonal antibody specific for human GAPDH is included to serve as an internal positive control in normalizing the target absorbance values. |
| 2. | Following the colorimetric measurement of HRP activity via substrate addition, the Crystal Violet whole-cell staining method may be used to determine cell density. After staining, the results can be analysed by normalizing the absorbance values to cell amounts, by which the plating difference can be adjusted. |
| Database Information: | Gene ID: 1147, UniProt ID: O15111, OMIM: 600664, Unigene: Hs.198998 |
| Gene Symbol: | CHUK |
| Sub Type: | Phospho |
| UniProt Protein Function: | IKKA: a kinase of the IKK family. Phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B, leading to their dissociation from NF-kappa-B and ultimately to their degradation. Phosphorylated and activated downstream of growth factor receptors, IL1R, and TNFR by NAK, IRAK and NIK, respectively. Preferentially found as a heterodimer with IKK-beta but also as an homodimer. Directly interacts with IKK-gamma/NEMO and TRPC4AP. Heterodimers form the active complex. The tripartite complex can also bind to MAP3K14/NIK, MEKK1, IKAP and IKB-alpha-p65-p50 complex. Inhibitors are under development to treat arthritis, inflammation, and apoptotic aspects of cancer. Aspirin (sodium salicylate) selectively binds IKK and reduces inflammation. Misexpression and inhibitors show involvement in insulin sensitization in obese rodents. Mutations in IKK-gamma are found in several immune deficiencies: hyper IgM syndrome, incontinentia pigmenti [embryonic lethal in males, defects in skin, hair, teeth in females] and hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia; recurrent infections and defects in teeth, hair, and sweat glands]. Inhibitors: CHS 828, NBD peptide, BMS-345541. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Protein kinase, Other; Kinase, protein; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); EC 2.7.11.10; Other group; IKK family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 10q24-q25 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; internal side of plasma membrane; intracellular membrane-bound organelle; cytoplasm; IkappaB kinase complex; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; protein homodimerization activity; IkappaB kinase activity; protein heterodimerization activity; ATP binding; protein kinase activity Biological Process: lactation; skeletal muscle contraction; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; response to toxin; response to lipopolysaccharide; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway; osteoclast differentiation; T cell receptor signaling pathway; protein amino acid phosphorylation; Rho protein signal transduction; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; toll-like receptor 10 signaling pathway; toll-like receptor 5 signaling pathway; positive regulation of interferon type I production; morphogenesis of an epithelial sheet; inflammatory response; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; response to drug; anatomical structure morphogenesis; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; response to virus; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation; response to amino acid stimulus; odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; response to hydroperoxide; toll-like receptor signaling pathway; striated muscle cell differentiation; innate immune response; immune response; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway; I-kappaB phosphorylation Disease: Cocoon Syndrome |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase family. The encoded protein, a component of a cytokine-activated protein complex that is an inhibitor of the essential transcription factor NF-kappa-B complex, phosphorylates sites that trigger the degradation of the inhibitor via the ubiquination pathway, thereby activating the transcription factor. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | O15111 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 317373368 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1147 |
| NCBI Accession: | O15111.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | O15111,O14666, Q13132, Q5W0I4, Q92467, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | O15111 |
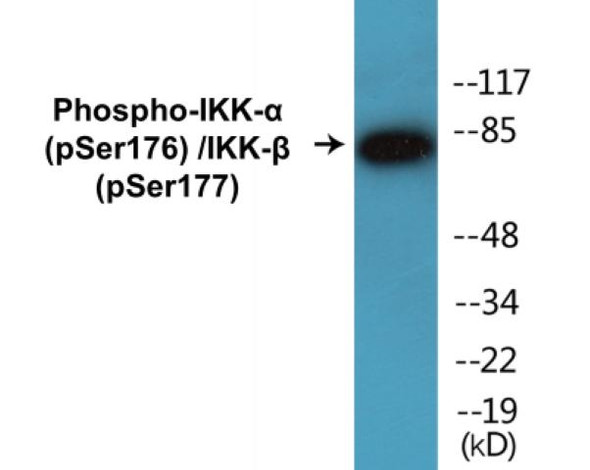
| Molecular Weight: | Calculated MW: 84kDaObserved MW: 85kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CHUK |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | IKK1; IKKA; IKBKA; TCF16; NFKBIKA; IKK-alpha |
| NCBI Protein Information: | inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha; TCF-16; IKK-a kinase; I-kappa-B kinase 1; I-kappa-B kinase-alpha; transcription factor 16; IkB kinase alpha subunit; Nuclear factor NFkappaB inhibitor kinase alpha |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase; I-kappa-B kinase 1; IKK1; Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B inhibitor kinase alpha; NFKBIKA; Transcription factor 16; TCF-16 |
| Protein Family: | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CHUK |
| UniProt Entry Name: | IKKA_HUMAN |
| Component | Quantity |
| 96-Well Cell Culture Clear-Bottom Microplate | 2 plates |
| 10X TBS | 24 mL |
| Quenching Buffer | 24 mL |
| Blocking Buffer | 50 mL |
| 15X Wash Buffer | 50 mL |
| Primary Antibody Diluent | 12 mL |
| 100x Anti-Phospho Target Antibody | 60 µL |
| 100x Anti-Target Antibody | 60 µL |
| Anti-GAPDH Antibody | 60 µL |
| HRP-Conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Antibody | 12 mL |
| HRP-Conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Antibody | 12 mL |
| SDS Solution | 12 mL |
| Stop Solution | 24 mL |
| Ready-to-Use Substrate | 12 mL |
| Crystal Violet Solution | 12 mL |
| Adhesive Plate Seals | 2 seals |
The following materials and/or equipment are NOT provided in this kit but are necessary to successfully conduct the experiment:
- Microplate reader able to measure absorbance at 450 nm and/or 595 nm for Crystal Violet Cell Staining (Optional)
- Micropipettes with capability of measuring volumes ranging from 1 µL to 1 ml
- 37% formaldehyde (Sigma Cat# F-8775) or formaldehyde from other sources
- Squirt bottle, manifold dispenser, multichannel pipette reservoir or automated microplate washer
- Graph paper or computer software capable of generating or displaying logarithmic functions
- Absorbent papers or vacuum aspirator
- Test tubes or microfuge tubes capable of storing ≥1 ml
- Poly-L-Lysine (Sigma Cat# P4832 for suspension cells)
- Orbital shaker (optional)
- Deionized or sterile water
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
| Step | Procedure |
| 1. | Seed 200 µL of 20,000 adherent cells in culture medium in each well of a 96-well plate. The plates included in the kit are sterile and treated for cell culture. For suspension cells and loosely attached cells, coat the plates with 100 µL of 10 µg/ml Poly-L-Lysine (not included) to each well of a 96-well plate for 30 minutes at 37 °C prior to adding cells. |
| 2. | Incubate the cells for overnight at 37 °C, 5% CO2. |
| 3. | Treat the cells as desired. |
| 4. | Remove the cell culture medium and rinse with 200 µL of 1x TBS, twice. |
| 5. | Fix the cells by incubating with 100 µL of Fixing Solution for 20 minutes at room temperature. The 4% formaldehyde is used for adherent cells and 8% formaldehyde is used for suspension cells and loosely attached cells. |
| 6. | Remove the Fixing Solution and wash the plate 3 times with 200 µL 1x Wash Buffer for five minutes each time with gentle shaking on the orbital shaker. The plate can be stored at 4 °C for a week. |
| 7. | Add 100 µL of Quenching Buffer and incubate for 20 minutes at room temperature. |
| 8. | Wash the plate 3 times with 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 9. | Add 200 µL of Blocking Buffer and incubate for 1 hour at room temperature. |
| 10. | Wash 3 times with 200 µL of 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 11. | Add 50 µL of 1x primary antibodies Anti-IKK-alpha (Phospho-Thr23) Antibody, Anti-IKK-alpha Antibody and/or Anti-GAPDH Antibody) to the corresponding wells, cover with Parafilm and incubate for 16 hours (overnight) at 4 °C. If the target expression is known to be high, incubate for 2 hours at room temperature. |
| 12. | Wash 3 times with 200 µL of 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 13. | Add 50 µL of 1x secondary antibodies (HRP-Conjugated AntiRabbit IgG Antibody or HRP-Conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Antibody) to corresponding wells and incubate for 1.5 hours at room temperature. |
| 14. | Wash 3 times with 200 µL of 1x Wash Buffer for 5 minutes each time. |
| 15. | Add 50 µL of Ready-to-Use Substrate to each well and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature in the dark. |
| 16. | Add 50 µL of Stop Solution to each well and read OD at 450 nm immediately using the microplate reader. |
(Additional Crystal Violet staining may be performed if desired – details of this may be found in the kit technical manual.)