Description
| Product Name: | Human VEGF C Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB1082 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | VEGF C |
| Synonyms: | VEGF-C, Vascular endothelial growth factor C, VRP, Flt4 ligand, Flt4-L, Vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein, VEGFC. |
| Source: | Sf9 Insect cells |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | Each mg of VEGF-C Human contains 50mg BSA and 1xPBS as buffer. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized VEGF-C in sterile 18M?-cm H2O not less than 100�g/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Stability: | Lyophilized VEGF-C although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution VEGF-C should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
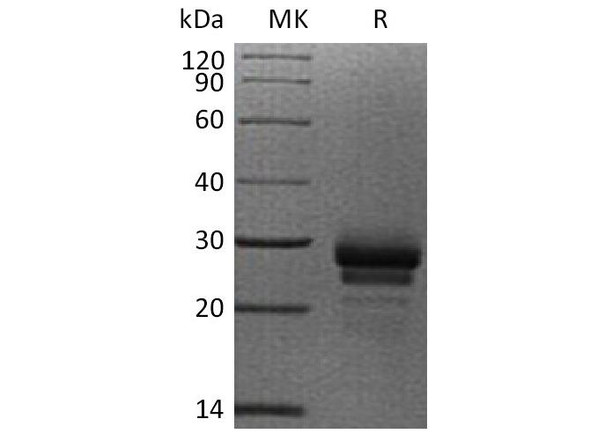
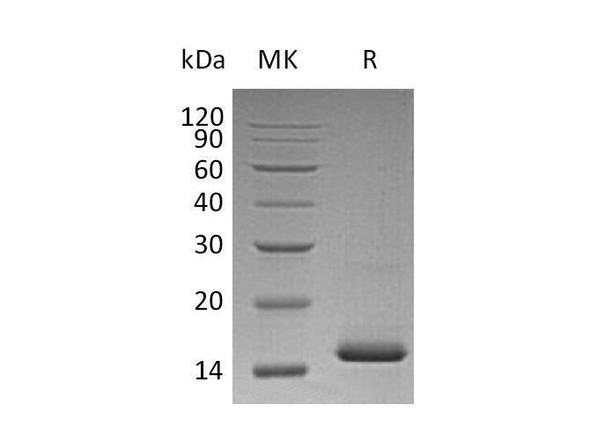
| Purity: | Greater than 90.0% as determined by�SDS-PAGE. |
| Biological Activity: | Measured by its ability to induce to the VEGFR-3/FLT-4 receptor phosphorylation inPAEC/VEGFR3 cells and VEGFC induced proliferation of primary HDLEC cells. |
VEGF-C, also known as Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Related Protein (VRP), is a recently discovered VEGF growth factor family member that is most closely related to VEGF-D. Human VEGF-C cDNA encodes a pre-pro-protein of 416 amino acids residues. It is almost identical to the mouse VEGF-C protein. Similar to VEGF-D, VEGF-C has a VEGF homology domain spanning the middle third of the precursor molecule and long N- and C-terminal extensions. In adults, VEGF-C is highly expressed in heart, placenta, ovary and small intestine. Recombinant human VEGF-C, lacking the N- and C-terminal extensions and containing only the middle VEGF homology domain, forms primarily non-covalently linked dimers. This protein is a ligand for both VEGFR-2/KDR and VEGFR-3/FLT-4. Since VEGFR-3 is strongly expressed in lymphatic endothelial cells, it has been postulated that VEGF-C is involved in the regulation of the growth and/or differentiation of lymphatic endothelium. Although recombinant human VEGF-C is also a mitogen for vascular endothelial cells, it is much less potent than VEGF-A.
VEGF-C Human Recombinant- contains 121 amino acids residues including 6 amino acid His-tag fused at the C-terminal end. As a result of glycosylation VEGF-C migrates as an 18-24 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions.
| UniProt Protein Function: | VEGFC: Growth factor active in angiogenesis, and endothelial cell growth, stimulating their proliferation and migration and also has effects on the permeability of blood vessels. May function in angiogenesis of the venous and lymphatic vascular systems during embryogenesis, and also in the maintenance of differentiated lymphatic endothelium in adults. Binds and activates VEGFR-2 (KDR/FLK1) and VEGFR-3 (FLT4) receptors. Homodimer; non-covalent and antiparallel. Spleen, lymph node, thymus, appendix, bone marrow, heart, placenta, ovary, skeletal muscle, prostate, testis, colon and small intestine and fetal liver, lung and kidney, but not in peripheral blood lymphocyte. Belongs to the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell cycle regulation; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Secreted, signal peptide; Secreted; Cytokine Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 4q34.3 Cellular Component: extracellular space; membrane; extracellular region Molecular Function:protein binding; growth factor activity; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 binding; chemoattractant activity Biological Process: signal transduction; induction of positive chemotaxis; negative regulation of cell proliferation; morphogenesis of embryonic epithelium; platelet degranulation; positive chemotaxis; regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of cell proliferation; negative regulation of blood pressure; angiogenesis; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion; response to drug; substrate-bound cell migration; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation; platelet activation; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration; positive regulation of protein amino acid autophosphorylation; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; organ morphogenesis; positive regulation of angiogenesis; positive regulation of protein secretion; positive regulation of cell division; blood coagulation; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation Disease: Lymphedema, Hereditary, Id |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family. The encoded protein promotes angiogenesis and endothelial cell growth, and can also affect the permeability of blood vessels. The proprotein is further cleaved into a fully processed form that can bind and activate VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 receptors. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014] |
| UniProt Code: | P49767 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1718154 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7424 |
| NCBI Accession: | P49767.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P49767,B2R9Q8, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P49767 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46,883 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Vascular endothelial growth factor C |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | vascular endothelial growth factor C |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | VEGFC�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | VRP; Flt4-L; LMPH1D�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | vascular endothelial growth factor C; FLT4 ligand DHM; vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Vascular endothelial growth factor C |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Flt4 ligand; Flt4-L; Vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein; VRP |
| Protein Family: | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | VEGFC�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | VEGFC_HUMAN |