Description
| Product Name: | Human TGFB1 (113 a.a.) Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0971 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | TGFB1 (113 a.a.) |
| Synonyms: | Transforming growth factor beta-1, TGF-beta-1, CED, DPD1, TGFB, TGF-b 1. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | The TGF-b 1 solution contains 10mM Sodium Citrate (pH3.5) and 10% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
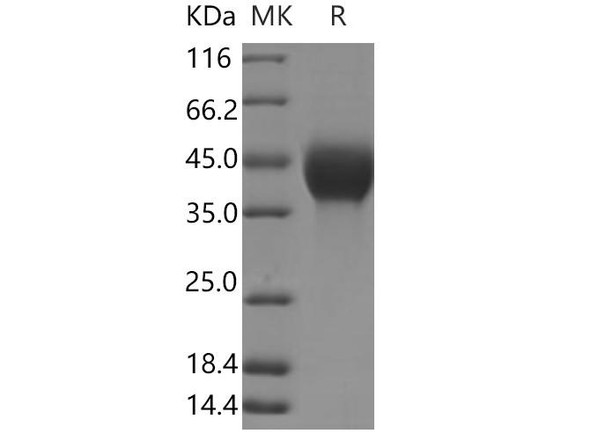
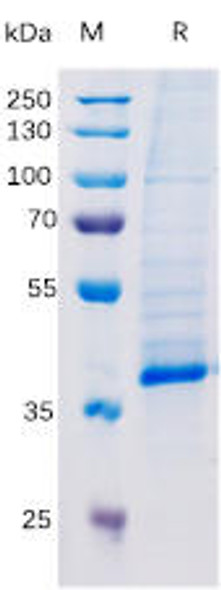
| Purity: | Greater than 95.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MALDTNYCFS STEKNCCVRQ LYIDFRKDLG WKWIHEPKGY HANFCLGPCP YIWSLDTQYS KVLALYNQHN PGASAAPCCV PQALEPLPIVYYVGRKPKVE QLSNMIVRSC KCS |
Transforming growth factor betas (TGFBetas) mediate many cell-cell interactions that occur during embryonic development. Three TGFBetas have been identified in mammals. TGFBeta1, TGFBeta2 and TGFBeta3 are each synthesized as precursor proteins that are very similar in that each is cleaved to yield a 112 amino acid polypeptide that remains associated with the latent portion of the molecule.
TGF-b 1 Human Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing 113 amino acids (279-390 a.a.) and having a total molecular mass of 12.9 kDa. TGF-b 1 (113 a.a.) is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | TGFB1: Multifunctional protein that controls proliferation, differentiation and other functions in many cell types. Many cells synthesize TGFB1 and have specific receptors for it. It positively and negatively regulates many other growth factors. It plays an important role in bone remodeling as it is a potent stimulator of osteoblastic bone formation, causing chemotaxis, proliferation and differentiation in committed osteoblasts. Homodimer; disulfide-linked, or heterodimer with TGFB2. Secreted and stored as a biologically inactive form in the extracellular matrix in a 290 kDa complex (large latent TGF-beta1 complex) containing the TGFB1 homodimer, the latency-associated peptide (LAP), and the latent TGFB1 binding protein-1 (LTBP1). The complex without LTBP1 is known as the'small latent TGF-beta1 complex'. Dissociation of the TGFB1 from LAP is required for growth factor activation and biological activity. Release of the large latent TGF-beta1 complex from the extracellular matrix is carried out by the matrix metalloproteinase MMP3. May interact with THSD4; this interaction may lead to sequestration by FBN1 microfibril assembly and attenuation of TGFB signaling. Interacts with the serine proteases, HTRA1 and HTRA3: the interaction with either inhibits TGFB1-mediated signaling. The HTRA protease activity is required for this inhibition. Interacts with CD109, DPT and ASPN. Activated in vitro at pH below 3.5 and over 12.5. Highly expressed in bone. Abundantly expressed in articular cartilage and chondrocytes and is increased in osteoarthritis (OA). Co-localizes with ASPN in chondrocytes within OA lesions of articular cartilage. Belongs to the TGF-beta family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Secreted, signal peptide Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 19q13.1 Cellular Component: extracellular space; proteinaceous extracellular matrix; microvillus; cell surface; cell soma; axon; Golgi lumen; cytoplasm; plasma membrane; extracellular region; nucleus Molecular Function:protein binding; enzyme binding; protein homodimerization activity; growth factor activity; protein heterodimerization activity; punt binding; cytokine activity; protein N-terminus binding; glycoprotein binding; antigen binding Biological Process: extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; positive regulation of apoptosis; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; SMAD protein nuclear translocation; female pregnancy; positive regulation of protein amino acid dephosphorylation; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; regulation of protein import into nucleus; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity; connective tissue replacement during inflammatory response; regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of ossification; cell cycle arrest; positive regulation of isotype switching to IgA isotypes; inner ear development; regulatory T cell differentiation; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production; response to drug; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation; positive regulation of chemotaxis; active induction of host immune response by virus; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration; regulation of sodium ion transport; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation; lymph node development; positive regulation of protein secretion; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; response to progesterone stimulus; endoderm development; positive regulation of odontogenesis; myelination; negative regulation of phagocytosis; evasion of host defenses by virus; positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; phosphate metabolic process; negative regulation of cell proliferation; negative regulation of T cell proliferation; ureteric bud development; regulation of DNA binding; negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol; positive regulation of cell proliferation; salivary gland morphogenesis; protein kinase B signaling cascade; protein export from nucleus; inflammatory response; aging; positive regulation of exit from mitosis; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; mitotic cell cycle checkpoint; common-partner SMAD protein phosphorylation; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity; positive regulation of bone mineralization; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; SMAD protein complex assembly; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; positive regulation of protein complex assembly; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus; response to hypoxia; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; negative regulation of cell growth; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of skeletal muscle development; mononuclear cell proliferation; protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of cell migration; hyaluronan catabolic process; regulation of apoptosis; response to vitamin D; negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation; positive regulation of superoxide release; receptor catabolic process; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; germ cell migration; response to glucose stimulus; chondrocyte differentiation; T cell homeostasis; defense response to fungus, incompatible interaction; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle; cell growth; tolerance induction to self antigen; regulation of striated muscle development; platelet activation; organ regeneration; negative regulation of DNA replication; virus-host interaction; hemopoietic progenitor cell differentiation; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process; viral infectious cycle; response to estradiol stimulus; negative regulation of cell cycle; positive regulation of histone deacetylation; response to radiation; platelet degranulation; negative regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; response to wounding; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway; adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; intercellular junction assembly and maintenance; regulation of binding; MAPKKK cascade; cellular calcium ion homeostasis; gut development; protein import into nucleus, translocation; ATP biosynthetic process; positive regulation of histone acetylation; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation; blood coagulation; positive regulation of cell migration Disease: Camurati-engelmann Disease; Cystic Fibrosis |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the transforming growth factor beta (TGFB) family of cytokines, which are multifunctional peptides that regulate proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, migration, and other functions in many cell types. Many cells have TGFB receptors, and the protein positively and negatively regulates many other growth factors. The secreted protein is cleaved into a latency-associated peptide (LAP) and a mature TGFB1 peptide, and is found in either a latent form composed of a TGFB1 homodimer, a LAP homodimer, and a latent TGFB1-binding protein, or in an active form composed of a TGFB1 homodimer. The mature peptide may also form heterodimers with other TGFB family members. This gene is frequently upregulated in tumor cells, and mutations in this gene result in Camurati-Engelmann disease.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P01137 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 135674 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 7040 |
| NCBI Accession: | P01137.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P01137,Q9UCG4, A8K792, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P01137 |
| Molecular Weight: | 44,341 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Transforming growth factor beta-1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | transforming growth factor, beta 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | TGFB1�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CED; LAP; DPD1; TGFB; TGFbeta�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | transforming growth factor beta-1; TGF-beta-1; latency-associated peptide; prepro-transforming growth factor beta-1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Transforming growth factor beta-1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | |
| Protein Family: | Transforming growth factor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | TGFB1�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TGFB1_HUMAN |