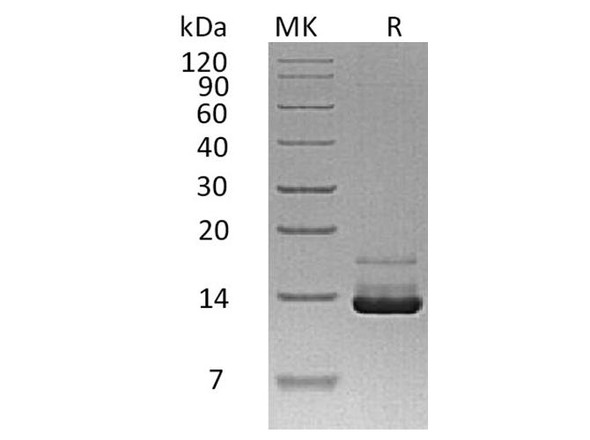
Description
| Product Name: | Human PTH (1-84) Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB1297 |
| Size: | 0.5mg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | PTH (1-84) |
| Synonyms: | Parathyrin, PTH, Parathormone. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | Lyophilized from a 0.2�m filtered concentrated solution in PBS pH7.4. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Parathormone in sterile 18M?-cm H2O not less than 100 �g/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Stability: | Lyophilized Parathyrin although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution PTH should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity: | Greater than 97.0% as determined by:(a) Analysis by RP-HPLC.(b) Analysis by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | SVSEIQLMHN LGKHLNSMER VEWLRKKLQD VHNFVALGAP LAPRDAGSQR PRKKEDNVLV ESHEKSLGEA DKADVNVLTK AKSQ |
| Biological Activity: | The activity is calculated by its ability to induce cAMP accumulation in murine MC3T3E1 cells and �is <50ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of greater than 2.0 x 104 Units/mg. |
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), or parathormone, is secreted by the parathyroid glands as a polypeptide containing 84 amino acids. It acts to increase the concentration of calciumin the blood, whereas calcitonin (a hormone produced by the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland) acts to decrease calcium concentration. PTH acts to increase the concentration of calcium in the blood by acting upon parathyroid hormone receptorin three parts of the body: In the bones- It enhances the release of calcium from the large reservoir contained in the bones. Bone resorption is the normal destruction of bone by osteoclasts, which are indirectly stimulated by PTH. Stimulation is indirect since osteoclasts do not have a receptor for PTH; rather, PTH binds to osteoblasts, the cells responsible for creating bone. Binding stimulates osteoblasts to increase their expression of RANKL, which can bind to osteoclast precursors containing RANK, a receptor for RANKL. The binding of RANKL to RANK stimulates these precursors to fuse, forming new osteoclasts which ultimately enhances the resorption of bone. In the kidney- It enhances active reabsorption of calcium from distal tubules and the thick ascending limb.In the intestine- It enhances the absorption of calcium in the intestine by increasing the production of vitamin D and upregulating the enzyme responsible for 1-alpha hydroxylationof 25-hydroxy vitamin D, converting vitamin D to its active form (1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D) which effects the actual absorption of calcium (as Ca2+ ions) by the intestine via calbindin.Recombinant Human full length PTH 1-84 has potential as an anti-osteoporotic agent, due to its properties as a bone formation stimulant, it increases bone turnover, stimulating osteoblasts and reducing both vertebral and non vertebral fractures.
Parathyroid Hormone 1-84 (full length) Human Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing 84 amino acids, having an MW of ~9.4kDa.The PTH is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | PTH: PTH elevates calcium level by dissolving the salts in bone and preventing their renal excretion. Stimulates [1-14C]-2- deoxy-D-glucose (2DG) transport and glycogen synthesis in osteoblastic cells. Defects in PTH are a cause of familial isolated hypoparathyroidism (FIH); also called autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism or autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. FIH is characterized by hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia due to inadequate secretion of parathyroid hormone. Symptoms are seizures, tetany and cramps. FIH exist both as autosomal dominant and recessive forms of hypoparathyroidism. Belongs to the parathyroid hormone family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted, signal peptide; Secreted; Hormone; Apoptosis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 11p15.3-p15.1 Cellular Component: extracellular space; extracellular region Molecular Function:RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, enhancer binding; type 1 parathyroid hormone receptor binding; parathyroid hormone receptor binding; peptide hormone receptor binding; hormone activity Biological Process: response to drug; transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of signal transduction; induction of apoptosis by hormones; positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; positive regulation of bone mineralization; G-protein signaling, adenylate cyclase activating pathway; Rho protein signal transduction; cellular calcium ion homeostasis; positive regulation of glucose import; G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; cAMP metabolic process; response to vitamin D; response to cadmium ion; response to ethanol; cell-cell signaling; regulation of gene expression; positive regulation of cAMP biosynthetic process; response to lead ion; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; skeletal development; bone resorption Disease: Hypoparathyroidism, Familial Isolated |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a hormone secreted by parathyroid cells. This hormone elevates blood Ca2+ level by dissolving the salts in bone and preventing their renal excretion. Defects in this gene are a cause of familial isolated hypoparathyroidism (FIH). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P01270 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 131547 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 5741 |
| NCBI Accession: | P01270.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P01270,Q4VB48, Q9UD38, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P01270 |
| Molecular Weight: | 12,861 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Parathyroid hormone |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | parathyroid hormone |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | PTH�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PTH1�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | parathyroid hormone; parathyrin; prepro-PTH; parathormone; parathyroid hormone 1; preproparathyroid hormone |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Parathyroid hormone |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Parathormone; Parathyrin |
| Protein Family: | Parathyroid hormone |
| UniProt Gene Name: | PTH�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | PTHY_HUMAN |