Description
| Product Name: | Human MCP 1 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB1187 |
| Size: | 50µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | MCP 1 |
| Synonyms: | Small inducible cytokine A2, CCL2, Monocyte chemotactic protein 1, MCP-1, Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, Monocyte chemotactic and activating factor, MCAF, Monocyte secretory protein JE, HC11, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2, MCP1, SCYA2, GDCF-2, SMC-CF, HSMCR30, MGC9434, GDCF-2 HC11. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered colorless clear solution. |
| Formulation: | The His Tag MCP-1 protein (1mg/ml) solution contains 20mM Tris-HCL pH-8.0, 1mM DTT and 20% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. Please avoid freeze thaw cycles. |
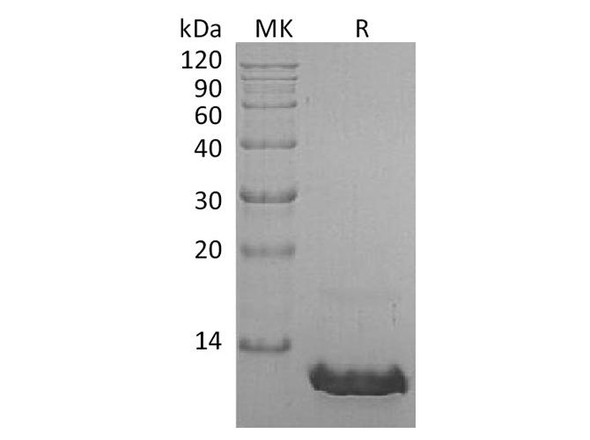
| Purity: | Greater than 95.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MQPDAINAPV TCCYNFTNRK ISVQRLASYR RITSSKCPKE AVIFKTIVAK EICADPKQKW VQDSMDHLDK QTQTPKT |
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family that is also known as monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1). It is found at the site of tooth eruption and bone degradation. In the bone, CCL2 is expressed by mature osteoclasts and osteoblasts and is under the control of nuclear factor kB (NFkB). CCL2 recruits immune cells, such as monocytes, to sites of tissue injury and infection. This chemokine is produced as a protein precursor containing signal peptide of 23 amino acids and a mature peptide of 76 amino acids. It is a monomeric polypeptide, with a molecular weight of approximately 13kDa. As with many other CC chemokines, CCL2 is located on chromosome 17 in humans. The cell surface receptors that bind CCL2 are CCR2 and CCR5.
MCP-1 Human Recombinant also known as Monocyte Chemotactic and Activating Factor (MCAF) produced in E.Coli is a non-glycosylated, Polypeptide chain containing 97 amino acids (24-99) and having a molecular mass of 10.9 kDa. The MCP-1 is fused to 20 amino acids His-Tag at N-terminus and purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | CCL2: Chemotactic factor that attracts monocytes and basophils but not neutrophils or eosinophils. Augments monocyte anti-tumor activity. Has been implicated in the pathogenesis of diseases characterized by monocytic infiltrates, like psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis or atherosclerosis. May be involved in the recruitment of monocytes into the arterial wall during the disease process of atherosclerosis. Monomer or homodimer; in equilibrium. Binds to CCR2 and CCR4. Is tethered on endothelial cells by glycosaminoglycan (GAG) side chains of proteoglycans. Belongs to the intercrine beta (chemokine CC) family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Chemokine; Secreted, signal peptide; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q11.2-q12 Cellular Component: extracellular space; rough endoplasmic reticulum; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; endocytic vesicle; dendrite; extracellular region; synapse; perikaryon; nerve terminal Molecular Function:heparin binding; chemokine activity; CCR2 chemokine receptor binding; receptor binding; protein kinase activity Biological Process: maternal process involved in pregnancy; protein amino acid phosphorylation; response to antibiotic; monocyte chemotaxis; regulation of cell shape; cell surface receptor linked signal transduction; response to vitamin B3; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of neuron apoptosis; cellular homeostasis; cell adhesion; neutrophil chemotaxis; organ regeneration; response to amino acid stimulus; JAK-STAT cascade; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production; G-protein signaling, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger; organ morphogenesis; unfolded protein response, activation of signaling protein activity; response to ethanol; cellular response to insulin stimulus; response to bacterium; response to heat; response to mechanical stimulus; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation; response to activity; response to progesterone stimulus; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process; signal transduction; chemotaxis; positive regulation of synaptic transmission; positive regulation of cellular extravasation; protein kinase B signaling cascade; response to wounding; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway; response to gamma radiation; angiogenesis; inflammatory response; lymphocyte chemotaxis; aging; unfolded protein response; cytokine and chemokine mediated signaling pathway; MAPKKK cascade; cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; viral genome replication; macrophage chemotaxis; humoral immune response; leukocyte migration during inflammatory response; cellular calcium ion homeostasis; G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway; negative regulation of angiogenesis; positive regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity; cellular protein metabolic process; maternal process involved in parturition; response to hypoxia; positive regulation of T cell activation; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; astrocyte cell migration Disease: Neural Tube Defects; Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, Susceptibility To; Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1, Susceptibility To |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is one of several cytokine genes clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Chemokines are a superfamily of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The superfamily is divided into four subfamilies based on the arrangement of N-terminal cysteine residues of the mature peptide. This chemokine is a member of the CC subfamily which is characterized by two adjacent cysteine residues. This cytokine displays chemotactic activity for monocytes and basophils but not for neutrophils or eosinophils. It has been implicated in the pathogenesis of diseases characterized by monocytic infiltrates, like psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. It binds to chemokine receptors CCR2 and CCR4. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013] |
| UniProt Code: | P13500 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 126842 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 6347 |
| NCBI Accession: | P13500.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P13500,Q9UDF3, B2R4V3, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P13500 |
| Molecular Weight: | 11,025 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | C-C motif chemokine 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CCL2�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HC11; MCAF; MCP1; MCP-1; SCYA2; GDCF-2; SMC-CF; HSMCR30�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | C-C motif chemokine 2; small-inducible cytokine A2; monocyte secretory protein JE; monocyte chemotactic protein 1; monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; monocyte chemotactic and activating factor; small inducible cytokine subfamily A (Cys-Cys), member 2; small inducible cytokine A2 (monocyte chemotactic protein 1, homologous to mouse Sig-je) |
| UniProt Protein Name: | C-C motif chemokine 2 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | HC11; Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; Monocyte chemotactic and activating factor; MCAF; Monocyte chemotactic protein 1; MCP-1; Monocyte secretory protein JE; Small-inducible cytokine A2 |
| Protein Family: | C-C motif chemokine |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CCL2�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CCL2_HUMAN |