Description
| Product Name: | Human MAPT Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB3928 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | MAPT |
| Synonyms: | TAU, DDPAC, FTDP-17, MAPTL, MSTD, MTBT1, MTBT2, PPND. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | The MAPT solution (0.5mg/ml) contains 20mM Tris-HCl pH-8, 1mM DTT, 0.2M NaCl & 10% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks.Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
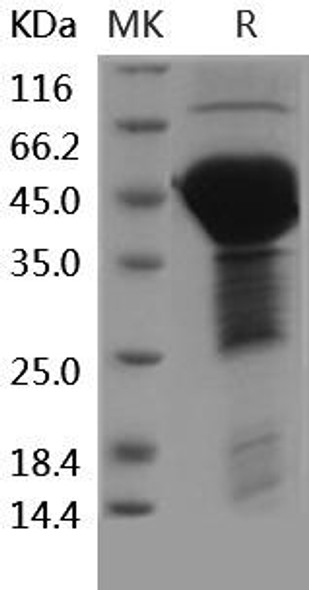
| Purity: | Greater than 85.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MAEPRQEFEV MEDHAGTYGL GDRKDQGGYT MHQDQEGDTD AGLKAEEAGI GDTPSLEDEA AGHVTQARMV SKSKDGTGSD DKKAKGADGK TKIATPRGAA PPGQKGQANA TRIPAKTPPA PKTPPSSGEP PKSGDRSGYS SPGSPGTPGS RSRTPSLPTP PTREPKKVAV VRTPPKSPSS AKSRLQTAPV PMPDLKNVKS KIGSTENLKH QPGGGKVQIV YKPVDLSKVT SKCGSLGNIH HKPGGGQVEV KSEKLDFKDR VQSKIGSLDN ITHVPGGGNK KIETHKLTFR ENAKAKTDHG AEIVYKSPVV SGDTSPRHLS NVSSTGSIDM VDSPQLATLA DEVSASLAKQ GL |
MAPT is a neuronal microtubule associated protein localized mostly on axons. MAPT promotes tubulin polymerisation and stabilizes microtubules, however it also serves to connect certain signalling pathways to the cytoskeleton. MAPT, in its hyperphosphorylated form, is the main part of paired helical filaments (PHF) and neurofibrillary lesions in Alzheimer''s disease (AD) brain.
MAPT Recombinant Human (Isoform-4) produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 372 amino acids (1-352 a.a.) and having a molecular mass of 38.9 kDa (Real molecular weight on SDS-PAGE will be shift up). The MAPT is fused to a 20 amino acid His-Tag at N-terminus and purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | Tau: a microtubule-associated protein that regulates microtubule assembly and stability. Apparently involved in the establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity. Mutations can result in several neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. The C-terminus binds axonal microtubules while the N-terminus binds neural plasma membrane components, suggesting that tau functions as a linker. Axonal polarity is predetermined by tau localization (in the neuronal cell) in the domain of the cell body defined by the centrosome. Nine differentially spliced isoforms have been described. The short isoforms allow plasticity of the cytoskeleton, whereas the longer isoforms may preferentially play a role in its stabilization. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cytoskeletal Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 17q21.1 Cellular Component: microtubule; microtubule associated complex; growth cone; axon; tubulin complex; plasma membrane; axoneme; cytosol Molecular Function:protein binding; enzyme binding; structural constituent of cytoskeleton; microtubule binding; apolipoprotein binding; protein kinase binding; SH3 domain binding Biological Process: axon extension; apoptosis; positive regulation of microtubule polymerization; positive regulation of axon extension; axon cargo transport; neuron migration; microtubule cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; adult walking behavior; regulation of microtubule polymerization; mitochondrion transport along microtubule; negative regulation of intracellular transport; generation of neurons; regulation of autophagy; cell structure disassembly during apoptosis Disease: Supranuclear Palsy, Progressive, 1; Pick Disease Of Brain; Frontotemporal Dementia; Parkinson-dementia Syndrome; Parkinson Disease, Late-onset; Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration With Tdp43 Inclusions, Grn-related |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes the microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) whose transcript undergoes complex, regulated alternative splicing, giving rise to several mRNA species. MAPT transcripts are differentially expressed in the nervous system, depending on stage of neuronal maturation and neuron type. MAPT gene mutations have been associated with several neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P10636 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 6754638 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 4137 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_005901 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P10636 |
| Molecular Weight: | 46kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | microtubule-associated protein tau isoform 2 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | microtubule associated protein tau |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | MAPT�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | TAU; MSTD; PPND; DDPAC; MAPTL; MTBT1; MTBT2; FTDP-17; PPP1R103�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | microtubule-associated protein tau |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Microtubule-associated protein tau |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Neurofibrillary tangle protein; Paired helical filament-tau |
| Protein Family: | Tautomerase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | MAPT�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | TAU_HUMAN |