Human ING1 Recombinant Protein (RPPB3750)
- SKU:
- RPPB3750
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
- Uniprot:
- Q9UK53
Description
| Product Name: | Human ING1 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB3750 |
| Size: | 20µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | ING1 |
| Synonyms: | Inhibitor Of Growth Family, Member 1, Growth Inhibitory Protein ING1, Tumor Suppressor ING1, Growth Inhibitor ING1, Inhibitor Of Growth Protein 1, Inhibitor Of Growth 1, P24ING1c,P33ING1b, P47ING1a, P33ING1, P33, P47, ING1 . |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered clear solution. |
| Formulation: | ING1 protein solution (1mg/ml) containing 20mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) and 10% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
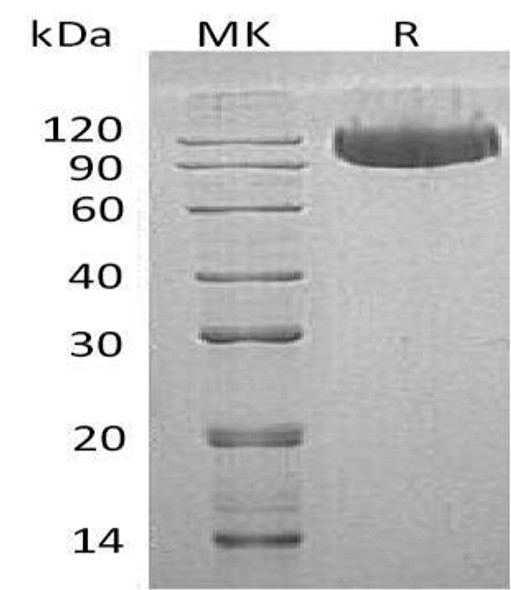
| Purity: | Greater than 90.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MGSMLSPANG EQLHLVNYVE DYLDSIESLP FDLQRNVSLM REIDAKYQEI LKELDECYER FSRETDGAQK RRMLHCVQRA LIRSQELGDE KIQIVSQMVE LVENRTRQVD SHVELFEAQQ ELGDTAGNSG KAGADRPKGE AAAQADKPNS KRSRRQRNNE NRENASSNHD HDDGASGTPK EKKAKTSKKK KRSKAKAERE ASPADLPIDP NEPTYCLCNQ VSYGEMIGCD NDECPIEWFH FSCVGLNHKP KGKWYCPKCR GENEKTMDKA LEKSKKERAY NR |
Inhibitor of Growth Family Member 1, also known as ING1 is a tumorsuppressor protein which is able to induce cell growth arrest and apoptosis. ING1is a nuclear protein which physically act together with the tumor suppressorprotein TP53 and is a component of the p53 signaling pathway. In addition, Reducedexpression and rearrangement of ING1 have been identified in various cancers.Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoformshave been described for ING1.
ING1 Human Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 302 amino acids (1-279 a.a) and having a molecular mass of 34.3kDa.ING1 is fused to a 23 amino acid His-tag at N-terminus & purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | ING1: Cooperates with p53/TP53 in the negative regulatory pathway of cell growth by modulating p53-dependent transcriptional activation. Implicated as a tumor suppressor gene. Defects in ING1 are a cause of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC); also known as squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Belongs to the ING family. 5 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Tumor suppressor Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 13q34 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; nucleoplasm Molecular Function:methylated histone residue binding; protein binding Disease: Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Head And Neck |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a tumor suppressor protein that can induce cell growth arrest and apoptosis. The encoded protein is a nuclear protein that physically interacts with the tumor suppressor protein TP53 and is a component of the p53 signaling pathway. Reduced expression and rearrangement of this gene have been detected in various cancers. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9UK53 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 212276438 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3621 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9UK53.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9UK53,O00532, O43658, Q53ZR3, Q5T9G8, Q5T9G9, Q5T9H0 Q5T9H1, Q9H007, Q9HD98, Q9HD99, Q9NS83, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9UK53 |
| Molecular Weight: | 29,572 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Inhibitor of growth protein 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | inhibitor of growth family member 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ING1�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | p33; p47; p33ING1; p24ING1c; p33ING1b; p47ING1a�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | inhibitor of growth protein 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Inhibitor of growth protein 1 |
| Protein Family: | Inhibitor of growth protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ING1�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | ING1_HUMAN |