Description
| Product Name: | Human IGF1 Des1-3 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0417 |
| Size: | 100µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | IGF1 Des1-3 |
| Synonyms: | Somatomedin C, IGF-I, IGFI, IGF1, IGF-IA, Mechano growth factor, MGF, Des(1-3), Des1-3, Des 1-3, Des (1-3), IGF-1 (4-70). |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | The protein (1mg/ml) was lyophilized was lyophilized from a 0.2�m filtered concentrated solution in 20mM PBS, pH 7.0. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to reconstitute the IGF-I des(1-3) in sterile 18M-cm H2O not less than 100�g/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Stability: | Lyophilized IGF-I des(1-3) although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution IGF1 des-1-3 should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
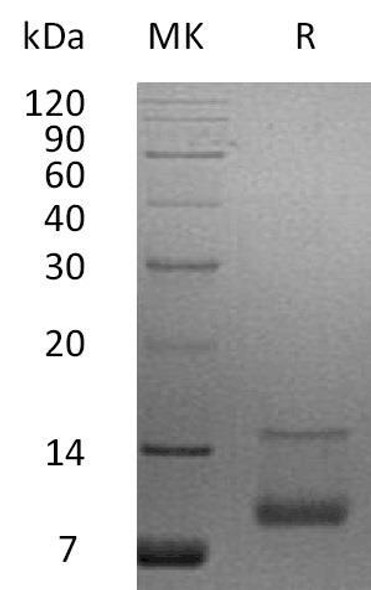
| Purity: | Greater than 97.0% as determined by:(a) Analysis by RP-HPLC.(b) Analysis by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | TLCGAELVDA LQFVCGDRGF YFNKPTGYGS SSRRAPQTGI VDECCFRSCD LRRLEMYCAP LKPAKSA |
| Biological Activity: | The ED50 as determined by a cell proliferation assay using FDC-P1 cells is less than 2.0 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of�> 5�105 units/mg. |
The somatomedins, or insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), comprise a family of peptides that play important roles in mammalian growth and development. IGF1 mediates many of the growth-promoting effects of growth hormone (GH; MIM 139250). Early studies showed that growth hormone did not directly stimulate the incorporation of sulfate into cartilage, but rather acted through a serum factor, termed 'sulfation factor,' which later became known as 'somatomedin' (Daughaday et al., 1972). Three main somatomedins have been characterized: somatomedin C (IGF1), somatomedin A (IGF2; MIM 147470), and somatomedin B (MIM 193190) (Rotwein, 1986; Rosenfeld, 2003).
IGF-I Des(1-3) Human Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing 67 amino acids (aa 4-70) and having a molecular mass of 7368.5 Dalton. IGF-1 Des1-3 is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | IGF1: The insulin-like growth factors, isolated from plasma, are structurally and functionally related to insulin but have a much higher growth-promoting activity. May be a physiological regulator of [1-14C]-2-deoxy-D-glucose (2DG) transport and glycogen synthesis in osteoblasts. Stimulates glucose transport in rat bone-derived osteoblastic (PyMS) cells and is effective at much lower concentrations than insulin, not only regarding glycogen and DNA synthesis but also with regard to enhancing glucose uptake. Defects in IGF1 are the cause of insulin-like growth factor I deficiency (IGF1 deficiency). IGF1 deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by growth retardation, sensorineural deafness and mental retardation. Belongs to the insulin family. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing.Protein type: Secreted; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Secreted, signal peptideChromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 12q23.2Cellular Component: insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex; extracellular space; plasma membrane; extracellular regionMolecular Function: integrin binding; insulin-like growth factor receptor binding; protein binding; growth factor activity; hormone activity; insulin receptor bindingBiological Process: muscle development; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process; exocrine pancreas development; glycolate metabolic process; water homeostasis; positive regulation of glucose import; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation; proteoglycan biosynthetic process; inner ear development; positive regulation of DNA binding; muscle hypertrophy; platelet activation; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus, translocation; positive regulation of mitosis; regulation of establishment and/or maintenance of cell polarity; positive regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase cascade; cell activation; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway; branching morphogenesis of a tube; regulation of gene expression; response to heat; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter; alveolus development; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation; negative regulation of apoptosis; positive regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway; myoblast proliferation; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation; positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process; positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration; signal transduction; negative regulation of cell proliferation; glial cell differentiation; platelet degranulation; mammary gland development; positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade; positive regulation of cell proliferation; DNA replication; skeletal development; positive regulation of granule cell precursor proliferation; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; multicellular organism growth; myotube cell development; regulation of multicellular organism growth; satellite cell compartment self-renewal involved in skeletal muscle regeneration; myoblast differentiation; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling cascade; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation; cell proliferation; cellular protein metabolic process; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat5 protein; Ras protein signal transduction; positive regulation of glycolysis; blood vessel remodeling; positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction; cell motility; blood coagulation; positive regulation of DNA replicationDisease: Insulin-like Growth Factor I Deficiency |
| UniProt Protein Details: | |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is similar to insulin in function and structure and is a member of a family of proteins involved in mediating growth and development. The encoded protein is processed from a precursor, bound by a specific receptor, and secreted. Defects in this gene are a cause of insulin-like growth factor I deficiency. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms that may undergo similar processing to generate mature protein. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P01343 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 11024682 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 3479 |
| NCBI Accession: | NP_000609.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P01343 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P01343,P05019 |
| Molecular Weight: | |
| NCBI Full Name: | insulin-like growth factor I isoform 4 preproprotein |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | insulin like growth factor 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | IGF1�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | IGF; MGF; IGFI; IGF-I�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | insulin-like growth factor I |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Insulin-like growth factor I |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Mechano growth factor; MGF; Somatomedin-C |
| Protein Family: | Adropin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | IGF1�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | IGF1_HUMAN |