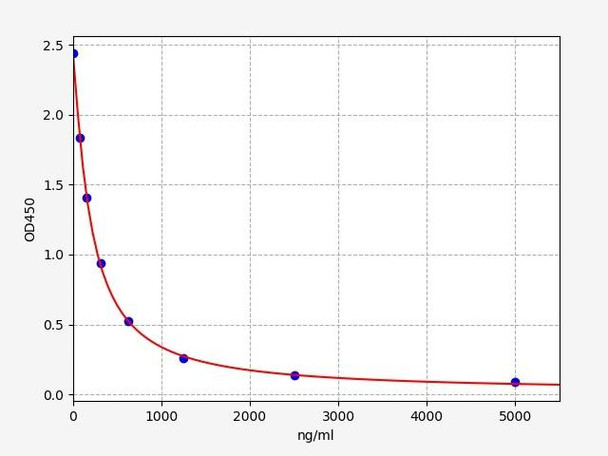
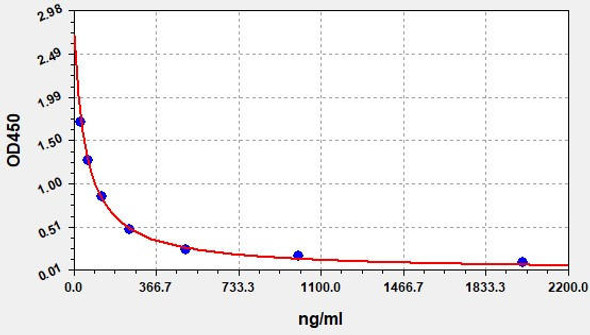
Description
Human HS (Heparan Sulfate) ELISA Kit
Heparan sulfate is a complex and essential molecule found on the surface of cells and in the extracellular matrix. Heparan sulfate serves as a dynamic modulator of cell signaling, cell adhesion, and cellular interactions, contributing to embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and wound healing. The Assay Genie Human Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit is a highly sensitive assay for the quantitative measurement of Heparan Sulfate in serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant and tissue samples.
Key Features
| Save Time | Pre-coated 96 well plate | |
| Quick Start | Kit includes all necessary reagents | |
| Publication Ready | Reproducible and reliable results |
Overview
| Product Name: | Human HS (Heparan Sulfate) ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | HUFI04766 |
| Size: | 96 Assays |
| Alias: | Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit |
| Detection Method: | Competitive ELISA, Coated with Antibody |
| Application: | This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Human HS (Heparan Sulfate) concentrations in serum plasma and other biological fluids. |
| Sensitivity: | < 46.9ng/ml |
| Range: | 78.125-5000ng/ml |
| Storage: | 4°C for 6 months |
| Note: | For Research Use Only |
Additional Information
| Recovery | Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Human HS (Heparan Sulfate) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Human HS (Heparan Sulfate) in samples.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Linearity | The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Human HS (Heparan Sulfate) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| CV(%) | Intra-Assay: CV<8% |
Kit Components
| Component | Quantity | Storage |
| ELISA Microplate (Dismountable) | 8x12 strips | 4°C for 6 months |
| Lyophilized Standard | 2 | 4°C/ -20°C |
| Sample/Standard Dlution Buffer | 20ml | 4°C |
| Biotin-labeled Antibody (Concentrated) | 120ul | 4°C (Protection from light) |
| Antibody Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate (SABC) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| SABC Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| TMB Substrate | 10ml | 4°C (Protection from light) |
| Stop Solution | 10ml | 4°C |
| Wash Buffer (25X) | 30ml | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 | - |
Other materials required:
- Microplate reader with 450 nm wavelength filter
- Multichannel Pipette, Pipette, microcentrifuge tubes and disposable pipette tips
- Incubator
- Deionized or distilled water
- Absorbent paper
- Buffer resevoir
Protocol
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
Equilibrate the TMB substrate for at least 30 min at 37°C beforeuse. When diluting samples and reagents, they must be mixed completely andevenly. It is recommended to plot a standard curve for each test.
| Step | Procedure |
| 1. | Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coatedplate respectively, and then, record their positions. It isrecommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Washplate 2 times before adding standard, sample and control (zero) wells! |
| 2. | Add Sample and Biotin-detection antibody: Add 50µL of Standard, Blank or Sample per well. The blankwell is added with Sample Dilution Buffer. Immediately add 50 µL of biotin-labelled antibody workingsolution to each well. Cover with the plate sealer provided. Gently tap the plate to ensure thoroughmixing. Incubate for 45 minutes at 37°C. (Solutions are added to the bottom of micro-ELISA platewell, avoid touching plate walls and foaming). |
| 3. | Wash: Aspirate each well and wash, repeating the process three timesWash by filling each well with Wash Buffer (approximately 350µL)using a squirt bottle, multi-channel pipette, manifold dispenser orautomated washer. Complete removal of liquid at each step is essentialto good performance. After the last wash, remove any remaining WashBuffer by aspirating or decanting. Invert the plate and pat it againstthick clean absorbent paper. |
| 4. | HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate(SABC): Add 100µL of SABC workingsolution to each well. Cover with a new Plate sealer. Incubate for30minutes at 37°C. |
| 5. | Wash: Repeat the aspiration/wash process for five times. |
| 6. | TMB Substrate: Add 90µL of TMB Substrate to each well. Coverwith a new Plate sealer. Incubate for about 10-20 minutes at 37°C.Protect from light. The reaction time can be shortened or extendedaccording to the actual color change, but not more than 30minutes.When apparent gradient appeared in standard wells, you can terminatethe reaction. |
| 7. | Stop: Add 50µL of Stop Solution to each well. Color turn toyellow immediately. The adding order of stop solution should be as thesame as the substrate solution. |
| 8. | OD Measurement: Determine the optical density (OD Value) of each wellat once, using a microplate reader set to 450 nm. You should open themicroplate reader ahead, preheat the instrument, and set the testing parameters. |
Sample Type
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clot overnight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Remove serum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |
Heparan Sulfate Background
Heparan Sulfate
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide present in all animal tissues. It exists as a proteoglycan known as Heparan Sulfate ProteoGlycan (HSPG), where two or three HS chains are closely bound to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. This molecular arrangement enables HS to interact with various protein ligands, such as Wnt, thereby regulating a diverse array of biological processes. HS's involvement spans critical activities like developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, inhibiting Granzyme B-induced detachment activity, and tumor metastasis. Furthermore, HS has demonstrated its role as a cellular receptor for multiple viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. Notably, research suggests that cellular heparan sulfate may play a part in SARS-CoV-2 infection, particularly when the virus engages with ACE2
Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) are a diverse group of molecules found in various cellular and extracellular matrix contexts. The primary HSPGs on the cell membrane consist of the transmembrane syndecans and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored glypicans, which play significant roles in cell signaling and adhesion. Additionally, there are minor forms of membrane HSPGs such as betaglycan and the V-3 isoform of CD44, which are specifically present on keratinocytes and activated monocytes. In the extracellular matrix, particularly in basement membranes and fractones, the main HSPG species include the multi-domain perlecan, agrin, and collagen XVIII core proteins. These HS-bearing molecules contribute to the structural integrity and functional regulation of various tissues and play essential roles in cellular interactions and tissue organization.
Heparan Sulfate Structure
Heparan sulfate, a member of the glycosaminoglycan family, closely resembles heparin in its structural composition. Both molecules consist of repeating disaccharide units with varying degrees of sulfation. The predominant disaccharide unit in heparan sulfate is composed of glucuronic acid (GlcA) linked to N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), comprising approximately 50% of the total disaccharide units. In contrast, heparin primarily consists of IdoA(2S)-GlcNS(6S) units, which account for around 85% in beef lung-derived heparins and approximately 75% in those from porcine intestinal mucosa. Challenges arise when categorizing hybrid glycosaminoglycans containing both heparin-like and heparan sulfate-like structures. It has been proposed that a glycosaminoglycan should be considered heparin only if its N-sulfate groups significantly outnumber N-acetyl groups, and the concentration of O-sulfate groups exceeds that of N-sulfate. Otherwise, it should be classified as heparan sulfate.
Heparan Sulfate ELISA FAQs
What is the Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit used for?
The Human HS ELISA Kit is a powerful research tool designed for the quantitative measurement of Human HS (Heparan Sulfate) levels in various biological samples. HS is a complex polysaccharide found on the cell surface and extracellular matrix, and it plays critical roles in various physiological and pathological processes. This ELISA kit allows researchers to investigate HS dynamics, its involvement in disease mechanisms, and its potential as a biomarker in diverse research areas such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and inflammation.
What are the advantages of using the Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit?
The Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit offers several advantages, including high sensitivity, accuracy, and reproducibility. It provides a user-friendly and reliable method to quantify Heparan sulfate levels in biological specimens, allowing for precise measurements and robust data analysis.
What sample types are compatible with the Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit?
The Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit is compatible with various sample types, including serum, plasma, cell lysates, and tissue homogenates. It provides flexibility in sample selection, allowing researchers to analyze Heparan sulfate levels in different biological matrices.
What are the storage requirements for the Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit?
The Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit components should be stored according to the instructions provided in the kit manual. Generally, it is recommended to store the kit components at the recommended temperature to ensure their stability and optimal performance.
What should I do if my assay results are not optimal?
If you encounter any issues or have suboptimal assay results, we recommend contacting our dedicated support team for assistance. They will be available to provide troubleshooting guidance, answer your questions, and ensure you achieve the best possible results with the Heparan Sulfate ELISA Kit.