Description
| Product Name: | Human GLB1 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB1691 |
| Size: | 5µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | GLB1 |
| Synonyms: | lacZ, beta-gal, b-gal, Acid beta-galactosidase, Lactase, Elastin receptor 1 |
| Source: | Sf9 Insect cells |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | GLB1 Human protein (0.25mg/ml) is formulated in 10% glycerol and Phosphate-Buffered Saline (pH 7.4). |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
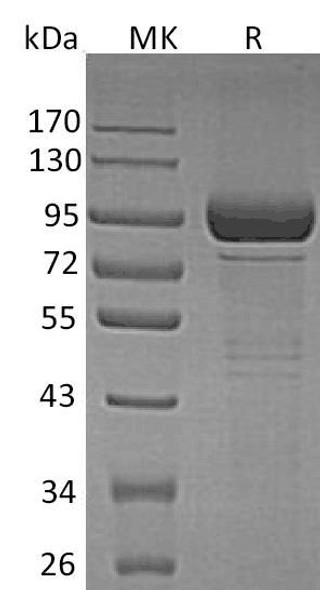
| Purity: | Greater than 90.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | LRNATQRMFE IDYSRDSFLK DGQPFRYISG SIHYSRVPRF YWKDRLLKMK MAGLNAIQTY VPWNFHEPWP GQYQFSEDHD VEYFLRLAHE LGLLVILRPG PYICAEWEMG GLPAWLLEKE SILLRSSDPD YLAAVDKWLG VLLPKMKPLL YQNGGPVITV QVENEYGSYF ACDFDYLRFL QKRFRHHLGD DVVLFTTDGA HKTFLKCGAL QGLYTTVDFG TGSNITDAFL SQRKCEPKGP LINSEFYTGW LDHWGQPHST IKTEAVASSL YDILARGASV NLYMFIGGTN FAYWNGANSP YAAQPTSYDY DAPLSEAGDL TEKYFALRNI IQKFEKVPEG PIPPSTPKFA YGKVTLEKLK TVGAALDILC PSGPIKSLYP LTFIQVKQHY GFVLYRTTLP QDCSNPAPLS SPLNGVHDRA YVAVDGIPQG VLERNNVITL NITGKAGATL DLLVENMGRV NYGAYINDFK GLVSNLTLSS NILTDWTIFP LDTEDAVRSH LGGWGHRDSG HHDEAWAHNS SNYTLPAFYM GNFSIPSGIP DLPQDTFIQF PGWTKGQVWI NGFNLGRYWP ARGPQLTLFV PQHILMTSAP NTITVLELEW APCSSDDPEL CAVTFVDRPV IGSSVTYDHP SKPVEKRLMP PPPQKNKDSW LDHVLEHHHH HH |
Beta-galactosidase or GLB1 is a B-galactosidase found in the lysosome. This enzyme hydrolyzes the finale B-galactose from the precursors ganglioside & keratin sulfate. GLB1 has a crucial part in the creation of elastogenesis (extracellular elastic fibers) and connective tissue development. This enzyme is similar to elastin-binding protein which is a key part in non-integrin cell surface receptor. In cells that extort elastin GLB1 is linked to tropoelastin intracellularly and act as recycling molecular chaperone.
GLB1 Human produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 662 amino acids (24-677 a.a.) and having a molecular mass of 74.6 kDa.GLB1 is fused to an 8 amino acid His tag at C-Terminus and purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | GLB1: Cleaves beta-linked terminal galactosyl residues from gangliosides, glycoproteins, and glycosaminoglycans. Defects in GLB1 are the cause of GM1-gangliosidosis type 1 (GM1G1); also known as infantile GM1- gangliosidosis. GM1-gangliosidosis is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease marked by the accumulation of GM1 gangliosides, glycoproteins and keratan sulfate primarily in neurons of the central nervous system. GM1G1 is characterized by onset within the first three months of life, central nervous system degeneration, coarse facial features, hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal dysmorphology reminiscent of Hurler syndrome, and rapidly progressive psychomotor deterioration. Urinary oligosaccharide levels are high. It leads to death usually between the first and second year of life. Defects in GLB1 are the cause of GM1-gangliosidosis type 2 (GM1G2); also known as late infantile/juvenile GM1- gangliosidosis. GM1G2 is characterized by onset between ages 1 and 5. The main symptom is locomotor ataxia, ultimately leading to a state of decerebration with epileptic seizures. Patients do not display the skeletal changes associated with the infantile form, but they nonetheless excrete elevated amounts of beta-linked galactose-terminal oligosaccharides. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. Defects in GLB1 are the cause of GM1-gangliosidosis type 3 (GM1G3); also known as adult or chronic GM1- gangliosidosis. GM1G3 is characterized by a variable phenotype. Patients show mild skeletal abnormalities, dysarthria, gait disturbance, dystonia and visual impairment. Visceromegaly is absent. Intellectual deficit can initially be mild or absent but progresses over time. Inheritance is autosomal recessive. Defects in GLB1 are the cause of mucopolysaccharidosis type 4B (MPS4B); also known as Morquio syndrome B. MPS4B is a form of mucopolysaccharidosis type 4, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease characterized by intracellular accumulation of keratan sulfate and chondroitin-6-sulfate. Key clinical features include short stature, skeletal dysplasia, dental anomalies, and corneal clouding. Intelligence is normal and there is no direct central nervous system involvement, although the skeletal changes may result in neurologic complications. There is variable severity, but patients with the severe phenotype usually do not survive past the second or third decade of life. Belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase 35 family. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Lipid Metabolism - sphingolipid; EC 3.2.1.23; Glycan Metabolism - glycosaminoglycan degradation; Hydrolase; Carbohydrate Metabolism - galactose; Glycan Metabolism - other glycan degradation; Glycan Metabolism - glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - ganglio series Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 3p21.33 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; Golgi apparatus; intracellular membrane-bound organelle; lysosomal lumen; vacuole Molecular Function:beta-galactosidase activity; exo-alpha-sialidase activity; protein binding Biological Process: cellular carbohydrate metabolic process; glycosaminoglycan catabolic process; glycosphingolipid metabolic process; keratan sulfate catabolic process Disease: Gm1-gangliosidosis, Type I; Gm1-gangliosidosis, Type Ii; Gm1-gangliosidosis, Type Iii; Mucopolysaccharidosis Type Ivb |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a member of the glycosyl hydrolase 35 family of proteins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate the mature lysosomal enzyme. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of a terminal beta-linked galactose residue from ganglioside substrates and other glycoconjugates. Mutations in this gene may result in GM1-gangliosidosis and Morquio B syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015] |
| UniProt Code: | P16278 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 215273939 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2720 |
| NCBI Accession: | P16278.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P16278,P16279, B2R7H8, B7Z6B0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P16278 |
| Molecular Weight: | 72,751 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Beta-galactosidase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | galactosidase beta 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GLB1�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | EBP; ELNR1; MPS4B�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | beta-galactosidase |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Beta-galactosidase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Acid beta-galactosidase; Lactase; Elastin receptor 1 |
| Protein Family: | Globulin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GLB1�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | BGAL_HUMAN |