Description
| Product Name: | Human GALE Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB1667 |
| Size: | 25µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | GALE |
| Synonyms: | UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, EC=5.1.3.2, Galactowaldenase, UDP-galactose 4 epimerase, GALE, SDR1E1, FLJ95174, FLJ97302. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | GALE Human solution containing 20mM Tris pH-8, 5mM DTT, 0.1M NaCl, 1mM EDTA & 10% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
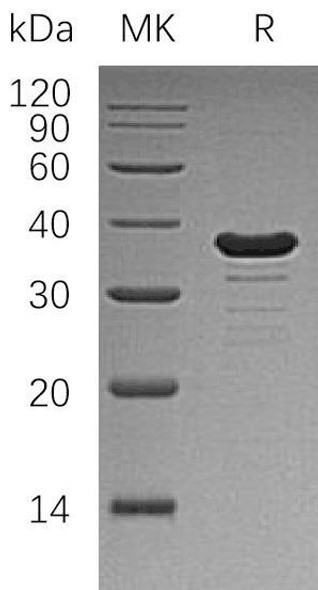
| Purity: | Greater than 95.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MAEKVLVTGG AGYIGSHTVL ELLEAGYLPV VIDNFHNAFR GGGSLPESLR RVQELTGRSV EFEEMDILDQ GALQRLFKKY SFMAVIHFAG LKAVGESVQK PLDYYRVNLT GTIQLLEIMK AHGVKNLVFS SSATVYGNPQ YLPLDEAHPT GGCTNPYGKS KFFIEEMIRD LCQADKTWNA VLLRYFNPTG AHASGCIGED PQGIPNNLMP YVSQVAIGRR EALNVFGNDY DTEDGTGVRD YIHVVDLAKG HIAALRKLKE QCGCRIYNLG TGTGYSVLQM VQAMEKASGK KIPYKVVARR EGDVAACYAN PSLAQEELGW TAALGLDRMC EDLWRWQKQN PSGFGTQA |
GALE is an enzyme that participates as the third enzyme in the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism. GALE is a homodimeric epimerase localized in bacterial, plant, and mammalian cells. GALE inhances the reverse chemical reaction, the conversion of UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose. UDP-galactose builds galactose-containing proteins and fats, which have a crucial part in chemical signaling, building cellular structures, transporting molecules, and producing energy.
GALE Recombinant Human produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 368 amino acids (1-348 a.a.) and having a molecular mass of 40.4 kDa. The GALE is fused to a 20 amino acids His-Tag at N-terminus and purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | GALE: Catalyzes two distinct but analogous reactions: the epimerization of UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose and the epimerization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-N- acetylgalactosamine. Defects in GALE are the cause of epimerase-deficiency galactosemia (EDG); also known as galactosemia type 3. Clinical features include early-onset cataracts, liver damage, deafness and mental retardation. There are two clinically distinct forms of EDG. (1) A benign, or 'peripheral' form with no detectable GALE activity in red blood cells and characterized by mild symptoms. Some patients may suffer no symptoms beyond raised levels of galactose-1-phosphate in the blood. (2) A much rarer 'generalized' form with undetectable levels of GALE activity in all tissues and resulting in severe features such as restricted growth and mental development. Belongs to the sugar epimerase family. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Carbohydrate Metabolism - amino sugar and nucleotide sugar; Isomerase; EC 5.1.3.2; Carbohydrate Metabolism - galactose; EC 5.1.3.7 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1p36-p35 Cellular Component: cytosol Molecular Function:UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase activity; protein homodimerization activity; UDP-glucose 4-epimerase activity; coenzyme binding Biological Process: galactose catabolic process; carbohydrate metabolic process; pathogenesis Disease: Galactose Epimerase Deficiency |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes UDP-galactose-4-epimerase which catalyzes two distinct but analogous reactions: the epimerization of UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose, and the epimerization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine. The bifunctional nature of the enzyme has the important metabolic consequence that mutant cells (or individuals) are dependent not only on exogenous galactose, but also on exogenous N-acetylgalactosamine as a necessary precursor for the synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids. Mutations in this gene result in epimerase-deficiency galactosemia, also referred to as galactosemia type 3, a disease characterized by liver damage, early-onset cataracts, deafness and mental retardation, with symptoms ranging from mild ('peripheral' form) to severe ('generalized' form). Multiple alternatively spliced transcripts encoding the same protein have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q14376 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 68056598 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2582 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q14376.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q14376,Q38G75, Q86W41, Q9BVE3, Q9UJB4, A0A024RAH5, B3KQ39 |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q14376 |
| Molecular Weight: | 348 |
| NCBI Full Name: | UDP-glucose 4-epimerase |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | UDP-galactose-4-epimerase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | GALE�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | SDR1E1�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | UDP-glucose 4-epimerase; galactowaldenase; UDP-GalNAc 4-epimerase; UDP-GlcNAc 4-epimerase; UDP-galactose 4-epimerase; UDP galactose-4'-epimerase; galactose-4-epimerase, UDP-; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase; UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine 4-epimerase; short chain dehydrogenase/reductase family 1E, member 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | UDP-glucose 4-epimerase |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | GalactowaldenaseUDP-N-acetylgalactosamine 4-epimerase; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase; UDP-galactose 4-epimerase |
| Protein Family: | Galectin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | GALE�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | GALE_HUMAN |