Description
| Product Name: | Human Fumarase Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB1652 |
| Size: | 50µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | Fumarase |
| Synonyms: | MCL, LRCC, HLRCC, MCUL1, FH, Fumarate hydratase, Fumarase. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | The Fumarase protein solution (1mg/ml) contains 20mM Tris-HCl, pH-8. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA). Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
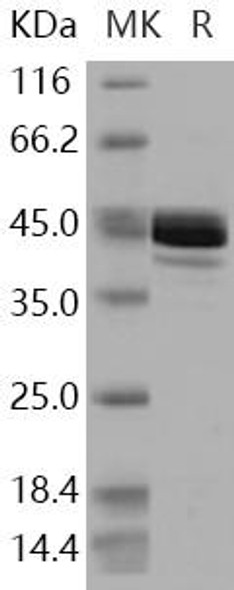
| Purity: | Greater than 95.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MASQNSFRIE YDTFGELKVP NDKYYGAQTV RSTMNFKIGG VTERMPTPVI KAFGILKRAA AEVNQDYGLD PKIANAIMKA ADEVAEGKLN DHFPLVVWQT GSGTQTNMNV NEVISNRAIE MLGGELGSKI PVHPNDHVNK SQSSNDTFPT AMHIAAAIEV HEVLLPGLQK LHDALDAKSK EFAQIIKIGR THTQDAVPLT LGQEFSGYVQ QVKYAMTRIK AAMPRIYELA AGGTAVGTGL NTRIGFAEKV AAKVAALTGL PFVTAPNKFE ALAAHDALVE LSGAMNTTAC SLMKIANDIR FLGSGPRSGL GELILPENEP GSSIMPGKVN PTQCEAMTMV AAQVMGNHVA VTVGGSNGHF ELNVFKPMMI KNVLHSARLL GDASVSFTEN CVVGIQANTE RINKLMNESL MLVTALNPHI GYDKAAKIAK TAHKNGSTLK ETAIELGYLT AEQFDEWVKP KDMLGPK |
| Biological Activity: | Specific activity is > 25 unit/mg, and is defined as the amount of enzyme that cleaves 1umole of L-Malate to Fumarate per minute at pH 7.5 at 37�C. |
Fumarase is an enzymatic factor of Krebs cycle, which catalyzes the formation of L-malate from fumarate. Fumarase exists in both a cytosolic form and an N-terminal extended form, differing only in the translation start site used. The N-terminal extended form is aimed to the mitochondrion, where the removal of the extension results in the same form as in the cytoplasm. Fumarase is similar to a number of thermostable Class-2 fumarases and functions as a homotetramer. Mutations in the Fumarase gene causes fumarase deficiency and leads to progressive encephalopathy, cerebral atrophy and developmental delay. Fumarase enzyme is also thought to act as a tumor suppressor. Leydig cell tumors are caused by Fumarase mutations and represents one of the first reports of germline mutations in any type of adult testicular tumor.
Fumarase Human Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 467 amino acids (44-510) and having a molecular mass of 50.2 kDa. Fumarate Hydratase is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | FH: a metabolic enzyme that participates in the tricarboxylic acid cycle that catalyzes the conversion of (S)-malate into fumarate + H2O. There are two substrate binding sites: the catalytic A site, and the non-catalytic B site that may play a role in the transfer of substrate or product between the active site and the solvent. Alternatively, the B site may bind allosteric effectors. Fumarate accumulates in the cell when FH is inactivated. Fumarate inhibits the dioxygenases that hydroxylate the transcription factor HIF and leads to its degradation by VHL. Since HIF turns on oncogenic pathways, FH has apparent tumor suppressor activity. Defects in FH are the cause of hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (HLRCC), a highly metastatic form of RCC. Defects in FH are the cause of fumarase deficiency (FD) also known as fumaricaciduria. FD is characterized by progressive encephalopathy, developmental delay, hypotonia, cerebral atrophy and lactic and pyruvic acidemia. Cells derived from a patient with HLRCC exhibit compromised oxidative phosphorylation, dependence on anaerobic glycolysis, rapid glycolytic flux, and overexpression of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) and GLUT1. Two human isoforms are produced by alternative initiation. The longer isoform is mitochondrial, while the shorter form, missing residues 1-43, is cytoplasmic. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Tumor suppressor; Mitochondrial; Carbohydrate Metabolism - citrate (TCA) cycle; Lyase; EC 4.2.1.2 Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1q42.1 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; cytosol; mitochondrial matrix; mitochondrion; tricarboxylic acid cycle enzyme complex Molecular Function:fumarate hydratase activity; protein binding Biological Process: cellular metabolic process; fumarate metabolic process; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue; malate metabolic process; protein tetramerization; tricarboxylic acid cycle Disease: Fumarase Deficiency |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is an enzymatic component of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, or Krebs cycle, and catalyzes the formation of L-malate from fumarate. It exists in both a cytosolic form and an N-terminal extended form, differing only in the translation start site used. The N-terminal extended form is targeted to the mitochondrion, where the removal of the extension generates the same form as in the cytoplasm. It is similar to some thermostable class II fumarases and functions as a homotetramer. Mutations in this gene can cause fumarase deficiency and lead to progressive encephalopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P07954 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1730117 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2271 |
| NCBI Accession: | P07954.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P07954,B1ANK7, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P07954 |
| Molecular Weight: | 50,213 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Fumarate hydratase, mitochondrial |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | fumarate hydratase |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FH�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | MCL; FMRD; LRCC; HLRCC; MCUL1�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | fumarate hydratase, mitochondrial |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Fumarate hydratase, mitochondrial |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FH�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FUMH_HUMAN |