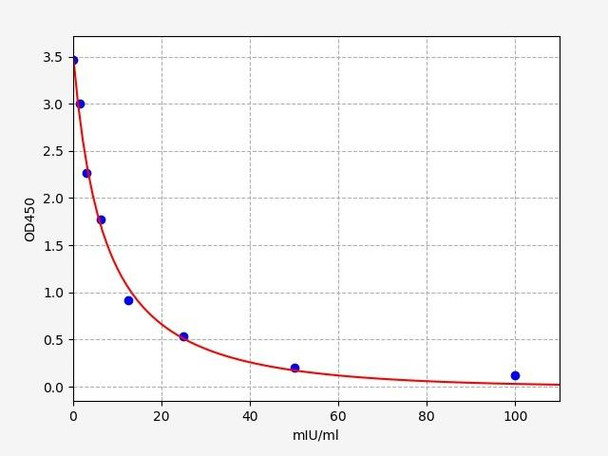
Description
Human Follicle-Stimulating Hormone/FSH ELISA Kit
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is a crucial hormone that plays a fundamental role in the reproductive system, particularly in the regulation of the menstrual cycle and the development and maturation of follicles in the ovaries. FSH is released by the pituitary gland and acts on the ovaries in females and the testes in males. Hypogonadism, PCOS, PCI, Klinefelter syndrome are some of the diseases associated with the FSH. The Assay Genie Human Follicle-Stimlating Hormone / FSH ELISA Kit is a highly sensitive assay for the quantitative measurement of FSH in serum, plasma, cell and tissue lysates.
Key Features
| Save Time | Pre-coated 96 well plate | |
| Quick Start | Kit includes all necessary reagents | |
| Publication Ready | Reproducible and reliable results |
Overview
| Product Name: | Human Follicle-Stimulating Hormone / FSH ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | HUFI00318 |
| Size: | 96 Assays |
| Alias: | FSH, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone |
| Detection Method: | Competitive ELISA, Coated with Antibody |
| Application: | This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Human FSH concentrations in serum plasma and other biological fluids. |
| Sensitivity: | 0.938mIU/ml |
| Range: | 1.563-100mIU/ml |
| Storage: | 4°C for 6 months |
| Note: | For Research Use Only |
Additional Information
| Recovery | Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Human FSH and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Human FSH in samples.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Linearity: | The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Human FSH and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| CV(%): | Intra-Assay: CV<8% Inter-Asay: Cv<10% |
Kit Components
| Component | Quantity | Storage |
| ELISA Microplate(Dismountable) | 8×12 strips | 4°C for 6 months |
| Lyophilized Standard | 2 | 4°C/-20°C |
| Sample/Standard Dilution Buffer | 20ml | 4°C |
| Biotin-labeled Antibody(Concentrated) | 60ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| Antibody Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate(SABC) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| SABC Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| TMB Substrate | 10ml | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| Stop Solution | 10ml | 4°C |
| Wash Buffer(25X) | 30ml | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 | - |
Other materials required:
- Microplate reader with 450 nm wavelength filter
- Multichannel Pipette, Pipette, microcentrifuge tubes and disposable pipette tips
- Incubator
- Deionized or distilled water
- Absorbent paper
- Buffer resevoir
Protein Information
| Uniprot | |
| UniProt Protein Function | FSHB: Stimulates development of follicle and spermatogenesis in the reproductive organs. Defects in FSHB are a cause of isolated follicle- stimulating hormone deficiency (IFSHD). Selective follicle-stimulating hormone deficiency is an uncommon cause of infertility, producing amenorrhea and hypogonadism in women and oligo or azoospermia with normal testosterone levels in normally virilised men. Belongs to the glycoprotein hormones subunit beta family. |
| NCBI Summary | The pituitary glycoprotein hormone family includes follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, chorionic gonadotropin, and thyroid-stimulating hormone. All of these glycoproteins consist of an identical alpha subunit and a hormone-specific beta subunit. This gene encodes the beta subunit of follicle-stimulating hormone. In conjunction with luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone induces egg and sperm production. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier | |
| NCBI Gene ID | |
| Molecular Weight | 14,700 Da |
Protocol
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
Equilibrate the TMB substrate for at least 30 min at 37°C beforeuse. When diluting samples and reagents, they must be mixed completely andevenly. It is recommended to plot a standard curve for each test.
| Step | Procedure |
| 1. | Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coatedplate respectively, and then, record their positions. It isrecommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Washplate 2 times before adding standard, sample and control (zero) wells! |
| 2. | Add Sample and Biotin-detection antibody: Add 50µL of Standard, Blank or Sample per well. The blankwell is added with Sample Dilution Buffer. Immediately add 50 µL of biotin-labelled antibody workingsolution to each well. Cover with the plate sealer provided. Gently tap the plate to ensure thoroughmixing. Incubate for 45 minutes at 37°C. (Solutions are added to the bottom of micro-ELISA platewell, avoid touching plate walls and foaming). |
| 3. | Wash: Aspirate each well and wash, repeating the process three timesWash by filling each well with Wash Buffer (approximately 350µL)using a squirt bottle, multi-channel pipette, manifold dispenser orautomated washer. Complete removal of liquid at each step is essentialto good performance. After the last wash, remove any remaining WashBuffer by aspirating or decanting. Invert the plate and pat it againstthick clean absorbent paper. |
| 4. | HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate(SABC): Add 100µL of SABC workingsolution to each well. Cover with a new Plate sealer. Incubate for30minutes at 37°C. |
| 5. | Wash: Repeat the aspiration/wash process for five times. |
| 6. | TMB Substrate: Add 90µL of TMB Substrate to each well. Coverwith a new Plate sealer. Incubate for about 10-20 minutes at 37°C.Protect from light. The reaction time can be shortened or extendedaccording to the actual color change, but not more than 30minutes.When apparent gradient appeared in standard wells, you can terminatethe reaction. |
| 7. | Stop: Add 50µL of Stop Solution to each well. Color turn toyellow immediately. The adding order of stop solution should be as thesame as the substrate solution. |
| 8. | OD Measurement: Determine the optical density (OD Value) of each wellat once, using a microplate reader set to 450 nm. You should open themicroplate reader ahead, preheat the instrument, and set the testing parameters. |
Sample Preparation
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plamsa | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |
FSH Background
FSH
FSH, also known as Follicle-Stimualting Hormone is a hormone produced and released by the pituitary gland that plays a crucial role in sexual development and reproductive processes. While its name may suggest a connection to hair follicles, FSH actually impacts the function of the ovaries and testicles. It received its name due to its effect on ovarian follicles, which are small fluid-filled sacs containing egg cells within the ovaries. FSH is part of a complex network of hormones that coordinate various functions in the body by transmitting messages through the bloodstream to organs, muscles, and tissues. These hormonal signals guide and regulate the activities of the body, providing instructions on what to do and when to do it. It's important to note that hair growth is primarily influenced by a separate group of hormones known as androgens, rather than FSH.
Role of FSH
The role of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is closely tied to its primary target organ, the gonads. In females, FSH acts on the ovaries, where it stimulates the growth and development of ovarian follicles. These follicles contain the immature eggs and undergo maturation under the influence of FSH. As FSH levels rise during the menstrual cycle, it triggers the selection and growth of a dominant follicle, eventually leading to ovulation. FSH also stimulates the production of estrogen, a crucial hormone involved in reproductive processes. In males, FSH acts on the testes, specifically within the seminiferous tubules. It promotes the development and maturation of sperm cells, a process known as spermatogenesis. By targeting the gonads, FSH plays a pivotal role in orchestrating the complex processes of ovulation and spermatogenesis, ensuring reproductive function and fertility in both males and females.
Normal range of FSH
For Females:
- Prepubertal girls (before puberty): Less than 4.0 mIU/mL
- Pubertal girls and adult women (follicular phase of menstrual cycle): 4.0 to 10.0 mIU/mL
- Peak levels during ovulation: 10.0 to 25.0 mIU/mL
- Postmenopausal women: Greater than 25.0 mIU/mL
For Males:
- Prepubertal boys (before puberty): Less than 4.0 mIU/mL
- Pubertal boys and adult men: 1.0 to 8.0 mIU/mL
FSH ELISA Kits FAQs
What is the FSH ELISA Kit used for?
The FSH ELISA Kit is designed for the quantitative measurement of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels in various sample types. It provides researchers and clinicians with a reliable tool to assess FSH concentrations, aiding in the evaluation of reproductive health and the diagnosis of conditions related to fertility and hormonal imbalances.
What are the advantages of using FSH ELISA Kit?
The FSH ELISA Kit offers several advantages for accurate and precise FSH measurements. It provides high sensitivity and specificity, ensuring reliable results. The kit is user-friendly, offering a streamlined protocol for easy handling and efficient analysis. Additionally, it provides a wide dynamic range, allowing for the detection of both low and high FSH levels, and it is suitable for both research and clinical applications.
What sample types are compatible with FSH ELISA kit?
The FSH ELISA Kit is compatible with various sample types, including serum, plasma, cell lysates, and tissue homogenates. It provides flexibility in sample selection, allowing researchers to analyze FSH levels in different biological matrices.
What are the storage requirements for the FSH ELISA Kit?
The FSH ELISA Kit components should be stored according to the instructions provided in the kit manual. Generally, it is recommended to store the kit components at the recommended temperature to ensure their stability and optimal performance.
What should I do if my assay results are not optimal?
If you encounter any issues or have suboptimal assay results, we recommend contacting our dedicated support team for assistance. They will be available to provide troubleshooting guidance, answer your questions, and ensure you achieve the best possible results with the FSH ELISA Kit.