Description
| Product Name: | Human FLT4 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB2533 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | FLT4 |
| Synonyms: | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor FLT4, PCL, FLT41, FMS-LIKE TYROSINE KINASE 4, VEGFR-3, VEGFR3. |
| Source: | Insect Cells |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | FLT4 was lyophilized from a concentrated (1mg/ml) sterile solution containing 1xPBS. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized FLT4 in sterile water not less than 100 �g/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Stability: | Lyophilized FLT4 although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution FLT4 should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
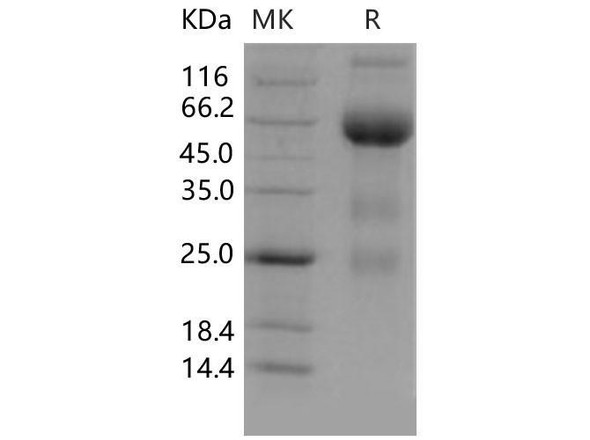
| Purity: | Greater than 90.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Biological Activity: | Measured by its ability to bind recombinant rat VEGF-C in a functional solid phase binding assay. Immobilised recombinant human VEGFR-3/FLT-4 at 5 �g/ml can bind recombinant rat VEGF-C in a linear range of 8-500 ng/ml. |
All three VEGF receptors belong to the class III subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) characterised by the seven immunoglobulin-like loops in the extracellular domain. The expression of VEGFR-1 to -3 is almost exclusively restricted to hematopoietic precursor cells, vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells and to the monocyte/macrophage lineage. They play key roles in vasculogenesis, hematopoiesis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. The FLT-4 cDNA encodes a 1298 amino acid (aa) residue precursor protein with a 23 aa residue signal peptide. Mature VEGFR-3/FLT-4 is composed of a 751 aa residue extracellular domain, a 22 aa transmembrane domain and a 482 aa residue cytoplasmic domain. Both VEGF family members VEGF-C and VEGF-D have been shown to bind and activate VEGFR-3/FLT-4. The Flt-4 gene is widely expressed in the early embryo but becomes restricted to the lymphatic endothelial a latter stages of development. It is important for lymphangiogenesis.
Soluble FLT4 Human Recombinant fused with a carboxy-terminal 6X histidine-tag produced in baculovirus is a monomeric, glycosylated, polypeptide containing the extracellular part, 25-774 amino acids and having a total molecular mass of 120 kDa. The soluble receptor protein contains only the first 7 extracellular domains, which contain all the information necessary for ligand binding.The FLT4 is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | VEGFR3: Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFC and VEGFD, and plays an essential role in adult lymphangiogenesis and in the development of the vascular network and the cardiovascular system during embryonic development. Promotes proliferation, survival and migration of endothelial cells, and regulates angiogenic sprouting. Signaling by activated FLT4 leads to enhanced production of VEGFC, and to a lesser degree VEGFA, thereby creating a positive feedback loop that enhances FLT4 signaling. Modulates KDR signaling by forming heterodimers. The secreted isoform 3 may function as a decoy receptor for VEGFC and/or VEGFD and play an important role as a negative regulator of VEGFC-mediated lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis. Binding of vascular growth factors to isoform 1 or isoform 2 leads to the activation of several signaling cascades; isoform 2 seems to be less efficient in signal transduction, because it has a truncated C-terminus and therefore lacks several phosphorylation sites. Mediates activation of the MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 signaling pathway, of MAPK8 and the JUN signaling pathway, and of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Phosphorylates SHC1. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3- kinase. Promotes phosphorylation of MAPK8 at 'Thr-183' and 'Tyr- 185', and of AKT1 at 'Ser-473'. Interacts with VEGFC and VEGFD. Monomer in the absence of bound VEGFC or VEGFD. Homodimer in the presence of bound VEGFC or VEGFD. Can also form a heterodimer with KDR. Interacts with PTPN14; the interaction is enhanced by stimulation with VEGFC. Interacts with CRK, GRB2, PTK2/FAK1, SHC1, PIK3R1 and PTPN11/SHP- 2. Identified in a complex with SRC and ITGB1. Detected in endothelial cells. Widely expressed. Detected in fetal spleen, lung and brain. Detected in adult liver, muscle, thymus, placenta, lung, testis, ovary, prostate, heart, and kidney. Present in an inactive conformation in the absence of bound ligand. Binding of VEGFC or VEGFD leads to dimerization and activation by autophosphorylation on tyrosine residues. Inhibited by MAZ51. Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Tyr protein kinase family. CSF-1/PDGF receptor subfamily. 3 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:EC 2.7.10.1; Kinase, protein; Membrane protein, integral; Protein kinase, TK; Protein kinase, tyrosine (receptor); TK group; VEGFR family Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 5q35.3 Cellular Component: plasma membrane; receptor complex Molecular Function:growth factor binding; protein binding; protein phosphatase binding; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity Biological Process: blood vessel morphogenesis; lymph vessel development; lymphangiogenesis; negative regulation of apoptosis; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; positive regulation of cell proliferation; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation; positive regulation of JNK cascade; positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; protein amino acid autophosphorylation; sprouting angiogenesis; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; vasculature development Disease: Hemangioma, Capillary Infantile; Lymphedema, Hereditary, Ia |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a tyrosine kinase receptor for vascular endothelial growth factors C and D. The protein is thought to be involved in lymphangiogenesis and maintenance of the lymphatic endothelium. Mutations in this gene cause hereditary lymphedema type IA. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P35916 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 357529070 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2324 |
| NCBI Accession: | P35916.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P35916,Q16067, Q86W07, Q86W08, A8K6L4, B5A926, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P35916,AAB23636 |
| Molecular Weight: | 153kDa |
| NCBI Full Name: | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | fms related tyrosine kinase 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FLT4�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | PCL; FLT-4; FLT41; LMPH1A; VEGFR3; VEGFR-3�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Fms-like tyrosine kinase 4; FLT-4; Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor FLT4 |
| Protein Family: | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FLT4�� |