Description
| Product Name: | Human FGF8 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0220 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | FGF8 |
| Synonyms: | FGF8B, FGF-8B, FGF8-B, KAL6, HBGF-8, HBGF8, AIGF, HBGF-8, MGC149376, fibroblast growth factor 8. |
| Source: | HEK293 Cells |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
| Formulation: | The FGF-8 was lyophilized in 10mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4 and 800mM NaCl. |
| Solubility: | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized FGF8 in sterile water containing 0.1% endotoxin-free recombinant HSA. |
| Stability: | Lyophilized FGF-8 although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon reconstitution FGF8 should be stored at 4°C between 2-7 days and for future use below -18°C.For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
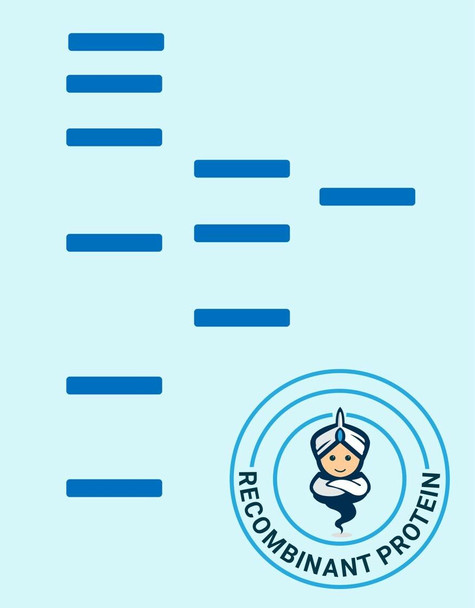
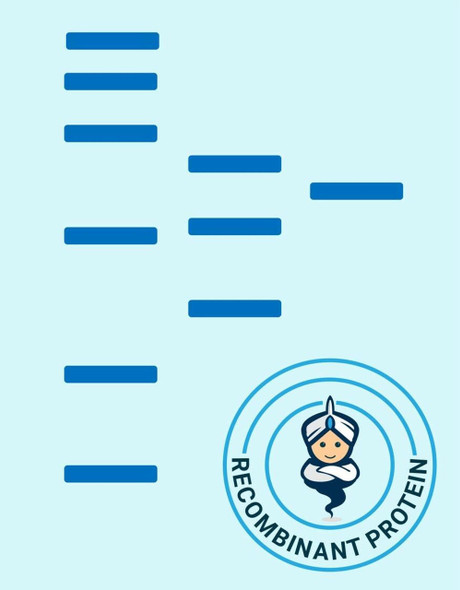
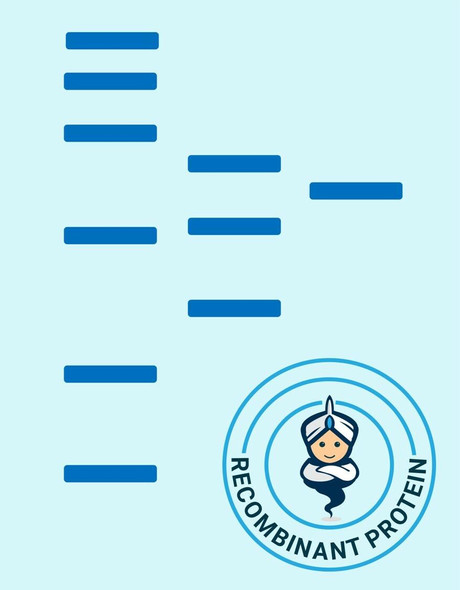
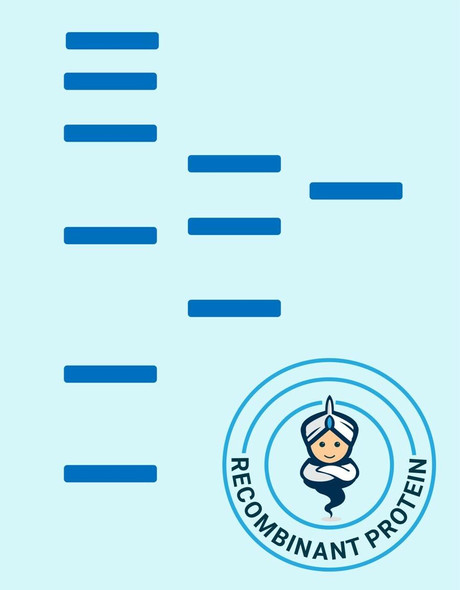
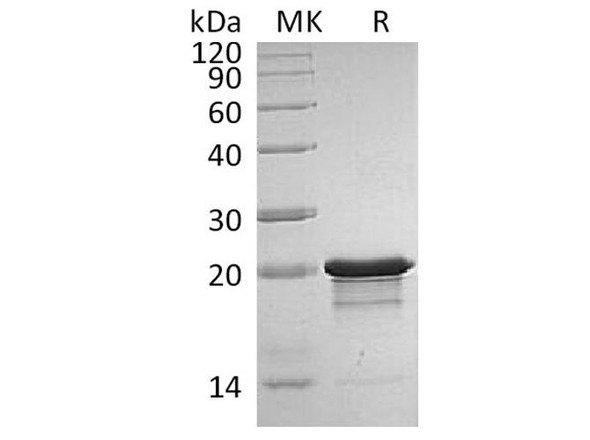
| Purity: | Greater than 95% as obsereved by SDS-PAGE. |
| Biological Activity: | The specific activity was determined by the dose-dependent stimulation of the proliferation of the Balb/3T3 cell line, the ED50 is <60ng/ml. |
FGF8 is part of the fibroblast growth factor family. FGF family members have wide mitogenic and cell survival activities, and participate in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF8 supports androgen and anchorage independent growth of mammary tumor cells. FGF8 over expression increases tumor growth and angiogensis. The adult expression of FGF-8 gene is restricted to testes and ovaries. FGF8 functions as an embryonic epithelial factor. FGF8 takes part in midbrain and limb development, organogenesis, embryo gastrulation and left-right axis determination.
FGF-8 Human Recombinant produced in HEK cells is a glycosylated monomer, having a molecular weight range of 30-45kDa due to glycosylation.The FGF8 is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | FGF8: Plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell migration. Required for normal brain, eye, ear and limb development during embryogenesis. Required for normal development of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal system. Defects in FGF8 are the cause of Kallmann syndrome type 6 (KAL6). Kallmann syndrome is a disorder that associates hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and anosmia. Anosmia or hyposmia is related to the absence or hypoplasia of the olfactory bulbs and tracts. Hypogonadism is due to deficiency in gonadotropin-releasing hormone and probably results from a failure of embryonic migration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone- synthesizing neurons. In some patients other developmental anomalies can be present, which include renal agenesis, cleft lip and/or palate, selective tooth agenesis, and bimanual synkinesis. In some cases anosmia may be absent or inconspicuous. Defects in FGF8 are a cause of idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH). IHH is defined as a deficiency of the pituitary secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, which results in the impairment of pubertal maturation and of reproductive function. Belongs to the heparin-binding growth factors family. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Secreted; Cytokine; Secreted, signal peptide Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 10q24 Cellular Component: extracellular space; extracellular region; external side of plasma membrane Molecular Function:growth factor activity; type 2 fibroblast growth factor receptor binding; type 1 fibroblast growth factor receptor binding; fibroblast growth factor receptor binding; chemoattractant activity Biological Process: gonad development; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; apoptosis; cell proliferation in forebrain; adrenocorticotropin hormone secreting cell differentiation; thyroid stimulating hormone secreting cell differentiation; gastrulation; forebrain dorsal/ventral pattern formation; motor axon guidance; Wnt receptor signaling pathway through beta-catenin; mesodermal cell migration; response to organic cyclic substance; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis; odontogenesis; BMP signaling pathway; positive chemotaxis; induction of an organ; positive regulation of cell proliferation; thyroid gland development; male genitalia development; mesonephros development; pallium development; heart looping; negative regulation of neuron apoptosis; otic vesicle formation; regulation of odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth; negative regulation of cardiac muscle development; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; response to drug; anatomical structure morphogenesis; pharyngeal system development; phosphoinositide-mediated signaling; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of mitosis; neural plate morphogenesis; MAPKKK cascade; subpallium development; forebrain morphogenesis; dorsal/ventral axon guidance; positive regulation of organ growth; patterning of blood vessels; ureteric bud branching; forebrain neuron development; midbrain-hindbrain boundary development; insulin receptor signaling pathway; innate immune response; blood vessel remodeling; response to oxidative stress; metanephros development Disease: Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism 6 With Or Without Anosmia |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. This protein is known to be a factor that supports androgen and anchorage independent growth of mammary tumor cells. Overexpression of this gene has been shown to increase tumor growth and angiogensis. The adult expression of this gene is restricted to testes and ovaries. Temporal and spatial pattern of this gene expression suggests its function as an embryonic epithelial factor. Studies of the mouse and chick homologs revealed roles in midbrain and limb development, organogenesis, embryo gastrulation and left-right axis determination. The alternative splicing of this gene results in four transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P55075 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 1706791 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2253 |
| NCBI Accession: | P55075.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P55075,Q14915, Q15766, A1A514, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P55075 |
| Molecular Weight: | 244 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Fibroblast growth factor 8 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | fibroblast growth factor 8 (androgen-induced) |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | FGF8�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | HH6; AIGF; KAL6; FGF-8; HBGF-8�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | fibroblast growth factor 8; androgen-induced growth factor; heparin-binding growth factor 8 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Fibroblast growth factor 8 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Androgen-induced growth factor; AIGF; Heparin-binding growth factor 8; HBGF-8 |
| UniProt Gene Name: | FGF8�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | FGF8_HUMAN |