Description
| Product Name: | Human F11R Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB3482 |
| Size: | 20µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | F11R |
| Synonyms: | Junctional adhesion molecule A, JAM-A, Junctional adhesion molecule 1, JAM-1, Platelet F11 receptor, Platelet adhesion molecule 1, PAM-1, CD321, F11R, JAM1, JCAM, JAM, KAT, JAMA. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | F11R protein solution (1mg/ml) containing 20mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH8.0), 10% glycerol, 0.15M NaCl and 1mM DTT. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
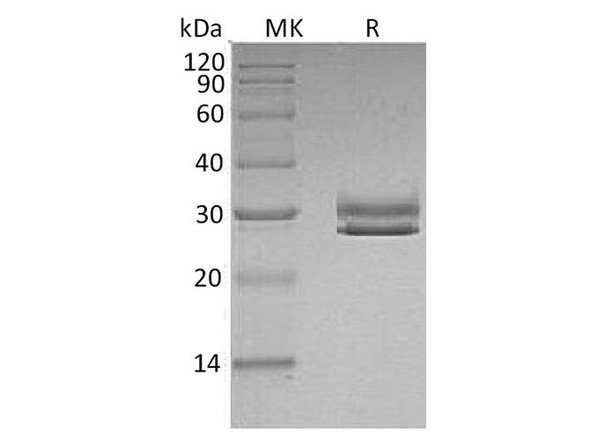
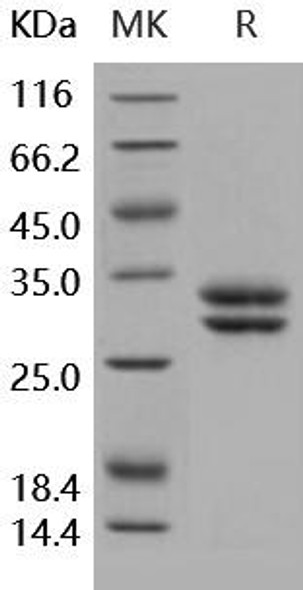
| Purity: | Greater than 90.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MGSHMLGSVT VHSSEPEVRI PENNPVKLSC AYSGFSSPRV EWKFDQGDTT RLVCYNNKIT ASYEDRVTFL PTGITFKSVT REDTGTYTCM VSEEGGNSYG EVKVKLIVLV PPSKPTVNIP SSATIGNRAV LTCSEQDGSP PSEYTWFKDG IVMPTNPKSTRAFSNSSYVL NPTTGELVFD PLSASDTGEY SCEARNGYGT PMTSNAVRME AVERNVGV |
F11R (CD321) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. F11R has a role in epithelial tight junction formation. Tight junctions exemplify one type of cell-to-cell adhesion in epithelial or endothelial cell sheets, establishing continuous seals around cells and acting as a physical barrier to thwart solutes and water from passing easily through the paracellular space. F11R protein can function as a receptor for reovirus, or as a ligand for the integrin LFA1, involved in leukocyte transmigration, or a platelet receptor.
F11R Human Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 238 amino acids (26-238 a.a) and having a molecular mass of 25.8kDa.F11R is fused to a 25 amino acid His-tag at N-terminus & purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | JAM-A: Seems to play a role in epithelial tight junction formation. Appears early in primordial forms of cell junctions and recruits PARD3. The association of the PARD6-PARD3 complex may prevent the interaction of PARD3 with JAM1, thereby preventing tight junction assembly. Plays a role in regulating monocyte transmigration involved in integrity of epithelial barrier. Involved in platelet activation. In case of orthoreovirus infection, serves as receptor for the virus. Belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell adhesion; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 1q21.2-q21.3 Cellular Component: microtubule cytoskeleton; tight junction; plasma membrane; integral to membrane; cytoplasmic vesicle; intercellular junction; cell junction Molecular Function:protein binding; PDZ domain binding Biological Process: intercellular junction assembly and maintenance; response to radiation; extracellular matrix organization and biogenesis; viral reproduction; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; actomyosin structure organization and biogenesis; cell adhesion; blood coagulation; inflammatory response; leukocyte migration; positive regulation of blood pressure; intestinal absorption |
| NCBI Summary: | Tight junctions represent one mode of cell-to-cell adhesion in epithelial or endothelial cell sheets, forming continuous seals around cells and serving as a physical barrier to prevent solutes and water from passing freely through the paracellular space. The protein encoded by this immunoglobulin superfamily gene member is an important regulator of tight junction assembly in epithelia. In addition, the encoded protein can act as (1) a receptor for reovirus, (2) a ligand for the integrin LFA1, involved in leukocyte transmigration, and (3) a platelet receptor. Multiple 5' alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified but their biological validity has not been established. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q9Y624 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 10720061 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 50848 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q9Y624.1 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q9Y624,B7Z941, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q9Y624 |
| Molecular Weight: | 299 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Junctional adhesion molecule A |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | F11 receptor |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | F11R�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | JAM; KAT; JAM1; JAMA; JCAM; CD321; PAM-1�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | junctional adhesion molecule A; platelet F11 receptor; platelet adhesion molecule 1; junctional adhesion molecule 1 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Junctional adhesion molecule A |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Junctional adhesion molecule 1; JAM-1; Platelet F11 receptor; Platelet adhesion molecule 1; PAM-1; CD_antigen: CD321 |
| Protein Family: | Junctional adhesion molecule |
| UniProt Gene Name: | F11R�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | JAM1_HUMAN |