Human Endoglin Recombinant Protein (RPPB0178)
- SKU:
- RPPB0178
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
- Uniprot:
- P17813
- Research Area:
- Cytokines
Description
| Product Name: | Human Endoglin Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0178 |
| Size: | 5µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | Endoglin |
| Synonyms: | CD105, ENG, END, ORW, HHT1, ORW1, FLJ41744, Endoglin. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile Filtered colorless liquid formulation. |
| Formulation: | Endoglin solution�in 50mM Tris-Acetate, pH-7.5, 1mM EDTA and 20% Glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks.Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
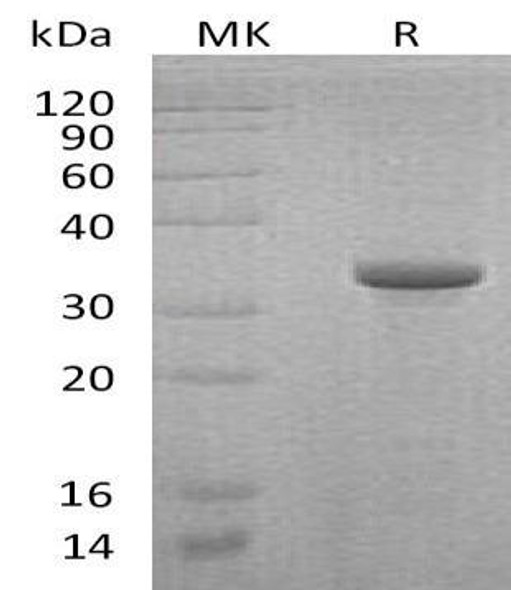
| Purity: | Greater than 90.0% as determined by:(a) Analysis by RP-HPLC.(b) Analysis by SDS-PAGE. |
Endoglin is a type I membrane glycoprotein located on cell surfaces and is part of the TGF beta receptor complex.The Endoglin protein consists of a homodimer of 180 kDA with disulfide links. Endoglin has been found on endothelial cells, activated macrophages, fibroblasts, and smooth muscle cells. Furthermore, Endoglin has been found to be part of the TGF-beta1 receptor complex. Endoglin thus may be involved in the binding of TGF-beta1, TGF-beta3, activin-A, BMP-2, and BMP-7. Beside TGF-beta signaling endoglin may have other functions. It has been postulated that endoglin is involved in the cytoskeletal organization affecting cell morphology and migration. Endoglin has a role in the development of the cardiovascular system and in vascular remodeling. Endoglin expression is regulated during heart development . Experimental mice without the endoglin gene die due to cardiovascular abnormalities.
Endoglin Human Recombinant extracellular domain produced in E.Coli is a single, glycosylated, Polypeptide containing 151 amino acids (26-176) and having a molecular mass of 43 kDa.The Endoglin is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | ENG: Major glycoprotein of vascular endothelium. May play a critical role in the binding of endothelial cells to integrins and/or other RGD receptors. Homodimer that forms an heteromeric complex with the signaling receptors for transforming growth factor-beta: TGFBR1 and/or TGFBR2. It is able to bind TGF-beta 1, and 3 efficiently and TGF-beta 2 less efficiently. Interacts with TCTEX1D4. Interacts with ARRB2. Endoglin is restricted to endothelial cells in all tissues except bone marrow. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Receptor, misc.; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 9q34.11 Cellular Component: cytoplasm; external side of plasma membrane; extracellular space; focal adhesion; nucleoplasm; receptor complex Molecular Function:activin binding; galactose binding; glycosaminoglycan binding; protein binding; punt binding; transforming growth factor beta binding; transforming growth factor beta receptor, cytoplasmic mediator activity Biological Process: artery morphogenesis; BMP signaling pathway; central nervous system vasculogenesis; heart looping; negative regulation of cell migration; negative regulation of protein amino acid autophosphorylation; patterning of blood vessels; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway; positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation; regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent; regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway; smooth muscle development; vasculogenesis; venous blood vessel morphogenesis Disease: Telangiectasia, Hereditary Hemorrhagic, Of Rendu, Osler, And Weber |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene encodes a homodimeric transmembrane protein which is a major glycoprotein of the vascular endothelium. This protein is a component of the transforming growth factor beta receptor complex and it binds to the beta1 and beta3 peptides with high affinity. Mutations in this gene cause hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, also known as Osler-Rendu-Weber syndrome 1, an autosomal dominant multisystemic vascular dysplasia. This gene may also be involved in preeclampsia and several types of cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013] |
| UniProt Code: | P17813 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 3041681 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 2022 |
| NCBI Accession: | P17813.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P17813,Q14248, Q14926, Q5T9C0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P17813 |
| Molecular Weight: | 67,542 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Endoglin |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | endoglin |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | ENG�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | END; HHT1; ORW1�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | endoglin |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Endoglin |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | CD_antigen: CD105 |
| Protein Family: | Endoglin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | ENG�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | EGLN_HUMAN |