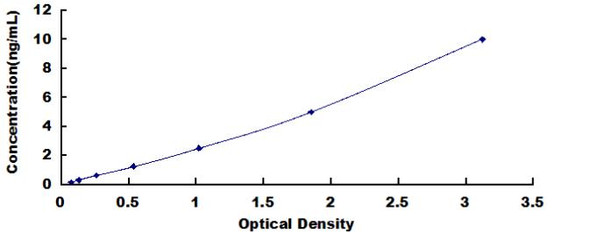
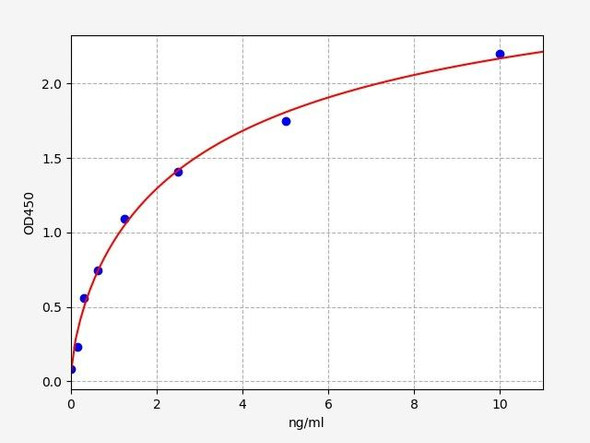
Human Cytochrome b-245 Beta Polypeptide ELISA Kit (HUFI08038)
- SKU:
- HUFI08038
- Product Type:
- ELISA Kit
- Size:
- 96 Assays
- Uniprot:
- P04839
- Sensitivity:
- 0.094ng/ml
- Range:
- 0.156-10ng/ml
- ELISA Type:
- Sandwich
- Synonyms:
- NOX2, CGD91-phox, NADPH oxidase 2, gp91phox, p22 phagocyte B-cytochrome, gp91-1, Superoxide-geneRating NADPH oxidase heavy chain subunit, Neutrophil cytochrome b 91 kDa polypeptide, Heme-binding membrane glycoprotein gp91phox
- Reactivity:
- Human
Description
Human Cytochrome b-245 Beta Polypeptide ELISA Kit (HUFI08038)
The Human Cytochrome b-245 Beta Polypeptide ELISA Kit is a reliable and efficient tool for the detection of cytochrome b-245 beta polypeptide levels in human samples such as serum, plasma, and cell culture supernatants. With high sensitivity and specificity, this kit provides accurate and reproducible results for a variety of research applications.Cytochrome b-245 beta polypeptide is a key component of the phagocytic NADPH oxidase enzyme complex, which plays a vital role in the immune system by generating reactive oxygen species.
Dysregulation of this enzyme complex has been implicated in various diseases, including chronic granulomatous disease and inflammatory conditions. The Human Cytochrome b-245 Beta Polypeptide ELISA Kit offers a valuable tool for studying the role of this protein in disease pathogenesis and potential therapeutic interventions.
| Product Name: | Human Cytochrome b-245 Beta Polypeptide ELISA Kit |
| Product Code: | HUFI08038 |
| Size: | 96 Assays |
| Alias: | NOX2 ELISA Kit, CGD91-phox ELISA Kit, NADPH oxidase 2 ELISA Kit, gp91phox ELISA Kit, p22 phagocyte B-cytochrome ELISA Kit, gp91-1 ELISA Kit, Superoxide-geneRating NADPH oxidase heavy chain subunit ELISA Kit, Neutrophil cytochrome b 91 kDa polypeptide ELISA Kit, Heme-binding membrane glycoprotein gp91phox ELISA Kit |
| Detection method: | Sandwich ELISA, Double Antibody |
| Application: | This immunoassay kit allows for the in vitro quantitative determination of Human Cytochrome b-245 Beta Polypeptide concentrations in serum plasma and other biological fluids. |
| Sensitivity: | < 0.094ng/ml |
| Range: | 0.156-10ng/ml |
| Storage: | 4°C for 6 months |
| Note: | For Research Use Only |
| Recovery: | Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Human Cytochrome b-245 Beta Polypeptide and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Human Cytochrome b-245 Beta Polypeptide in samples. | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Linearity: | The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Human Cytochrome b-245 Beta Polypeptide and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected. | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| CV(%): | Intra-Assay: CV<8% Inter-Assay: CV<10% |
| Component | Quantity | Storage |
| ELISA Microplate (Dismountable) | 8×12 strips | 4°C for 6 months |
| Lyophilized Standard | 2 | 4°C/-20°C |
| Sample/Standard Dilution Buffer | 20ml | 4°C |
| Biotin-labeled Antibody(Concentrated) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| Antibody Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| HRP-Streptavidin Conjugate(SABC) | 120ul | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| SABC Dilution Buffer | 10ml | 4°C |
| TMB Substrate | 10ml | 4°C (Protect from light) |
| Stop Solution | 10ml | 4°C |
| Wash Buffer(25X) | 30ml | 4°C |
| Plate Sealer | 5 | - |
Other materials and equipment required:
- Microplate reader with 450 nm wavelength filter
- Multichannel Pipette, Pipette, microcentrifuge tubes and disposable pipette tips
- Incubator
- Deionized or distilled water
- Absorbent paper
- Buffer resevoir
| UniProt Protein Function: | CYBB: Critical component of the membrane-bound oxidase of phagocytes that generates superoxide. It is the terminal component of a respiratory chain that transfers single electrons from cytoplasmic NADPH across the plasma membrane to molecular oxygen on the exterior. Also functions as a voltage-gated proton channel that mediates the H(+) currents of resting phagocytes. It participates in the regulation of cellular pH and is blocked by zinc. Defects in CYBB are a cause of granulomatous disease,chronic, X-linked (CGD). A disorder characterized by the inability of neutrophils and phagocytes to kill microbes that they have ingested. Patients suffer from life- threatening bacterial/fungal infections. Defects in CYBB are a cause of mycobacteriosis atypical X-linked type 2 (AMCBX2). A rare condition characterized by predisposition to illness caused by moderately virulent mycobacterial species, such as Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine and environmental non-tuberculous mycobacteria, and by the more virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Other microorganisms rarely cause severe clinical disease in individuals with susceptibility to mycobacterial infections. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Membrane protein, multi-pass; EC 1.-.-.-; Membrane protein, integral; Oxidoreductase; Mitochondrial Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xp21.1 Cellular Component: Golgi apparatus; phagocytic vesicle membrane; cell soma; mitochondrion; rough endoplasmic reticulum; integral to plasma membrane; dendrite; plasma membrane; NADPH oxidase complex Molecular Function:protein binding; FAD binding; electron carrier activity; protein heterodimerization activity; metal ion binding; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activity; heme binding; voltage-gated ion channel activity Biological Process: response to drug; respiratory burst; interaction with host; superoxide metabolic process; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I, TAP-dependent; antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I; innate immune response; ion transport; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; inflammatory response; superoxide release; response to nutrient; hydrogen peroxide biosynthetic process Disease: Immunodeficiency 34; Granulomatous Disease, Chronic, X-linked |
| NCBI Summary: | Cytochrome b (-245) is composed of cytochrome b alpha (CYBA) and beta (CYBB) chain. It has been proposed as a primary component of the microbicidal oxidase system of phagocytes. CYBB deficiency is one of five described biochemical defects associated with chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). In this disorder, there is decreased activity of phagocyte NADPH oxidase; neutrophils are able to phagocytize bacteria but cannot kill them in the phagocytic vacuoles. The cause of the killing defect is an inability to increase the cell's respiration and consequent failure to deliver activated oxygen into the phagocytic vacuole. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P04839 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 115211 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1536 |
| NCBI Accession: | P04839.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P04839,Q2PP16, A8K138, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P04839 |
| Molecular Weight: | 65,336 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cytochrome b-245 heavy chain |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cytochrome b-245, beta polypeptide |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CYBB |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CGD; NOX2; IMD34; AMCBX2; GP91-1; GP91PHOX; p91-PHOX; GP91-PHOX |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cytochrome b-245 heavy chain; CGD91-phox; NADPH oxidase 2; p22 phagocyte B-cytochrome; cytochrome b558 subunit beta; neutrophil cytochrome b 91 kDa polypeptide; heme-binding membrane glycoprotein gp91phox; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase heavy chain subunit |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cytochrome b-245 heavy chain |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | CGD91-phox; Cytochrome b(558) subunit beta; Cytochrome b558 subunit beta; Heme-binding membrane glycoprotein gp91phox; NADPH oxidase 2; Neutrophil cytochrome b 91 kDa polypeptide; Superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase heavy chain subunit; gp91-1; gp91-phox; p22 phagocyte B-cytochrome |
| Protein Family: | Cytochrome |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CYBB |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CY24B_HUMAN |
*Note: Protocols are specific to each batch/lot. For the correct instructions please follow the protocol included in your kit.
Before adding to wells, equilibrate the SABC working solution and TMB substrate for at least 30 min at 37 °C. When diluting samples and reagents, they must be mixed completely and evenly. It is recommended to plot a standard curve for each test.
| Step | Protocol |
| 1. | Set standard, test sample and control (zero) wells on the pre-coated plate respectively, and then, record their positions. It is recommended to measure each standard and sample in duplicate. Wash plate 2 times before adding standard, sample and control (zero) wells! |
| 2. | Aliquot 0.1ml standard solutions into the standard wells. |
| 3. | Add 0.1 ml of Sample / Standard dilution buffer into the control (zero) well. |
| 4. | Add 0.1 ml of properly diluted sample ( Human serum, plasma, tissue homogenates and other biological fluids.) into test sample wells. |
| 5. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37 °C for 90 min. |
| 6. | Remove the cover and discard the plate content, clap the plate on the absorbent filter papers or other absorbent material. Do NOT let the wells completely dry at any time. Wash plate X2. |
| 7. | Add 0.1 ml of Biotin- detection antibody working solution into the above wells (standard, test sample & zero wells). Add the solution at the bottom of each well without touching the side wall. |
| 8. | Seal the plate with a cover and incubate at 37 °C for 60 min. |
| 9. | Remove the cover, and wash plate 3 times with Wash buffer. Let wash buffer rest in wells for 1 min between each wash. |
| 10. | Add 0.1 ml of SABC working solution into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37 °C for 30 min. |
| 11. | Remove the cover and wash plate 5 times with Wash buffer, and each time let the wash buffer stay in the wells for 1-2 min. |
| 12. | Add 90 µL of TMB substrate into each well, cover the plate and incubate at 37 °C in dark within 10-20 min. (Note: This incubation time is for reference use only, the optimal time should be determined by end user.) And the shades of blue can be seen in the first 3-4 wells (with most concentrated standard solutions), the other wells show no obvious color. |
| 13. | Add 50 µL of Stop solution into each well and mix thoroughly. The color changes into yellow immediately. |
| 14. | Read the O.D. absorbance at 450 nm in a microplate reader immediately after adding the stop solution. |
When carrying out an ELISA assay it is important to prepare your samples in order to achieve the best possible results. Below we have a list of procedures for the preparation of samples for different sample types.
| Sample Type | Protocol |
| Serum | If using serum separator tubes, allow samples to clot for 30 minutes at room temperature. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Collect the serum fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. If serum separator tubes are not being used, allow samples to clot overnight at 2-8°C. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1,000x g. Remove serum and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Plasma | Collect plasma using EDTA or heparin as an anticoagulant. Centrifuge samples at 4°C for 15 mins at 1000 × g within 30 mins of collection. Collect the plasma fraction and assay promptly or aliquot and store the samples at -80°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Note: Over haemolysed samples are not suitable for use with this kit. |
| Urine & Cerebrospinal Fluid | Collect the urine (mid-stream) in a sterile container, centrifuge for 20 mins at 2000-3000 rpm. Remove supernatant and assay immediately. If any precipitation is detected, repeat the centrifugation step. A similar protocol can be used for cerebrospinal fluid. |
| Cell culture supernatant | Collect the cell culture media by pipette, followed by centrifugation at 4°C for 20 mins at 1500 rpm. Collect the clear supernatant and assay immediately. |
| Cell lysates | Solubilize cells in lysis buffer and allow to sit on ice for 30 minutes. Centrifuge tubes at 14,000 x g for 5 minutes to remove insoluble material. Aliquot the supernatant into a new tube and discard the remaining whole cell extract. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Tissue homogenates | The preparation of tissue homogenates will vary depending upon tissue type. Rinse tissue with 1X PBS to remove excess blood & homogenize in 20ml of 1X PBS (including protease inhibitors) and store overnight at ≤ -20°C. Two freeze-thaw cycles are required to break the cell membranes. To further disrupt the cell membranes you can sonicate the samples. Centrifuge homogenates for 5 mins at 5000xg. Remove the supernatant and assay immediately or aliquot and store at -20°C or -80°C. |
| Tissue lysates | Rinse tissue with PBS, cut into 1-2 mm pieces, and homogenize with a tissue homogenizer in PBS. Add an equal volume of RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors and lyse tissues at room temperature for 30 minutes with gentle agitation. Centrifuge to remove debris. Quantify total protein concentration using a total protein assay. Assay immediately or aliquot and store at ≤ -20 °C. |
| Breast Milk | Collect milk samples and centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 60 min at 4°C. Aliquot the supernatant and assay. For long term use, store samples at -80°C. Minimize freeze/thaw cycles. |