Description
| Product Name: | Human CTLA4 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB0149 |
| Size: | 10µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | CTLA4 |
| Synonyms: | CytotoxicT-Lymphocyte Associated Protein 4, Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4,Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus 12, Celiac Disease 3, CTLA-4, CD152, LigandAnd Transmembrane Spliced Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Associated Antigen 4, CytotoxicT Lymphocyte Associated Antigen 4 Short Spliced Form, CytotoxicT-Lymphocyte-Associated Serine Esterase-4, Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-AssociatedAntigen 4, CD152 Isoform, CD152 Antigen, CELIAC3, IDDM12, ALPS5, GRD4, GSE, CD,Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4, CTLA4. |
| Source: | Sf9 Insect cells |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | CTLA4 protein solution (0.25mg/ml) contains PhosphateBuffered Saline (pH 7.4) and 20% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
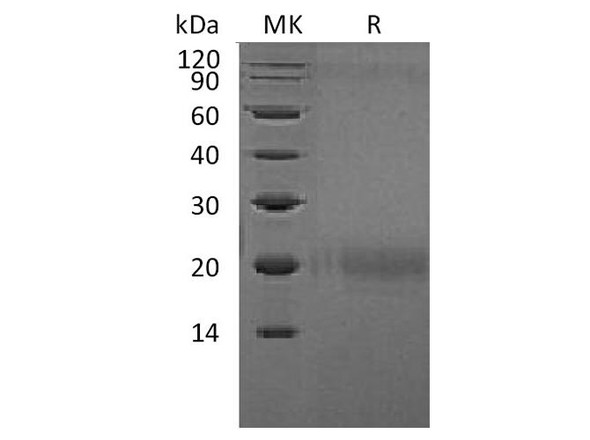
| Purity: | Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | ADLKAMHVAQPAVVLASSRG IASFVCEYAS PGKATEVRVT VLRQADSQVT EVCAATYMMG NELTFLDDSI CTGTSSGNQVNLTIQGLRAM DTGLYICKVE LMYPPPYYLG IGNGTQIYVI DPEPCPDSDH HHHHH |
| Biological Activity: | Determined by IL-2 ELISA via Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cells. The ED50 range ? 150 ng/ml with Human B7-1/CD80. |
CTLA-4 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and encodes a protein which transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells. The protein contains a V domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. The membrane-bound isoform functions as a homodimer interconnected by a disulfide bond, while the soluble isoform functions as a monomer. Mutations in this gene have been associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, Graves disease, Hashimoto thyroiditis, celiac disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, thyroid-associated orbitopathy, and other autoimmune diseases.
CTLA4 produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 135 amino acids (36-161a.a.) and having a molecular mass of 14.6kDa (Molecular size on SDS-PAGE will appear at approximately 18-28kDa). CTLA4 is expressed with a�6 amino acid His tag at C-Terminus and purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | CTLA-4: Inhibitory receptor acting as a major negative regulator of T-cell responses. The affinity of CTLA4 for its natural B7 family ligands, CD80 and CD86, is considerably stronger than the affinity of their cognate stimulatory coreceptor CD28. Genetic variation in CTLA4 influences susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). SLE is a chronic, inflammatory and often febrile multisystemic disorder of connective tissue. It affects principally the skin, joints, kidneys and serosal membranes. SLE is thought to represent a failure of the regulatory mechanisms of the autoimmune system. Genetic variations in CTLA4 may influence susceptibility to Graves disease, an autoimmune disorder associated with overactivity of the thyroid gland and hyperthyroidism. Genetic variation in CTLA4 is the cause of susceptibility to diabetes mellitus insulin-dependent type 12 (IDDM12). A multifactorial disorder of glucose homeostasis that is characterized by susceptibility to ketoacidosis in the absence of insulin therapy. Clinical fetaures are polydipsia, polyphagia and polyuria which result from hyperglycemia-induced osmotic diuresis and secondary thirst. These derangements result in long-term complications that affect the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels. Genetic variation in CTLA4 is the cause of susceptibility to celiac disease type 3 (CELIAC3). It is a multifactorial disorder of the small intestine that is influenced by both environmental and genetic factors. It is characterized by malabsorption resulting from inflammatory injury to the mucosa of the small intestine after the ingestion of wheat gluten or related rye and barley proteins. In its classic form, celiac disease is characterized in children by malabsorption and failure to thrive. 4 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Immunoglobulin superfamily; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 2q33 Cellular Component: Golgi apparatus; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; integral to plasma membrane; plasma membrane; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle; external side of plasma membrane Molecular Function:protein binding Biological Process: B cell receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of T cell proliferation; positive regulation of apoptosis; negative regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation; T cell costimulation; negative regulation of immune response; immune response; negative regulation of B cell proliferation; response to DNA damage stimulus Disease: Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome, Type V; Celiac Disease, Susceptibility To, 3; Diabetes Mellitus, Insulin-dependent, 12; Hashimoto Thyroiditis; Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| NCBI Summary: | This gene is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and encodes a protein which transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells. The protein contains a V domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. The membrane-bound isoform functions as a homodimer interconnected by a disulfide bond, while the soluble isoform functions as a monomer. Mutations in this gene have been associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, Graves disease, Hashimoto thyroiditis, celiac disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, thyroid-associated orbitopathy, and other autoimmune diseases. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | P16410 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 27735177 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1493 |
| NCBI Accession: | P16410.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P16410,O95653, Q0PP65, Q52MC1, Q53TD5, Q5S005, Q8WXJ1 Q96P43, Q9UKN9, A0N1S0, E9PDH0, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P16410 |
| Molecular Weight: | 223 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CTLA4�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CD; GSE; GRD4; ALPS5; CD152; CTLA-4; IDDM12; CELIAC3�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4; CD152 isoform; celiac disease 3; insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus 12; cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated serine esterase-4; cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen 4 short spliced form; ligand and transmembrane spliced cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen 4 |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; CTLA-4; CD_antigen: CD152 |
| Protein Family: | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CTLA4�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CTLA4_HUMAN |