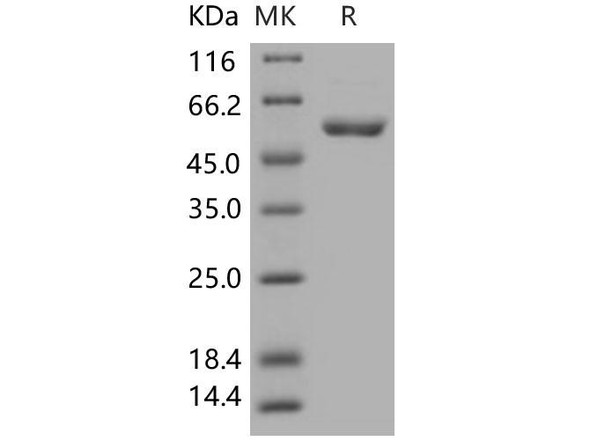
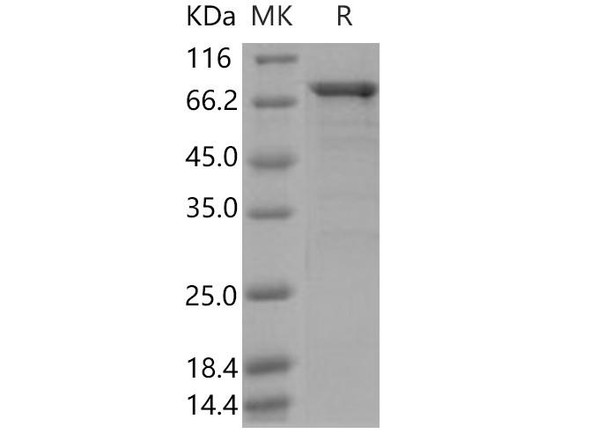
Human CDK1 Recombinant Protein (RPPB2458)
- SKU:
- RPPB2458
- Product Type:
- Recombinant Protein
- Species:
- Human
- Uniprot:
- P06493
- Research Area:
- Enzymes
Description
| Product Name: | Human CDK1 Recombinant Protein |
| Product Code: | RPPB2458 |
| Size: | 20µg |
| Species: | Human |
| Target: | CDK1 |
| Synonyms: | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1, CDC2, Cell Division Cycle 2,G1 To S And G2 To M, Cell Division Control Protein 2 Homolog, Cell DivisionProtein Kinase 1, P34 Protein Kinase, P34CDC2, CDC28A, Cell Cycle ControllerCDC2, EC 2.7.11.22, EC 2.7.11.23, CDKN1, Cyclin-dependent kinase 1, CDK1. |
| Source: | Escherichia Coli |
| Physical Appearance: | Sterile filtered colorless solution. |
| Formulation: | CDK1protein solution (1mg/ml) containing 20mM Tris-HCl (pH8.0) and 10% glycerol. |
| Stability: | Store at 4°C if entire vial will be used within 2-4 weeks. Store, frozen at -20°C for longer periods of time. For long term storage it is recommended to add a carrier protein (0.1% HSA or BSA).Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Purity: | Greater than 85.0% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Amino Acid Sequence: | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSHMEDYTKIEKI GEGTYGVVYK GRHKTTGQVV AMKKIRLESE EEGVPSTAIR EISLLKELRH PNIVSLQDVLMQDSRLYLIF EFLSMDLKKY LDSIPPGQYM DSSLVKSYLY QILQGIVFCH SRRVLHRDLK PQNLLIDDKGTIKLADFGLA RAFGIPIRVY THEVVTLWYR SPEVLLGSAR YSTPVDIWSI GTIFAELATK KPLFHGDSEIDQLFRIFRAL GTPNNEVWPE VESLQDYKNT FPKWKPGSLA SHVKNLDENG LDLLSKMLIY DPAKRISGKMALNHPYFNDL DNQIKKM |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) plays a significant part in the control of the eukaryotic cell cycle through modulating the centrosome cycle in addition to mitotic onset; CDK1 promotes G2-M transition and regulates G1 progress and G1-S transition using association with multiple interphase cyclins. CDK1 is essential in higher cells for the entry into S-phase and mitosis.
CDK1 Human Recombinant produced in E.Coli is a single, non-glycosylatedpolypeptide chain containing 317 amino acids (1-297 a.a) and having a molecularmass of 36.2kDa.CDK1 is fused to a 20 aminoacid His-tag at N-terminus & purified by proprietary chromatographictechniques.
| UniProt Protein Function: | CDK1: a protein kinase of the CDK family. Catalytic subunit of the conserved protein complex known as M-phase promoting factor (MPF), which is essential for G1/S and G2/M phase transitions. Mitotic cyclins stably associate with this protein and function as regulatory subunits. Its activity is controlled by cyclin availability and phosphorylation through the cell cycle. Activated in many cancers including colon, liver and breast. The T isoform, which lacks a regulatory region, is expressed in breast cancer. Inhibition in cancer cells may drive cells into apoptosis. May also drive cell migration. Inhibitors: BMS-265246, BMS-265246-01. 2 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Cell cycle regulation; EC 2.7.11.23; EC 2.7.11.22; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Kinase, protein; Protein kinase, CMGC; Protein kinase, Ser/Thr (non-receptor); CMGC group; CDK family; CDK/CDK1 subfamily; CDK1 subfamily Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: 10q21.1 Cellular Component: nucleoplasm; centrosome; membrane; mitochondrion; spindle microtubule; cytoplasm; midbody; nucleus; cytosol Molecular Function:RNA polymerase subunit kinase activity; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; protein binding; cyclin binding; cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity; histone kinase activity; Hsp70 protein binding; ATP binding; protein kinase activity Biological Process: regulation of Schwann cell differentiation; activation of MAPKK activity; nerve growth factor receptor signaling pathway; activation of MAPK activity; histone phosphorylation; response to toxin; ventricular cardiac muscle cell development; regulation of embryonic development; centrosome cycle; stress-activated MAPK cascade; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway; response to organic cyclic substance; toll-like receptor 5 signaling pathway; small GTPase mediated signal transduction; protein complex assembly; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation; response to drug; mitosis; organ regeneration; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus, translocation; cell aging; pronuclear fusion; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway; chromosome condensation; response to ethanol; cell division; response to activity; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway; response to amine stimulus; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle; negative regulation of apoptosis; positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; axon guidance; apoptosis; mitotic nuclear envelope disassembly; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle; toll-like receptor 10 signaling pathway; epithelial cell differentiation; anaphase-promoting complex-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; response to axon injury; DNA replication; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; cell migration; MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; organelle organization and biogenesis; MAPKKK cascade; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation; microtubule cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis; DNA repair; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; G1/S-specific transcription in mitotic cell cycle; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; response to cadmium ion; regulation of ubiquitin-protein ligase activity during mitotic cell cycle; response to copper ion; mitotic cell cycle G2/M transition DNA damage checkpoint; Ras protein signal transduction; insulin receptor signaling pathway; toll-like receptor signaling pathway; innate immune response; mitotic cell cycle; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of DNA replication |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is a catalytic subunit of the highly conserved protein kinase complex known as M-phase promoting factor (MPF), which is essential for G1/S and G2/M phase transitions of eukaryotic cell cycle. Mitotic cyclins stably associate with this protein and function as regulatory subunits. The kinase activity of this protein is controlled by cyclin accumulation and destruction through the cell cycle. The phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of this protein also play important regulatory roles in cell cycle control. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] |
| UniProt Code: | P06493 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 334302921 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 983 |
| NCBI Accession: | P06493.3 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | P06493,O60764, A8K7C4, C9J497, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | P06493 |
| Molecular Weight: | 297 |
| NCBI Full Name: | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | CDK1�� |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | CDC2; CDC28A; P34CDC2�� |
| NCBI Protein Information: | cyclin-dependent kinase 1; p34 protein kinase; cell cycle controller CDC2; cell division protein kinase 1; cell division control protein 2 homolog; cell division cycle 2, G1 to S and G2 to M |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Cell division control protein 2 homolog; Cell division protein kinase 1; p34 protein kinase |
| UniProt Gene Name: | CDK1�� |
| UniProt Entry Name: | CDK1_HUMAN |